Kaiser Health News
Many People Living in the ‘Diabetes Belt’ Are Plagued With Medical Debt
by Robert Benincasa, NPR and Nick McMillan, NPR
Tue, 30 May 2023 09:00:00 +0000
Delores Lowery remembers vividly the day in 2016 when she was working in a weaving plant near her home in Bennettsville, South Carolina, and the world around her seemed to go dim.
She turned to her co-workers. “And I asked, I said, ‘Why y’all got it so dark in here? They said, ‘Delores, it’s not dark in here.’ I said, ‘Yes, it is. It’s so dark in here.’”
She landed in the hospital. Her A1C level, which shows the average percentage of sugar in someone’s blood over the past few months, was 14%.
A reading of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.
Lowery’s home in Marlboro County is at the heart of what the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention calls the “Diabetes Belt” — 644 mostly Southern counties where rates of the disease are high.
And of those counties, NPR found that more than half have high levels of medical debt. That means at least 1 in 5 people have medical debt in collections.
That’s much higher than the national rate, which is 13%, according to the Urban Institute, a social-policy nonprofit. In Marlboro County, 37% of people have medical debt in collections.
NPR measured the overlap of Diabetes Belt counties and high medical debt counties by merging the institute’s medical debt database with the CDC’s list of Diabetes Belt counties.
Loading…
Urban Institute economist Breno Braga said medical debt, like diabetes, is concentrated in the South.
“The single most important predictor of a county’s medical debt is the prevalence of chronic conditions. So it’s basically the share of the population that has disease, such as diabetes, hypertension, and other types,” he said.
That finding is from an analysis conducted by the Urban Institute for KFF Health News and NPR as part of an investigation into medical debt published last year. The investigation found, among other things, that 100 million people in the U.S. have some kind of health care debt, a burden that can be devastating for people with chronic illnesses such as diabetes and cancer.
Lowery has been dealing with both the medical and financial challenges of Type 2 diabetes, and much more. The years since her diagnosis have been extremely difficult, with one life-changing event having overwhelming health and financial consequences.
In 2017, she came home one day to find her daughter, Ella Shantrica, on the floor, stabbed to death. The body of her granddaughter, 8-year-old Iyana, was found 12 days later in a nearby creek. In February, a man was found guilty of the killings and sentenced to life in prison.
In an interview in the front room of that tidy single-family home in Bennettsville, Lowery said it took time before she could bring herself to return to the house.
“Every day, 24 hours a day, that incident is in my head,” she said. “It will never, ever go away.”
She credits her church’s pastor with helping her go back to the house, which she shares with grandson Tyreon, a teenager on the autism spectrum. With her daughter gone, Lowery said, she is Tyreon’s sole caregiver.
Paying for diabetes care along with bills for food and housing has been a constant financial strain that eventually put her in debt.
“The cost of living was so extremely high in trying to raise my grandson that I just got behind,” she said.
Many Americans are facing similar hardships. In addition to NPR’s findings, research from the American Diabetes Association said people with the disease have more than twice the medical expenses annually as those without the disease.
“Because diabetes is a chronic illness, there are always six-month appointments,” said Donna Dees, who lives in Georgia and was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes in 2008. “Every six months, go to the doctor, you’ve got lab work. So that’s how the costs keep building up and building up.”
Dees built up thousands of dollars in medical debt and got help from RIP Medical Debt, a nonprofit group that says it has wiped out more than $8 billion in medical debt.
Lowery will tell you that she gets high-quality and compassionate health care from a local provider. But the financial challenge of living with diabetes has put her health into decline.
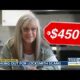
A drug that once helped her, Ozempic, is now too costly for her. She said the medicine had been helping bring her diabetes under control. She was getting it delivered to her home, but she didn’t meet her copays, and the bills piled up as unpaid debt. Soon, the deliveries stopped and Lowery tried to renew the prescription at the local pharmacy.
“I went to get it and the woman told me, ‘I don’t think you’re going to be able to afford this.’ I said, ‘Why not?’ She said, ‘Because it’s seven hundred and some dollars.’”
Worse, as the drug’s profile skyrocketed in recent months as a treatment for weight loss among celebrities, demand increased and a shortage developed.
Lowery said this year that she hadn’t been able to get Ozempic for several months and that her diabetes was getting worse. Her insurance company has been of no help.
“Nobody is willing to work with me with Ozempic. I don’t know what to do,” Lowery said. “They won’t send me the medicine.”
She and her provider even talked about getting physician samples, but given Ozempic’s growing popularity, that didn’t work.
A Changing Economy
In Lowery’s hometown, others are struggling too.
More than 1 in 3 residents of the surrounding county have medical debt in collections, and 1 in 3 live in poverty.
It wasn’t always this way, locals told NPR. The area once hummed with manufacturing companies, restaurants, and other amenities. There were plenty of good jobs to go around.
But one by one, employers moved out. Today, downtown Bennettsville is pretty quiet. South Carolina as a whole has nearly 100,000 fewer manufacturing jobs than it did in 2000.
“Bennettsville used to be a more thriving community years ago,” said Lowery’s health care provider, nurse practitioner Pat Weaver. “With a lot of our plants leaving for, you know, overseas in the last 15-20 years really made a devastating impact. We used to have a hospital here and now we no longer have that. It is very poor.”
Weaver works for CareSouth, a nonprofit health center that has a federal government designation as a safety-net provider.
As she walks the halls of the clinic, checking on colleagues and patients, she says that of the 3,300 appointments she takes every year, more than 90% of the people she treats have Type 2 diabetes.
She and others point to Bennettsville’s changing economic fortune as a source of health problems in the community. Half the households in the city have an income of less than $32,000. Lower-income residents often can’t or don’t choose the kinds of healthy meals that would help them control their diabetes, she said.
“The fast foods don’t help at all, and a lot of people just eat it every day, and that’s a problem. It truly is,” Weaver said. “But we have programs to help them. We even have a program where we take patients to the grocery store and we teach them what to buy.”
CareSouth takes other steps, too, to fight the effects of poverty and disease in Bennettsville. The center has a sliding-fee scale based on ability to pay and an in-house pharmacy that uses a federal program to keep drug prices down.
For Lowery, having a medical provider like Weaver has been a lifeline. “She’s seen me through so much,” Lowery said. “She tried different medicines to get my diabetes intact.”
Finding Weaver came at a time when her family’s murders threw her into depression, her finances spiraled out of control, and her diabetes worsened. Weaver, she said, helped get her into counseling.
“When she found out what had happened, I honestly believe in my heart that she cried just like I cried,” Lowery said. “She did so much for me.”
South Carolina’s Choice on Medicaid
While there is no easy solution for Lowery, who is over 65 and enrolled in Medicare, the Urban Institute and others say a simple policy change could prevent others from getting to such a difficult stage in their disease and finances: Expand Medicaid.
“Seventy-nine out of the 100 counties with the highest levels of medical debt are in states that have not expanded Medicaid under the ACA,” the Urban Institute’s Braga said, referring to the Affordable Care Act.
Also known as Obamacare, the ACA offered states the option to expand their health insurance programs for the poor.
South Carolina is one of 10 states that have declined to do so, and where NPR identified more than two dozen counties that fall within the Diabetes Belt and have high rates of medical debt. There’s evidence from other states that people became healthier and owed less money to medical providers after Medicaid expansion.
A Boston University researcher looked at health centers just like CareSouth — more than 900 of them serving nearly 20 million patients.
The centers in states that did expand Medicaid reported better diabetes control than those in states that didn’t expand the program, and the effect was quick — within three years of the expansion.
Those improvements happened consistently among Black and Hispanic patients, who have higher rates of diabetes.
A study in Louisiana found that people who gained Medicaid coverage after an expansion there had reduced medical debt.
Lowery said that going forward she will continue to rely on her faith and her church community to help her through the tough times.
Still, she worries about the possible worsening of her diabetes and the financial stress of daily life.
“I wish things would get better,” she said. “I think I would sleep a little better, because sometimes it’s kind of hard for me to try to keep some food on the table.”
This article is from a partnership with NPR, where it was edited by Robert Little and Kamala Kelkar and produced by Meg Anderson; the photos were edited by Virginia Lozano.
About This Project
“Diagnosis: Debt” is a reporting partnership between KFF Health News and NPR exploring the scale, impact, and causes of medical debt in America.
The series draws on original polling by KFF, court records, federal data on hospital finances, contracts obtained through public records requests, data on international health systems, and a yearlong investigation into the financial assistance and collection policies of more than 500 hospitals across the country.
Additional research was conducted by the Urban Institute, which analyzed credit bureau and other demographic data on poverty, race, and health status for KFF Health News to explore where medical debt is concentrated in the U.S. and what factors are associated with high debt levels.
The JPMorgan Chase Institute analyzed records from a sampling of Chase credit card holders to look at how customers’ balances may be affected by major medical expenses. And the CED Project, a Denver nonprofit, worked with KFF Health News on a survey of its clients to explore links between medical debt and housing instability.
KFF Health News journalists worked with KFF public opinion researchers to design and analyze the “KFF Health Care Debt Survey.” The survey was conducted Feb. 25 through March 20, 2022, online and via telephone, in English and Spanish, among a nationally representative sample of 2,375 U.S. adults, including 1,292 adults with current health care debt and 382 adults who had health care debt in the past five years. The margin of sampling error is plus or minus 3 percentage points for the full sample and 3 percentage points for those with current debt. For results based on subgroups, the margin of sampling error may be higher.
Reporters from KFF Health News and NPR also conducted hundreds of interviews with patients across the country; spoke with physicians, health industry leaders, consumer advocates, debt lawyers, and researchers; and reviewed scores of studies and surveys about medical debt.
By: Robert Benincasa, NPR and Nick McMillan, NPR
Title: Many People Living in the ‘Diabetes Belt’ Are Plagued With Medical Debt
Sourced From: kffhealthnews.org/news/article/many-people-living-in-the-diabetes-belt-are-plagued-with-medical-debt/
Published Date: Tue, 30 May 2023 09:00:00 +0000
Did you miss our previous article…
https://www.biloxinewsevents.com/mammograms-at-40-breast-cancer-screening-guidelines-spark-fresh-debate/
Kaiser Health News
A California Lawmaker Leans Into Her Medical Training in Fight for Health Safety Net
SACRAMENTO, Calif. — State Sen. Akilah Weber Pierson anticipates that California’s sprawling Medicaid program, known as Medi-Cal, may need to be dialed back after Gov. Gavin Newsom releases his latest budget, which could reflect a multibillion-dollar deficit.
Even so, the physician-turned-lawmaker, who was elected to the state Senate in November, says her priorities as chair of a budget health subcommittee include preserving coverage for the state’s most vulnerable, particularly children and people with chronic health conditions.
“We will be spending many, many hours and long nights figuring this out,” Weber Pierson said of the lead-up to the state’s June 15 deadline for lawmakers to pass a balanced budget.
With Medicaid cuts on the table in Washington and Medi-Cal running billions of dollars over budget due to rising drug prices and higher-than-anticipated costs to cover immigrants without legal status, Weber Pierson’s dual responsibilities — maintaining a balanced budget and delivering compassionate care to the state’s poorest residents — could make her instrumental in leading Democrats through this period of uncertainty.
President Donald Trump has said GOP efforts to cut federal spending will not touch Medicaid beyond “waste, fraud, and abuse.” Congressional Republicans are considering going after states such as California that extend coverage to immigrants without legal status and imposing restrictions on provider taxes. California voters in November made permanent the state’s tax on managed-care health plans to continue funding Medi-Cal.
The federal budget megabill is winding its way through Congress, where Republicans have set a target of $880 billion in spending cuts over 10 years from the House committee that oversees the Medicaid program.
Health care policy researchers say that would inevitably force the program to restrict eligibility, narrow the scope of benefits, or both. Medi-Cal covers 1 in 3 Californians, and more than half of its nearly $175 billion budget comes from the federal government.
One of a handful of practicing physicians in the state legislature, Weber Pierson is leaning heavily on her experience as a pediatric and adolescent gynecologist who treats children with reproductive birth defects — one of only two in Southern California.
Weber Pierson spoke to KFF Health News correspondent Christine Mai-Duc in Sacramento this spring. She has introduced bills to improve timely access to care for pregnant Medi-Cal patients, require developers to mitigate bias in artificial intelligence algorithms used in health care, and compel health plans to cover screenings for housing, food insecurity, and other social determinants of health.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Q: You’re a state senator, you practice medicine in your district, and you’re also a mom. What does that look like day to day?
A: When you grow up around someone who juggles a lot, that just kind of becomes the norm. I saw this with my mom [former state Assembly member Shirley Weber, who is now secretary of state].
I’m really happy that I’m able to continue with my clinical duties. Those in the health care profession understand how much time, energy, effort, and money we put into becoming a health care provider, and I’m still fairly early in my career. With my particular specialty, it would also be a huge void in the San Diego region for me to step back.
Q: What are the biggest threats or challenges in health care right now?
A: The immediate threats are the financial issues and our budget. A lot of people do not understand the overwhelming amount of dollars that go into our health care system from the federal government.
Another issue is access. Almost everybody in California is covered by insurance. The problem is that we have not expanded access to providers. If you have insurance but your nearest labor and delivery unit is still two hours away, what exactly have we really done for those patients?
The third thing is the social determinants of health. The fact that your life expectancy is based on the ZIP code in which you were born is absolutely criminal. Why are certain areas devoid of having supermarkets where you can go and get fresh fruits and vegetables? And then we wonder why certain people have high blood pressure and diabetes and obesity.
Q: On the federal level, there’s a lot of conversation happening around Medicaid cuts, reining in the MCO tax, and potentially dropping Affordable Care Act premium subsidies. Which is the biggest threat to California?
A: To be quite honest with you, all of those. The MCO tax was a recognition that we needed more providers, and in order to get more providers, we need to increase the Medi-Cal reimbursement rates. The fact that now it is at risk is very, very concerning. That is how we are able to care for those who are our most vulnerable in our state.
Q: If those cuts do come, what do we cut? How do we cut it?
A: We are in a position where we have to talk about it at this point. Our Medi-Cal budget, outside of what the federal government may do, is exploding. We definitely have to ensure that those who are our most vulnerable — our kids, those with chronic conditions — continue to have some sort of coverage. What will that look like?
To be quite honest with you, at this point, I don’t know.
Q: How can the state make it the least painful for Californians?
A: Sometimes the last one to the table is the first one to have to leave the table. And so I think that’s probably an approach that we will look at. What were some of the more recent things that we’ve added, and we’ve added a lot of stuff lately. How can we trim down — maybe not completely eliminate, but trim down on — some of these services to try to make them more affordable?
Q: When you say the last at the table, are you talking about the expansion of Medi-Cal coverage to Californians without legal status? Certain age groups?
A: I don’t want to get ahead of this conversation, because it is a very large conversation between not only me but also the [Senate president] pro tem, the Assembly speaker, and the governor’s office. But those conversations are being had, keeping in mind that we want to provide the best care for as many people as possible.
Q: You’re carrying a bill related to AI in health care this year. Tell me what you’re trying to address.
A: It has just exploded at a speed that I don’t know any of us were anticipating. We are trying to play catch-up, because we weren’t really at the table when all of this stuff was being rolled out.
As we advance in technology, it’s been great; we’ve extended lives. But we need to make sure that the biases that led to various discrepancies and health care outcomes are not the same biases that are inputted into that system.
Q: How does Sacramento policy impact your patients and what experience as a physician do you bring to policymaking?
A: I speak with my colleagues with actual knowledge of what’s happening with our patients, what’s happening in the clinics. My patients and my fellow providers will often come to me and say, “You guys are getting ready to do this, and this is why it’s going to be a problem.” And I’m like, “OK, that’s really good to know.”
I work at a children’s facility, and right after the election, specialty hospitals were very concerned around funding and their ability to continue to practice.
In the MCO discussion, I was hearing from providers, hospitals on the ground on a regular basis. With the executive order [on gender-affirming care for transgender youth], I have seen people that I work with concerned, because these are patients that they take care of. I’m very grateful for the opportunity to be in both worlds.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
The post A California Lawmaker Leans Into Her Medical Training in Fight for Health Safety Net appeared first on kffhealthnews.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This content leans center-left due to its focus on preserving and protecting Medi-Cal, a Medicaid program serving vulnerable populations, particularly children and immigrants. It highlights concerns about federal budget cuts proposed by Republicans and emphasizes the importance of maintaining social services, healthcare access, and addressing social determinants of health. The perspective is generally supportive of expanding healthcare coverage and cautious about fiscal reductions affecting marginalized groups, which aligns with moderate Democratic and progressive viewpoints.
Kaiser Health News
Cutting Medicaid Is Hard — Even for the GOP
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
After narrowly passing a budget resolution this spring foreshadowing major Medicaid cuts, Republicans in Congress are having trouble agreeing on specific ways to save billions of dollars from a pool of funding that pays for the program without cutting benefits on which millions of Americans rely. Moderates resist changes they say would harm their constituents, while fiscal conservatives say they won’t vote for smaller cuts than those called for in the budget resolution. The fate of President Donald Trump’s “one big, beautiful bill” containing renewed tax cuts and boosted immigration enforcement could hang on a Medicaid deal.
Meanwhile, the Trump administration surprised those on both sides of the abortion debate by agreeing with the Biden administration that a Texas case challenging the FDA’s approval of the abortion pill mifepristone should be dropped. It’s clear the administration’s request is purely technical, though, and has no bearing on whether officials plan to protect the abortion pill’s availability.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Anna Edney of Bloomberg News, Maya Goldman of Axios, and Sandhya Raman of CQ Roll Call.
Panelists
Anna Edney
Bloomberg News
Maya Goldman
Axios
Sandhya Raman
CQ Roll Call
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- Congressional Republicans are making halting progress on negotiations over government spending cuts. As hard-line House conservatives push for deeper cuts to the Medicaid program, their GOP colleagues representing districts that heavily depend on Medicaid coverage are pushing back. House Republican leaders are eying a Memorial Day deadline, and key committees are scheduled to review the legislation next week — but first, Republicans need to agree on what that legislation says.
- Trump withdrew his nomination of Janette Nesheiwat for U.S. surgeon general amid accusations she misrepresented her academic credentials and criticism from the far right. In her place, he nominated Casey Means, a physician who is an ally of HHS Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s and a prominent advocate of the “Make America Healthy Again” movement.
- The pharmaceutical industry is on alert as Trump prepares to sign an executive order directing agencies to look into “most-favored-nation” pricing, a policy that would set U.S. drug prices to the lowest level paid by similar countries. The president explored that policy during his first administration, and the drug industry sued to stop it. Drugmakers are already on edge over Trump’s plan to impose tariffs on drugs and their ingredients.
- And Kennedy is scheduled to appear before the Senate’s Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee next week. The hearing would be the first time the secretary of Health and Human Services has appeared before the HELP Committee since his confirmation hearings — and all eyes are on the committee’s GOP chairman, Sen. Bill Cassidy of Louisiana, a physician who expressed deep concerns at the time, including about Kennedy’s stances on vaccines.
Also this week, Rovner interviews KFF Health News’ Lauren Sausser, who co-reported and co-wrote the latest KFF Health News’ “Bill of the Month” installment, about an unexpected bill for what seemed like preventive care. If you have an outrageous, baffling, or infuriating medical bill you’d like to share with us, you can do that here.
Plus, for “extra credit” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: NPR’s “Fired, Rehired, and Fired Again: Some Federal Workers Find They’re Suddenly Uninsured,” by Andrea Hsu.
Maya Goldman: STAT’s “Europe Unveils $565 Million Package To Retain Scientists, and Attract New Ones,” by Andrew Joseph.
Anna Edney: Bloomberg News’ “A Former TV Writer Found a Health-Care Loophole That Threatens To Blow Up Obamacare,” by Zachary R. Mider and Zeke Faux.
Sandhya Raman: The Louisiana Illuminator’s “In the Deep South, Health Care Fights Echo Civil Rights Battles,” by Anna Claire Vollers.
Also mentioned in this week’s podcast:
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
We encourage organizations to republish our content, free of charge. Here’s what we ask:
You must credit us as the original publisher, with a hyperlink to our kffhealthnews.org site. If possible, please include the original author(s) and KFF Health News” in the byline. Please preserve the hyperlinks in the story.
It’s important to note, not everything on kffhealthnews.org is available for republishing. If a story is labeled “All Rights Reserved,” we cannot grant permission to republish that item.
Have questions? Let us know at KHNHelp@kff.org
The post Cutting Medicaid Is Hard — Even for the GOP appeared first on kffhealthnews.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
The content provides a balanced overview of current health policy issues with a slight lean towards framing Republican budget efforts and Medicaid cuts critically, emphasizing the potential negative impacts on constituents reliant on these programs. The coverage fairly presents multiple viewpoints, including fiscal conservatives and moderates within the Republican Party, but the tone suggests some skepticism towards conservative budget priorities and Trump administration policies. Overall, the focus on health care access and concerns about cuts aligns with a center-left perspective without strong partisan language or ideological bias.
Kaiser Health News
As Republicans Eye Sweeping Medicaid Cuts, Missouri Offers a Preview
CRESTWOOD, Mo. — The prospect of sweeping federal cuts to Medicaid is alarming to some Missourians who remember the last time the public medical insurance program for those with low incomes or disabilities was pressed for cash in the state.
In 2005, Missouri adopted some of the strictest eligibility standards in the nation, reduced benefits, and increased patients’ copayments for the joint federal-state program due to state budget shortfalls totaling about $2.4 billion over several prior years. More than 100,000 Missourians lost coverage as a result, and the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia reported that the changes led to increases in credit card borrowing and debt in third-party collections.
A woman told NPR that year that her $6.70-an-hour McDonald’s job put her over the new income limits and rendered her ineligible, even though she was supporting three children on about $300 a week. A woman receiving $865 a month in disability payments worried at a town hall meeting about not being able to raise her orphaned granddaughter as the state asked her to pay $167 a month to keep her health coverage.
Now, Missouri could lose an estimated $2 billion a year in federal funding as congressional Republicans look to cut at least $880 billion over a decade from a pool of funding that includes Medicaid programs nationwide. Medicaid and the closely related Children’s Health Insurance Program together insure roughly 79 million people — about 1 in 5 Americans.
“We’re looking at a much more significant impact with the loss of federal funds even than what 2005 was,” said Amy Blouin, president of the progressive Missouri Budget Project think tank. “We’re not going to be able to protect kids. We’re not going to be able to protect people with disabilities from some sort of impact.”
At today’s spending levels, a cut of $880 billion to Medicaid could lead to states’ losing federal funding ranging from $78 million a year in Wyoming to $13 billion a year in California, according to an analysis from KFF, a health information nonprofit that includes KFF Health News. State lawmakers nationwide would then be left to address the shortfalls, likely through some combination of slashing benefits or eligibility, raising taxes, or finding a different large budget item to cut, such as education spending.
Republican lawmakers are floating various proposals to cut Medicaid, including one to reduce the money the federal government sends to states to help cover adults who gained access to the program under the Affordable Care Act’s provision known as Medicaid expansion. The 2010 health care law allowed states to expand Medicaid eligibility to cover more adults with low incomes. The federal government is picking up 90% of the tab for that group. About 20 million people nationwide are now covered through that expansion.
Missouri expanded Medicaid in 2021. That has meant that a single working-age adult in Missouri can now earn up to $21,597 a year and qualify for coverage, whereas before, nondisabled adults without children couldn’t get Medicaid coverage. That portion of the program now covers over 329,000 Missourians, more than a quarter of the state’s Medicaid recipients.
For every percentage point that the federal portion of the funding for that group decreases, Missouri’s Medicaid director estimated, the state could lose $30 million to $35 million a year.
But the equation is even more complicated given that Missouri expanded access via a constitutional amendment. Voters approved the expansion in 2020 after the state’s Republican leadership resisted doing so for a decade. That means changes to Medicaid expansion in Missouri would require voters to amend the state constitution again. The same is true in South Dakota and Oklahoma.
So even if Congress attempted to narrowly target cuts to the nation’s Medicaid expansion population, Washington University in St. Louis health economist Timothy McBride said, Missouri’s expansion program would likely stay in place.
“Then you would just have to find the money elsewhere, which would be brutal in Missouri,” McBride said.
In Crestwood, a suburb of St. Louis, Sandra Smith worries her daughter’s in-home nursing care would be on the chopping block. Nearly all in-home services are an optional part of Medicaid that states are not required to include in their programs. But the services have been critical for Sandra and her 24-year-old daughter, Sarah.
Sarah Smith has been disabled for most of her life due to seizures from a rare genetic disorder called Dravet syndrome. She has been covered by Medicaid in various ways since she was 3.

She needs intensive, 24-hour care, and Medicaid pays for a nurse to come to their home 13 hours a day. Her mother serves as the overnight caregiver and covers when the nurses are sick — work Sandra Smith is not allowed to be compensated for and that doesn’t count toward the 63-year-old’s Social Security.
Having nursing help allows Sandra Smith to work as an independent podcast producer and gives her a break from being the go-to-person for providing care 24 hours a day, day after day, year after year.
“I really and truly don’t know what I would do if we lost the Medicaid home care. I have no plan whatsoever,” Sandra Smith said. “It is not sustainable for anyone to do infinite, 24-hour care without dire physical health, mental health, and financial consequences, especially as we parents get into our elder years.”
Elias Tsapelas, director of fiscal policy at the conservative Show-Me Institute, said potential changes to Medicaid programs depend on the extent of any budget cuts that Congress ultimately passes and how much time states have to respond.
A large cut implemented immediately, for example, would require state legislators to look for parts of the budget they have the discretion to cut quickly. But if states have time to absorb funding changes, he said, they would have more flexibility.
“I’m not ready to think that Congress is going to willingly put us on the path of making every state go cut their benefits for the most vulnerable,” Tsapelas said.
Missouri’s congressional delegation split along party lines over the recent budget resolution calling for deep spending cuts, with the Republicans who control six of the eight House seats and both Senate seats all voting for it.
But 76% of the public, including 55% of Republicans, say they oppose major federal funding cuts to Medicaid, according to a national KFF poll conducted April 8-15.
And Missouri Sen. Josh Hawley, a Republican, has said that he does not support cutting Medicaid and posted on the social platform X that he was told by President Donald Trump that the House and Senate would not cut Medicaid benefits and that Trump won’t sign any benefit cuts.
“I hope congressional leadership will get the message,” Hawley posted. He declined to comment for this article.
U.S. House Republicans are aiming to pass a budget by Memorial Day, after many state legislatures, including Missouri’s, will have adjourned for the year.
Meanwhile, Missouri lawmakers are poised to pass a tax cut that is estimated to reduce state revenue by about $240 million in the first year.
The post As Republicans Eye Sweeping Medicaid Cuts, Missouri Offers a Preview appeared first on kffhealthnews.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This content displays a center-left political bias by emphasizing the negative impacts of proposed Republican-led federal cuts to Medicaid funding. It highlights the struggles of low-income and disabled individuals who rely on Medicaid, underscores the importance of Medicaid expansion, and includes perspectives from progressive advocates concerned about the consequences of funding reductions. Although it presents some conservative viewpoints, such as those from the Show-Me Institute and mentions Republican lawmakers’ positions, the overall tone supports maintaining or expanding social welfare programs, reflecting a center-left leaning perspective.
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days agoMissouri family, two Oklahoma teens among 8 killed in Franklin County crash
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed4 days agoMotel in Roswell shutters after underage human trafficking sting | FOX 5 News
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed3 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed3 days agoAerospace supplier, a Fortune 500 company, chooses North Carolina site | North Carolina
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed2 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed2 days agoRaleigh woman gets 'miracle' she prayed for after losing thousands in scam
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed2 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed2 days agoPalm Bay suspends school zone speed cameras again, this time through rest of school year
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed7 days agoGas station employee killed, customer assaulted in Harnett Co. robbery
-

 Mississippi Today5 days ago
Mississippi Today5 days agoCoast protester suffers brain bleed after alleged attack by retired policeman
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed7 days ago72nd Annual Reunion for those who once lived in Dunbarton, Sc