Mississippi Today
‘Transformative’ mental health bill awaits governor’s signature, funding
‘Transformative’ mental health bill awaits governor’s signature, funding
A bill passed unanimously by the Legislature is expected to bring some reform to Mississippi’s long-troubled mental health care system, which often strands people with mental health issues in jail with long delays in treatment and has been under scrutiny from federal authorities for years.
“House Bill 1222 provides solid solutions to national mental health issues and is so transformative that it could be a really strong model for other states to implement,” said Dr. Katherine Pannel, a psychiatrist, president elect of the Mississippi Psychiatric Association and longtime Mississippi mental health advocate.
The measure, authored by Rep. Sam Creekmore, R-New Albany, would provide mental health training for Mississippi’s law enforcement, often the first point of contact for those suffering illness. It would also expand a court-liaison program, helping families dealing with the court system. It also seeks to improve cooperation between county governments and regional commissions that oversee community mental health centers.
The bill faced some realpolitik setbacks as it made its way through the Legislature. The initial version would have created a tax on vaping products that was expected to bring in $6.5 million a year, more than half of which would go to help counties house people people needed mental health services. But the GOP supermajority in the Legislature would not go for any new tax, so now the measure awaits lawmakers approval of a general appropriation. Creekmore expects the Legislature to provide about $4 million a year for the program.
At one point the bill was amended to include measures proposed by Rep. Kevin Felsher, R-Biloxi, that would have set some stringent restrictions on people with mental illness being held in jail to await treatment. It would also have allowed counties to contract for people to receive private mental health services instead of waiting in jail, with counties paying rates capped at what Medicaid would pay. These measures faced political opposition and were removed, but supporters say the final bill is a major step in the right direction for mental health reform.
“It’s not a panacea,” said Senate Public Health and Welfare Chairman Hob Bryan, D-Amory. “But one of the most important things that has happened in mental health here over the last several years is that there’s attention being focused on the problem.”
Creekmore was tasked last year with leading a House subcommittee on mental health. He is credited with working to get mental health services, law enforcement, the courts and local governments on the same page in dealing with people with mental health issues in authoring “The Mississippi Collaborative Response to Mental Health Act.”
The final version of the bill passed both the House and Senate unanimously, and awaits Gov. Tate Reeves’ signature and approval of funding in the final days of the legislative session. Creekmore said he is confident both will happen.
“Within eight years, every police officer in Mississippi will have a basic knowledge of how to deal with mental health issues, which will help keep them safer, and help others dealing with mental health crises,” Creekmore said. He said that similar training in Tennessee has greatly decreased the numbers of injuries to officers.
Mississippi Department of Mental Health Director Wendy Bailey said, “HB 1222 aims to provide assistance by both providing training for law enforcement and in helping expand programs that work to divert individuals from inpatient stays at state hospitals to community services near them.”
DMH provides Mental Health First Aid training for law enforcement. The bill would require all officers to receive this eight-hour training over the next eight years. Crisis intervention team officers would receive more intensive, 40-hour training. Creekmore said each law enforcement department would be required to have a CIT officer, or to contract with another nearby agency to have one it could call.
The bill would expand the state’s pilot court liaison program, requiring counties with 20 or more mental health commitments a year to have one, either in the local community mental health center or chancery clerk’s office. These liaisons families as they approach the court system help find treatment options other than commitment to a hospital where appropriate. Bailey said, “We have already seen positive outcomes from the pilot court liaisons over the last year.”
Creekmore said the bill would also require better reporting of mental health cases and issues on the state and local level, and revamp requirements for the state mental health board and regional commissions that help oversee community mental health centers. This will help the state better track where issues are and be able to address them, and improve coordination.
“We believe that services and supports are the shared responsibility of state and local governments, communities, family members and service providers,” Bailey said. “We’re in favor of anything that can strengthen communication, relationships and partnerships, and believe this bill aims to do exactly that.”
Bryan said: “One of the things that’s in Sam’s bill is based on something tried in Monroe, Itawamba and Lee counties. When a family member gets to the point they don’t know what to do, they go to the county clerk’s office, because they know they will do something — same as going to the emergency room, because you know they’ll do something. That starts a legal process, and commitment is necessary in some cases, but to a large extent that’s left over from a time when we didn’t know better and didn’t have any services. This will have someone from the community mental health center on call to go to the clerk’s office and talk to the family, discuss some alternatives and what things are available in the community. That conversation has had a very good effect in reducing the number of commitments, and that’s a good thing in and of itself.”
Pannel said, “We have not seen our Legislature this active on mental health and substance abuse issues in a while.”
“Representative Creekmore has been a true mental health champion in Mississippi,” Pannel said.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
This superintendent took a failing Delta school district to a ‘B’ rating. Now, she’s leaving
INDIANOLA — The top of the Jeep was down, and Miskia Davis was behind the wheel, leading a parade through downtown Indianola.
It was 2019, just two years after the now 50-year-old Davis became superintendent of Sunflower County Consolidated School District. Back then, she wasn’t sure this moment would ever come.
She recalled feeling the first cool breeze of October as she waved at people who lined the street, smiling and celebrating.
But it had — the district’s first “C” rating, its first passing grade, and the community had shown up to a parade to celebrate the achievement. Generations of teachers and Sunflower County graduates stood on the sidewalk, proudly cheering the assembly of cars and students.
“It was … Oh my God,” Davis said. “My children were like, ‘We did something.’”
The work hadn’t been easy, but it had been worth it, Davis thought — the number crunching, the doubt and lukewarm welcome she felt from the community, the tough decisions she’d had to make.
Now, she’s ready to move on.
Daughter of the Delta
From starting kindergarten to subbing for elementary classes, Davis’ childhood and career in Sunflower County and her identity as a daughter of the Delta were her strengths in the classroom, she said.
“I grew up in Drew, poor and with two young parents,” Davis said. “We didn’t have elaborate meals, and when I went home, the lights may have been off. But it made me who I am, and these children were experiencing the same things I experienced as a child.”
So Davis was relatable. But as a young high school teacher at Ruleville Central High School, some of her students looked older than her and many were taller than she was. She was forced to learn how to command respect, too.
One particular child taught her an invaluable lesson. He was a star football player in her biology class, and he was failing the course by two points. He caused trouble in class and Davis was determined to fail him, despite more experienced teachers prodding her not to, to look past her own ego.
So Davis gave him another chance. She had him do extra work and spent hours talking to him. She learned why he behaved poorly in class — he was one of seven children to a young, single mother.
“He was angry at the world, and I just happened to be in the world,” she said. “It taught me the power of relationships. I think that’s the most important catalyst in transforming education.”
It was during that time that her superintendent “saw something” in her and pushed her to become a school leader. That kickstarted her journey in administration.

Davis soon learned she had a particular gift for turning failing schools around. Under her leadership as principal, Ruleville Middle School went from failing to an “A” letter grade in three years.
Her school improvement strategy began to take shape, similar to her teaching style. Davis was both a disciplinarian and someone to whom teachers and students could relate. She prioritized building strong relationships with teachers who were invested in their students. But she didn’t shy away from making controversial decisions, either. In Ruleville, she fired nearly all of the staff when she arrived.
But as Davis was gaining her footing as an administrator, Sunflower County School District was struggling.
After consistent failing grades resulted in the state takeovers of Indianola, Sunflower and Drew school districts, the Legislature decided to consolidate the three systems in 2012.
District consolidation is a massive undertaking for any community, but especially for Sunflower County — smack dab in the middle of the Delta, an under-resourced region with a shrinking population, high poverty rates and a deep history of racial exploitation.
Davis arrived in 2014 to a school district that had lost hope — a district that she didn’t recognize.
All Sunflower knew was ‘failure’
Davis never wanted to be superintendent.
She spent three years working under the leader of the consolidated district. But when the superintendent was dismissed in 2017, Davis was appointed to the head role in an interim capacity. She got the job in January of 2018 without ever applying.
So with another state takeover looming, Davis went to work. The biggest challenge? The district and the community seemed resigned to failure.
“We had been failing so long, that’s all we knew,” she said. “No one was even sad.”
Early on, Davis visited a school to discuss recent test results. She was so struck by teachers’ apathy that she stopped the meeting midway and had them tear off a scrap of paper and write “yes” or “no” to a question: Did the teachers believe their school could ever be successful?
More than half said no.
“They were teaching my children,” Davis said, tearing up. “And they didn’t think they would ever be successful.”
Davis went to the school board to tell members that she wouldn’t be renewing many of those teachers’ contracts. That’s when she realized she didn’t just need to boost test scores — she needed to change attitudes.
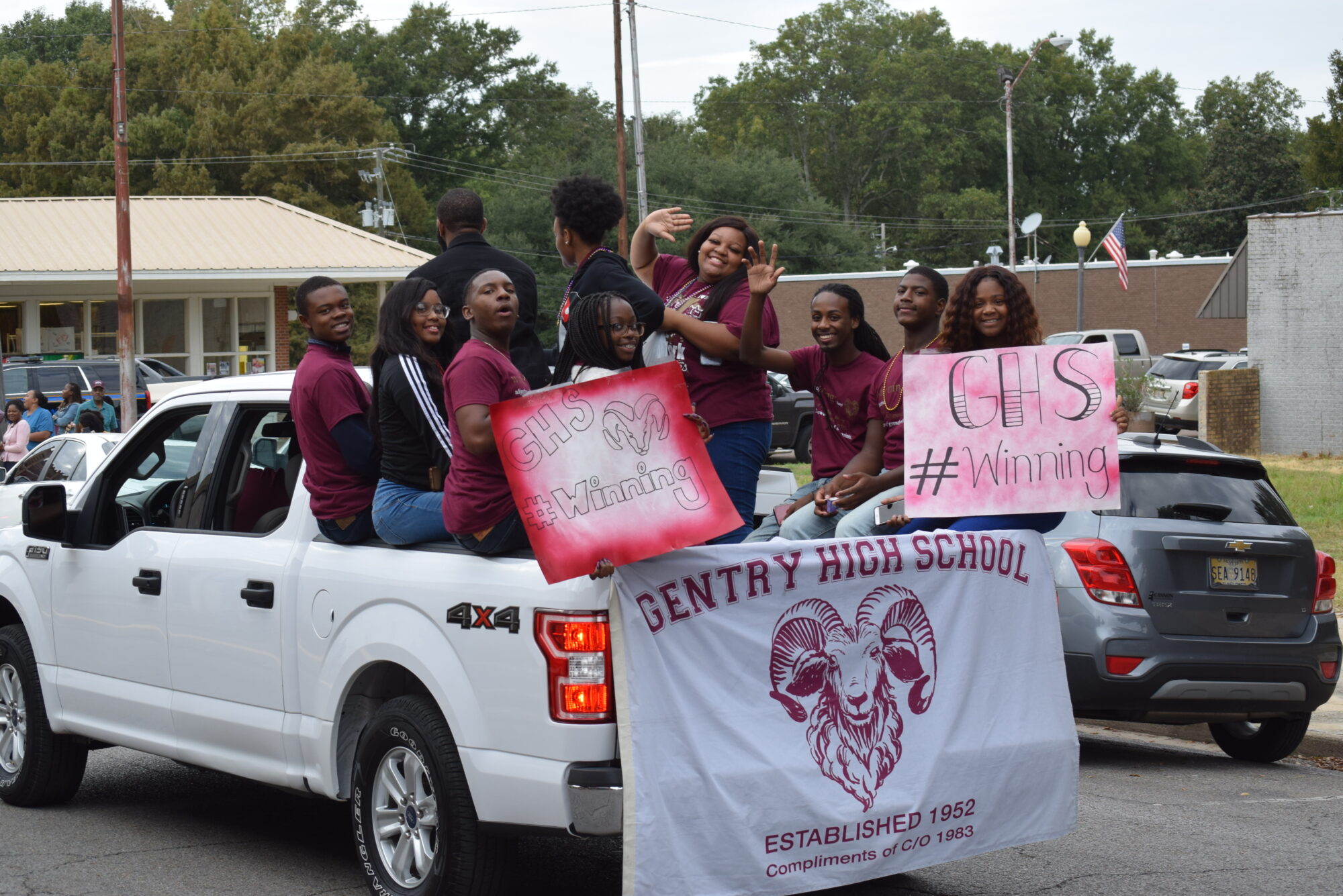
The hashtag #WINNING was born.
“We started to celebrate every little accomplishment,” Davis said. “We got T-shirts, shades, whatever. That was our mantra.”
Children received certificates for a week of perfect attendance. When students did well on benchmark assessments, teachers were ushered into the hallway to be celebrated by students and colleagues. Davis created the “Killin’ It” awards, given to students and teachers for meeting their testing benchmarks.
They were just certificates, at the end of the day. But it led to a changed school culture, a renewed belief that they could succeed.
As an administrator, Davis leaned on what she knew worked as a teacher, relationship-building and strong discipline (she even sent her nephew to alternative school for fighting), and combined it with a data-driven approach and an eagle-eyed focus on testing.
She put an academic coach in every building, whose sole responsibility was supporting teachers.
Davis took teacher Dylan Jones out of the classroom and put him in the central office, where he was tasked with tracking district metrics.
Jones uncovered which consultants were working and which were uselessly costing the district millions. The district went from contracting with 30 firms to just four.
Jones also created an accountability system for teachers. With one click, Davis could see how each teacher’s students were performing, and she gave everyone access to the data. If teachers weren’t meeting their goals, Davis hosted regular meetings and had them explain — in front of everyone — what they needed to succeed.
Davis’ methods weren’t popular at first. Educators went to the school board and complained that the system was “punitive.” Some even quit. But Davis was steadfast and implored board members to see the work she and her team could do, if given the chance.
The district’s rating didn’t budge in 2018.
But in fall 2019, after Davis’ first full year as superintendent, Sunflower County Consolidated School District had earned its first “C” rating.
What happened after the first ‘C’
Those early years were difficult, Davis remembered, because she felt so isolated, just her and her team “in the trenches.”
She hosted community meetings, imploring local parents, leaders and business owners to support the district.
“They told me to come back when we were no longer failing,” Davis said.
So after that first “C,” when she started seeing the district’s hashtags on Facebook, when more people started coming to school events, when she started to get invited to speak at the local Rotary Club, it was bittersweet.
Teachers, too, took a while to come around. Their performance was being closely monitored through the accountability system, but soon they realized that Davis wasn’t giving them mandates outside of improving test scores. She gave them autonomy in their classrooms. Teachers had the final say on how to improve their students’ achievement. That kind of trust isn’t common, Sunflower County teachers told Mississippi Today.
It wasn’t until 2021, when voters passed a $31 million bond issue that would pay for major school renovations, that Davis felt the full support of the community.
Davis even won over Betty Petty, a local matriarch and fierce advocate for kids and parents.
“She has actually shown a presence at the schools, constantly meeting with teachers and making sure all children are learning,” Petty said. “We had community meetings where she would actually come out and listen to our concerns.”
Petty attended the ribbon-cutting ceremony at Gentry High School last July. Before renovations, plumbing problems caused flooding when it rained, so students had to wade through water to get from class to class. Davis said she’d never forget the sight of generations of Gentry graduates in the school atrium, looking around in wonder at the new facility.
“At first, I chose the community,” Davis said. “But eventually, the community chose me.”

The legacy she leaves behind
Strong schools make strong communities, but it can take time for results to show. Indianola Mayor Ken Featherstone hopes to see the dividends soon.
Featherstone took office four years ago, around the same time the district got its first “B” grade. It has maintained the grade ever since, the highest in the entire region.
He, like Davis, was reared in the Delta, but empathizes with her struggle garnering the support of a community deeply impacted by gun violence and low investment from state officials.

“People are very result-oriented,” he said, leaning back at his desk in city hall. “You till the soil, but it’s not until you start your seed breaking the ground do you see other people starting to water it. That’s just human nature.”
He’s hoping the district’s academic gains will be a boon for Indianola’s struggling economy.
“We’re seeing things slowly come to our area,” Featherstone said. “To get manufacturing jobs to come to our area, we have to improve our public school system. Directors and presidents of manufacturing plants … they need to know where their kids are going to attend school.”
Davis announced in October 2024 that she would be leaving the superintendent job at the end of the school year. Now, she travels the state, consulting with other districts on how to replicate what she did in Indianola, as a director of District and School Performance and Accountability for The Kirkland Group, an education consulting firm based in Ridgeland.
Her departure was a tough blow, Featherstone said, and leaves the district’s hard-fought success hanging in balance.
Petty and her network of parents are concerned, too.
“I don’t think any of us know what will happen moving forward,” she said.
Davis said there was no big epiphany. She just felt her mission was accomplished. She said she’s adamant that the district’s “best days are ahead,” under new superintendent James Johnson-Waldington.
Johnson-Waldington, who was most recently serving as superintendent of Greenwood Leflore Consolidated School District, is also Sunflower-grown, and he was Davis’ principal when she taught at Ruleville Central High School. He plans on employing strategies similar to Davis: holding teachers accountable and celebrating their achievements.
After all, if it’s working, why change it?
“I feel a good kind of pressure,” Johnson-Waldington said. “I like challenges, and this is a new challenge for me. I’m not taking a failing school district to success. This is about maintaining and growing, and I accept that challenge for the very reason that this is home. I’m going to work very hard to maintain what Miskia has done.”
Davis leaves behind a legacy, Featherstone said, that makes her hometown proud. He was in the crowd that day at the parade. He remembers the excitement, the pride.
“Older teachers were there, and you could see the look on their faces that they knew they had reared someone who threw the oar out to a sinking district and brought it back up,” he said.
“She made us see ourselves in a better light, and we can’t thank her enough.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post This superintendent took a failing Delta school district to a ‘B’ rating. Now, she’s leaving appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article presents a positive and detailed profile of an educational leader working to improve a struggling school district in a historically under-resourced and economically challenged region. The focus on community uplift, education reform, accountability, and addressing systemic challenges aligns with themes often emphasized by center-left perspectives. However, the article maintains a largely neutral and factual tone without overt political framing or partisan language, emphasizing pragmatic solutions and community collaboration rather than ideological positions.
Mississippi Today
Theology student’s ‘brain drains back home’ despite economics, safety concerns
Editor’s note: This Mississippi Today Ideas essay is published as part of our Brain Drain project, which seeks answers to why Mississippians move out of state. To read more about the project, click here.
Though I imagine I’ll never return, more often than not, my brain drains back to Mississippi. My whole adult life has been a journey up and down the Hudson River, from New York City to the Adirondacks, but inevitably, I find my thoughts leaking toward another river.
I grew up fearing being left behind in the Rapture, but in earnest, it feels like I’m the one who left everyone behind. I’m not proud of this, but I’m certainly not ashamed. I have roots in the Northeast now, and a life that isn’t easily transplanted elsewhere, especially to the Red Clay Hills of Neshoba County. Life took me from Mississippi, and life keeps me away.
I left Mississippi for New York in 2015, and I estimate that I’ve returned only 11 times. My sporadic trips home have been mostly because I’m consistently broke, but now it’s a combination of that and concerns for my safety.
My mother, also limited by finances and Mississippi’s minimum wage, has visited me twice in 10 years, once in the spring of 2016 and then when I graduated from Yale Divinity School in 2023.
I haven’t been back since I came out as a trans woman and began medically transitioning in the winter of 2024. I try not to be overwhelmed with guilt or grief for the imagined, shared life I don’t experience with my mother. Rather, I’ve learned to cherish what we do have.
It’s strange to be who I am, mostly for her but also for me. She has learned to love me regardless of whether or not she understands what I’m doing. In her mind, if you go to college, you become a nurse or a lawyer. You settle down, probably in Jackson, maybe Oxford, most likely in my hometown of Philadelphia, and commute by car more than an hour to work. You probably see your mom weekly. She sees her grandkids as often as possible.
That is not how life turned out. We do talk on the phone. Sometimes we get into once-a-week phone call sprees, other times, I drop off for weeks, maybe a month, when I’m depressed.
When I come home, she picks me up from the airport and drives me back a few weeks later. We crack the windows, smoke cheap Mississippi cigarettes and try to cram 10 years of a strange-to-us mother-daughter relationship into a 90-minute ride to the airport in Jackson. Usually, we talk about suffering, death, sin, God, the end of the world, and what the hell I am doing with my life.
You go to college to get a job, to make more money than your parents and to buy a strange suburban-but-rural McMansion just beyond city limits where you start a family around the age of 25 at the latest.
According to my mother, I went to the University of Mississippi and got brainwashed. She tells me often that it’s like she doesn’t know who I am, and she’s mostly right. She hasn’t met anyone I’ve dated in person since high school. She hasn’t seen me in person since transitioning, and I changed my name to Romy. I explain my relationship with my family to friends, peers, new partners and congregations, always with an articulate sense of heartbreak that I’ve learned to intellectualize and package up in a story of “working-class origins,” single motherhood, a white Christian nationalist rural community and my stumbling through adulthood “refusing not to live by my values.”
I originally left Mississippi to be an AmeriCorps Vista volunteer in the Capital Region of New York. I’d never been there. I took a Greyhound from Memphis to New York City to Albany, New York with two large suitcases and a backpack. Several of my friends from college had moved to New York City, and their couches and shared beds provided a safe launching pad for more of us. I had also fallen in love with a fashion student turned designer that I met on a trip to the city the year prior. Though that romance flamed and flickered for many years and ultimately flamed out, my reason for staying in the North was the life I was increasingly stumbling into.
I went there because, at the time, I had an insatiable desire to live out my values and politics. After all, I was maybe one of two socialist public policy majors at the Trent Lott Leadership Institute at the University of Mississippi, and I didn’t want to be a lawyer, a lobbyist or a policy wonk.
I wanted to be poor and engage in building sustainable autonomous communities. I wanted to learn how to be a person who had no work/life distinction, but a vocation and calling.
Through AmeriCorps, I luckily found a small group of activists, urban homestead types, organizers and ex-social workers living together helping others at the margins and themselves start businesses and worker-cooperatives while struggling through mental health crises, and taking on an impossible but seemingly always plausible dream of a directly democratic community owned, operated and governed only by those who live there.
This was my first “job” out of college. It was my dream come true, and the most difficult thing I’d ever done. I burnt out pretty hard after two years, and probably made somewhere between $25,000 and $30,000 during that whole time. Since then, the most I’ve made in a year is my current PhD stipend of about $34,000.
I was, however, helped along by friends, colleagues and the activist communities that I was stumbling into. Through them, I was encouraged to go to Union Theological Seminary, land a job at a prestigious artist residency in the mountains, go to Yale Divinity School, discern that I was called to be a priest and come to know myself as a trans woman.
My life outside of Mississippi has been sustained solely by relationships that transgress the boundaries between work and life, co-workers and friends. I regularly reflect on and often worry about how fragile this all is, and if my own vocational and intellectual pursuits have been worth what I’ve left behind or never had.
I’m not sure I’ll ever know. However, I’ve managed to find profound meaning in it all so far, and it keeps me digging myself into this hole in which I will hopefully find what I am looking for, or dig my own damn grave.
Originally from Philadelphia, Romy Felder (she/her) is currently a PhD student at Union Theological Seminary. She is also pursuing the priesthood in the Episcopal Diocese of New York. She has a background in worker-cooperative development, community organizing, popular education and arts management. Romy lives cavalierly but contentedly in Brooklyn, New York.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Theology student's 'brain drains back home' despite economics, safety concerns appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Left-Leaning
This essay reflects a distinctly personal and ideological perspective rather than neutral reporting. The author frames Mississippi as economically limiting and socially unsafe, particularly for marginalized identities such as transgender individuals, while presenting Northern activist and academic communities in a sympathetic and aspirational light. References to socialism, worker-cooperatives, and critiques of conservative Mississippi culture suggest a worldview aligned with progressive or left-leaning politics. The tone is introspective and critical of traditional Southern expectations, while valorizing alternative, activist-driven lifestyles. As such, the piece is less about balanced reporting and more an expression of lived experience through a progressive lens.
Mississippi Today
‘Get a life,’ Sen. Roger Wicker says of constituents
A note from Adam Ganucheau: A couple hours after this column published, Sen. Roger Wicker’s office reached out and demanded a correction, saying the senator’s “get a life” comment was directed to himself and not to constituents. That’s certainly not how I nor hundreds of Mississippians who commented on and shared the viral video heard it. Mississippi Today has updated portions of this column to reflect concerns raised by Wicker’s office. Here’s a link to the video/audio of his response to the question about constituent concerns. Mississippians can decide for themselves what Wicker meant.
When 34-year-old Thad Cochran arrived in Washington after his first election in 1972, the Republican felt it important to document what he’d heard and learned from Mississippians on the campaign trail and share it with his young staff.
He sat down at a typewriter and wrote a memo titled “General Responsiveness” and dated March 14, 1973:
During the campaign I detected a very strong animosity among the people toward government and those associated with government bureaus and agencies. This included elected officials and those associated with them. Part of the cause of this attitude was due to a lack of feeling or understanding by government people for the needs and opinions of the average citizen. We are all in a job to represent all our constituents. We are not the bureaucracy. A constituent who asks us for help should be assured to be in need of help with our office as his last resort. A constituent who writes a letter should be made to feel by our response that he is glad he wrote us. A constituent who claims to have been wronged by the government should be assumed to be correct. Everyone should guard against developing the attitude that we are better than, smarter than or more important than any constituent. We do not hold a position of authority over any constituent. We are truly servants of the people who selected us for this job.
Every year from 1973 through 2018, over his three U.S. House terms and six U.S. Senate terms, Cochran shared that memo with every staffer who worked in his offices. The guidance, he said all those years, was a necessary reminder to show respect to the people who offer feedback or need help. He never wanted his staff or himself to forget who sent them to Washington.
The memo, like so many other things, serves as a stark reminder that Cochran was among the last in a bygone era of American politics. The perspective he wrote and shared is a far cry from what Mississippians have been getting recently from our current U.S. senators.
“Surely everybody else has better things to do with their time,” senior U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker said to a room full of constituents earlier this month when asked about calls and emails his office has been getting. After half-heartedly explaining that he does see a list of names of people who reach out to his office, he quipped: “Get a life.”
Wicker’s office said Friday that the senator directed “Get a life” to himself, not to constituents.
Wicker, who typically chooses his words a little more carefully, perhaps has been trying to match his junior colleague’s energy.
“Why is everyone’s head exploding?” U.S. Sen. Cindy Hyde-Smith said in April to Mississippi constituents who had expressed concerns over slashing federal Medicaid spending. “I can’t understand why everyone’s head is exploding.”
There are many kind staffers working for Republicans Wicker and Hyde-Smith who are helpful to Mississippi constituents in any number of ways privately or behind the scenes. These people care deeply about serving their home state and they do it well, and they cannot help how their bosses address the public. But, boy, their phones must be blowing up more than ever since the senators made these comments.
Consider, for a moment, what it means that we have devolved from having a leader who believed that “a constituent who claims to have been wronged by the government should be assumed to be correct” to one who thinks telling constituents to “get a life” is appropriate. Think about the fact that we replaced a leader who regularly reminded his staff that “we are truly servants of the people who selected us for this job” with one whose gut response to legitimate concerns from constituents is that their “heads are exploding.”
Just … wow. To call it alarming doesn’t fully encapsulate the gravity of their behavior. It’s enough to discourage even the most optimistic among us about the present and future of our state and our nation.
It’s enough to inspire you to ponder, in this intense political climate when unprecedented and harrowing federal government decisions are being made and going largely unchecked every day, whether our current U.S. senators even remember why they’re in Washington, why we sent them there.
It is necessary, in the shortest possible order, to ask and answer for ourselves what we should expect of our elected officials and whether we should feel OK about being dismissed or ignored outright like this.
You don’t have to be a Democrat to think that this behavior is out of line. Plenty of Republicans — some publicly and many privately — are increasingly disturbed by what’s happening in Washington. Regardless of your own personal political beliefs, be honest with yourself about whether you can read these comments from our senators and still feel that your best interests are being represented.
Sadly, we can no longer ask Cochran to help us answer these questions, but it sure seems clear where he’d stand. What about you?
READ MORE: Mississippi, where ‘We Dissent’ means nothing to elected officials
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post 'Get a life,' Sen. Roger Wicker says of constituents appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
The content critiques Republican senators for their dismissive attitude toward constituents, contrasting them with a more respectful past leader. It highlights concerns about current political behavior and governance, emphasizing accountability and responsiveness to the public. While it acknowledges that some Republicans privately share these concerns, the tone and framing suggest a leaning that favors more progressive or reform-minded perspectives, typical of center-left commentary.
-
News from the South - Texas News Feed3 days ago
New Texas laws go into effect as school year starts
-
News from the South - Texas News Feed5 days ago
Kratom poisoning calls climb in Texas
-
News from the South - Tennessee News Feed5 days ago
GRAPHIC VIDEO WARNING: Man shot several times at point-blank range outside Memphis convenience store
-
News from the South - Florida News Feed3 days ago
Floridians lose tens of millions to romance scams
-
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed5 days ago
Unsealed warrant reveals IRS claims of millions in unreported sales at Central Kentucky restaurants
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
Idaho is losing OB-GYNs. Doctors who remain are trying to shoulder the extra burdens.
-
Mississippi Today5 days ago
‘Get a life,’ Sen. Roger Wicker says of constituents
-
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days ago
Woman charged in 2024 drowning death of Logan County toddler appears in court





















































