Mississippi Today
‘It’s just an old place’: Senate bill would shutter most of Parchman prison

Mississippi’s oldest and infamous State Penitentiary at Parchman could be forced to shut down by 2028, sending its thousands of inmates and staff to other prisons and reimagining some of the space to be used for other needs.
Senate Bill 2353 by Sen. Juan Barnett proposes phasing down the use of the 123-year-old prison starting this summer.
“It’s just an old place,” Barnett, a Democrat from Heidelberg, told Mississippi Today. “I don’t want to keep spending millions of taxpayers’ dollars on something that can’t ever be fixed.”
He estimated the effort could cost about $150 million – cheaper than putting money into a prison that’s beyond repair and, according to the bill, savings could be redirected to paying correctional officers and addressing officer turnover.
Years of neglect and a lack of funding have led to deteriorating infrastructure, decrepit conditions and violence, a 2020 investigation by the Mississippi Center for Investigative Reporting and ProPublica found.
Months after a string of deaths and violent disturbances across several state prison facilities, but mostly concentrated in Parchman’s Unit 29, the U.S. Department of Justice opened a civil rights investigation into Parchman and four other prisons. By 2022, the DOJ released a report detailing conditions that violate the Constitution.
The bill directs Corrections Commissioner Burl Cain to develop a plan to shut down Parchman and submit it to the Legislature by Jan. 1, 2025.
A spokesperson from MDOC was not immediately available for comment Tuesday.
Part of the phase down plan could mean contracting with the Tallahatchie County Correctional Facility, the Tutweiler prison run by private contractor CoreCivic, to house people from Parchman, according to the bill. The Tutwiler facility would be renamed the “Northwest Mississippi Correctional Facility.”
MDOC can also contract with any regional facility, private prison or approved county jail to incarcerate people under the decentralization plan, according to the proposed legislation.
The bill sets a benchmark to reduce Parchman’s population by 1,700 by July 1, 2026. The prison’s numbers have hovered around 2,400 during the month of February, according to MDOC records.
HB 2353 has been referred to the Senate’s Corrections Committee, which Barnett chairs, and the Appropriations Committee.
Barnett sees what has been going on in Alabama, which faces a DOJ lawsuit over prison conditions, violence and crowding.
Building new prisons is part of that state’s plans to address unconstitutional conditions. He said Mississippi could avoid that fate by shutting down Parchman.
“We don’t want to one day be forced to do what Alabama has had to do,” Barnett said. “We definitely don’t need the Department of Justice breathing down our neck. I’m tired of us being last on everything.”
He anticipates a small part of Parchman might continue to be used as a training facility and mental health facility. Death row inmates housed at Unit 29 would continue to be housed at Parchman, according to the proposed legisaltion.
The nearly 4,000 acres of land where the prison and other buildings stand would be held in trust by MDOC to lease out for agricultural, industrial, commercial, residential, recreational or catfish farming for no longer than 40 years. All would be public bids subject to Public Procurement Review Board requirements.
The bill comes with some oversight.
Among its other duties, the Criminal Justice Oversight Task Force would track and assess outcomes for the phase down plan, and the executive director of Joint Legislative Committee on Performance Evaluation and Expenditure to assign an analyst to review and monitor the correctional system’s financial condition and the efficiency and effectiveness of programs and operations, and the analyst would have the ability to inspect MDOC facilities.
Barnett’s legislation also incorporates proposals from several other bills introduced this session:
- Allow Rankin, Harrison and Lee counties to establish pilot work release programs with a limit of 25 participants and track outcomes and demographics.
- Extend the repealer on MDOC’s Mississippi Prison Industries Act to 2028.
- Extend the repealer on state inmates being housed in county jails and regional facilities to 2028.
- Extend repealer on MDOC’s Prison Industry Enhancement Program to 2028.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Judge: Felony disenfranchisement a factor in ruling on Mississippi Supreme Court districts
The large number of Mississippians with voting rights stripped for life because they committed a disenfranchising felony was a significant factor in a federal judge determining that current state Supreme Court districts dilute Black voting strength.
U.S. District Judge Sharion Aycock, who was appointed to the federal bench by George W. Bush, last week ruled that Mississippi’s Supreme Court districts violate the federal Voting Rights Act and that the state cannot use the same maps in future elections.
Mississippi law establishes three Supreme Court districts, commonly referred to as the northern, central and southern districts. Voters elect three judges from each to the nine-member court. These districts have not been redrawn since 1987.
READ MORE: Mississippians ask U.S. Supreme court to strike state’s Jim Crow-era felony voting ban
The main district at issue in the case is the central district, which comprises many parts of the majority-Black Delta and the majority-Black Jackson Metro Area.
Several civil rights legal organizations filed a lawsuit on behalf of Black citizens, candidates, and elected officials, arguing that the central district does not provide Black voters with a realistic chance to elect a candidate of their choice.
The state defended the districts arguing the map allows a fair chance for Black candidates. Aycock sided with the plaintiffs and is allowing the Legislature to redraw the districts.
The attorney general’s office could appeal the ruling to the U.S. 5th Circuit Court of Appeals. A spokesperson for the office stated that the office is reviewing Aycock’s decision, but did not confirm whether the office plans to appeal.
In her ruling, Aycock cited the testimony of William Cooper, the plaintiff’s demographic and redistricting expert, who estimated that 56,000 felons were unable to vote statewide based on a review of court records from 1994 to 2017. He estimated 60% of those were determined to be Black Mississippians.
Cooper testified that the high number of people who were disenfranchised contributed to the Black voting age population falling below 50% in the central district.
Attorneys from Attorney General Lynn Fitch’s office defended the state. They disputed Cooper’s calculations, but Aycock rejected their arguments.
The AG’s office also said Aycock should not put much weight on the number of disenfranchised people because the U.S. Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals previously ruled that Mississippi’s disenfranchisement system doesn’t violate the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment.
Aycock, however, distinguished between the appellate court’s ruling that the system did not have racial discriminatory intent and the current issue of the practice having a racially discriminatory impact.
“Notably, though, that decision addressed only whether there was discriminatory intent as required to prove an Equal Protection claim,” Aycock wrote. “The Fifth Circuit did not conclude that Mississippi’s felon disenfranchisement laws have no racially disparate impact.”
Mississippi has one of the harshest disenfranchisement systems in the nation and a convoluted method for restoring voting rights to people.
Other than receiving a pardon from the governor, the only way for someone to regain their voting rights is if two-thirds of legislators from both chambers at the Capitol, the highest threshold in the Legislature, agree to restore their suffrage.
Lawmakers only consider about a dozen or so suffrage restoration bills during the session, and they’re typically among the last items lawmakers take up before they adjourn for the year.
Under the Mississippi Constitution, people convicted of a list of 10 types of felonies lose their voting rights for life. Opinions from the Mississippi Attorney General’s Office have since expanded the list of specific disenfranchising felonies to 23.
The practice of stripping voting rights away from people for life is a holdover from the Jim Crow era. The framers of the 1890 Mississippi Constitution believed Black people were most likely to commit certain crimes.
Leaders in the state House have attempted to overhaul the system, but none have gained any significant traction in both chambers at the Capitol.
Last year, House Constitution Chairman Price Wallace, a Republican from Mendenhall, advocated a constitutional amendment that would have removed nonviolent offenses from the list of disenfranchising felonies, but he never brought it up for a vote in the House.
Wallace and House Elections Chairman Noah Sanford, a Republican from Collins, are leading a study committee on Sept. 11 to explore reforms to the felony suffrage system and other voting legislation.
Wallace previously said on an episode of Mississippi Today’s “The Other Side” podcast that he believes the state should tackle the issue because one of his core values, part of his upbringing, is giving people a second chance, especially once they’ve made up for a mistake.
“This issue is not a Republican or Democratic issue,” Wallace said. “It allows a woman or a man, whatever the case may be, the opportunity to have their voice heard in their local elections. Like I said, they’re out there working. They’re paying taxes just like you and me. And yet they can’t have a decision in who represents them in their local government.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Judge: Felony disenfranchisement a factor in ruling on Mississippi Supreme Court districts appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article presents a focus on voting rights and racial justice issues, highlighting the impact of felony disenfranchisement on Black voters in Mississippi. It emphasizes civil rights concerns and critiques longstanding policies rooted in the Jim Crow era, which aligns with center-left perspectives advocating for expanded voting access and systemic reform. The coverage is factual and includes viewpoints from multiple sides, but the framing and emphasis on racial disparities and voting rights restoration suggest a center-left leaning.
Mississippi Today
Jackson police chief steps down to take another job, national search to come
Jackson Police Department Chief Joseph Wade told the mayor last week he was choosing to retire after 29 years of service and two years at the helm of the force. Wade said he’d been given another job opportunity, which has yet to be announced.
His last day is Sept. 5.
Mayor John Horhn said he told Wade the officer would be crazy not to take the job — one that comes with less stress and more pay.
“His wife has been on his back, his blood pressure has been up,” Horhn said during Tuesday’s City Council meeting. “He has done a commendable job.”
Wade became chief during a period in which Jackson was called the murder capital of America. Under his tenure, Wade said crime has fallen markedly, including a roughly 45% reduction in homicides so far this year compared to the same period in 2024, the Clarion Ledger reported. He said he’s also increased JPD’s force by 37, for a total of 258 officers.
Wade said his biggest accomplishment is reestablishing trust. “We are no longer the laughing stock of the law enforcement community,” he said.
The chief’s departure comes less than two months after Horhn took office, replacing former Mayor Chokwe Antar Lumumba who originally appointed Wade, and on the heels of a spate of shootings that Wade said were driven by gangs of young men.
“I have received so many calls from the community: ‘Chief, please don’t leave us,'” Wade told the crowd in council chambers.
But Wade said he “would rather leave prematurely than overstay my welcome,” adding that the average tenure of a police chief is 2.5 years.
Wade said that last year he stood next to Jackson Councilman Kenny Stokes and told the media he was going to cut crime in half, “And what did I do? Cut it in half,” he said.
“What I’ve seen in our community in some situations is people want police, but they don’t want to be policed,” Wade said.
Hinds County Sheriff Tyree Jones will serve as interim police chief until the administration finds a replacement. Jones said he has not finalized a contract with the city, responding to a question about whether he will draw a salary from both agencies.
“I could think of no one better than the sheriff of Hinds County,” Horhn said, adding that the appointment is temporary.
Jones said during the meeting that his responsibility as sheriff will continue uninterrupted and that his goal within JPD is to ensure continued professionalism in the department.
“I extend my heartfelt gratitude to my dear friend and retired police chief Joe Wade,” Jones said. “Again, let me be clear, I have no aspirations to permanently hold the position.”
Horhn said there is precedence for the dual role that “Chief Sheriff Jones is about to embark upon,” citing former mayor Frank Melton’s hiring of Sheriff Malcolm McMillin.
The city has enlisted help from former U.S. Marshal George White and the former chief of the Mississippi Highway Patrol, Col. Charles Haynes, to lead the Law Enforcement Task Force that will conduct a nationwide search to fill the position. The administration expects that to take between 30 and 60 days, according to a city press release.
The release said the task force will also examine safety challenges in Jackson more broadly, such as youth crime, drug crimes, departmental needs and interagency coordination.
“I am grateful that Marshal White and Col. Haynes have agreed to lead this important effort. Their breadth of experience, commitment to public safety and deep understanding of law enforcement challenges will ensure the task force conducts a rigorous search for our next chief,” said Horhn. “I am confident they will help shape solutions that address the evolving needs of Jackson.”
The city said it would soon release details about the opportunity for the public to offer input on the process.
“Hinds County is all in for whatever we have to do to make Jackson and Hinds County the safest it can be,” Hinds County Supervisors President Robert Graham said during the meeting.
Wade, who hails from nearby Terry, graduated from JPD’s 23rd recruit class in 1995, rising from a police recruit and hitting every rung of the ladder on his way to chief. “I was homegrown,” he said.
Wade said he received “an amazing offer in a private sector at an amazing organization. Don’t ask me where. That will be released at the appropriate time.”
This story may be updated.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Jackson police chief steps down to take another job, national search to come appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Centrist
The article presents a straightforward news report on the resignation of a police chief, focusing on facts, quotes from officials, and crime statistics without evident ideological framing. It covers perspectives from multiple local government figures and avoids partisan language, reflecting a neutral, balanced tone typical of centrist reporting.
Mississippi Today
Bluesky blocks access in Mississippi, citing free speech and privacy concerns over state law
Mississippians can no longer access the Bluesky app after the social media platform blocked access to users in the state.
Bluesky said on Friday that it made the decision after the U.S. Supreme Court declined for now to block a Mississippi state law that the platform said limits free expression, invades people’s privacy and unfairly targets smaller social media companies. The state law, passed in 2024, requires users of websites and other digital services to verify their age.
“The Supreme Court’s recent decision leaves us facing a hard reality: comply with Mississippi’s age assurance law—and make every Mississippi Bluesky user hand over sensitive personal information and undergo age checks to access the site—or risk massive fines,” the company wrote in a statement. “The law would also require us to identify and track which users are children, unlike our approach in other regions. We think this law creates challenges that go beyond its child safety goals, and creates significant barriers that limit free speech and disproportionately harm smaller platforms and emerging technologies.”
Mississippi Attorney General Lynn Fitch, whose office defended the law, told the justices that age verification could help protect young people from “sexual abuse, trafficking, physical violence, sextortion and more,” activities that the First Amendment does not protect.
The age verification law added Mississippi to a list of Republican-led states where similar legal challenges are playing out.
NetChoice is challenging laws passed in Mississippi and other states that require social media users to verify their ages, and asked the Supreme Court to keep the measure on hold while a lawsuit plays out.
That came after a federal judge prevented the 2024 law from taking effect. But a three-judge panel of the 5th Circuit U.S. Court of Appeals ruled in July that the law could be enforced while the lawsuit proceeds.
On Aug. 14, the Supreme Court rejected an emergency appeal from a tech industry group representing major platforms such as Facebook, X and YouTube.
There were no noted dissents from the brief, unsigned order. Justice Brett Kavanaugh wrote that there’s a good chance NetChoice will eventually succeed in showing that the law is unconstitutional, but hadn’t shown it must be blocked while the lawsuit unfolds.
Bluesky grew after the 2024 presidential election. Many users of X, which is owned by Elon Musk, retreated from the platform in response to the billionaire’s strong support of Donald Trump.
In Bluesky’s statement explaining its decision to block access in Mississippi, the company said age verification systems “require substantial infrastructure and developer time investments, complex privacy protections, and ongoing compliance monitoring — costs that can easily overwhelm smaller providers.”
“This dynamic entrenches existing big tech platforms while stifling the innovation and competition that benefits users,” the company added.
Bluesky said it did follow other digital safety regulations, such as the United Kingdom’s Online Safety Act. Under that statute, age checks are required only for accessing certain content and features, and Bluesky does not track which users are under 18, the platform said:
“Mississippi’s law, by contrast, would block everyone from accessing the site—teens and adults—unless they hand over sensitive information, and once they do, the law in Mississippi requires Bluesky to keep track of which users are children.”
The Mississippi law, authored by Rep. Jill Ford, a Republican from Madison, is called the “Walker Montgomery Protecting Children Online Act,” named after a Mississippi teen who reportedly committed suicide after an overseas online predator threatened to blackmail him.
The Associated Press contributed to this report
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Bluesky blocks access in Mississippi, citing free speech and privacy concerns over state law appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
The content presents a perspective that emphasizes concerns about free speech, privacy, and the impact of government regulation on smaller tech companies, which aligns with a more progressive or liberal viewpoint on digital rights and corporate regulation. It critiques a Republican-led state law as potentially overreaching and harmful to innovation, while also acknowledging the law’s intent to protect children. The balanced presentation of both sides, with a slight emphasis on the tech platform’s viewpoint and civil liberties, suggests a center-left bias.
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
New I-55 bridge between Arkansas, Tennessee named after region’s three ‘Kings’
-
News from the South - Texas News Feed5 days ago
DEA agents uncover 'torture chamber,' buried drugs and bones at Kentucky home
-
News from the South - Virginia News Feed7 days ago
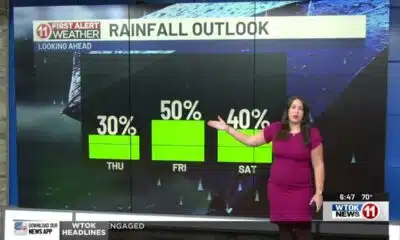
Erin: Tropical storm force winds 600 miles wide eases into Atlantic | North Carolina
-
Our Mississippi Home7 days ago
Vardaman: The Sweet Potato Capital Serving Up Love, Tradition, and Flavor at Sweet Potato Sweets
-
News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days ago
Missouri settles lawsuit over prison isolation policies for people with HIV
-
The Center Square6 days ago
Georgia ICE arrests up 367 percent from 2021, making for ‘safer streets, open jobs | Georgia
-
Local News6 days ago
Florida must stop expanding ‘Alligator Alcatraz’ immigration center, judge says
-
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days ago
Quintissa Peake, ‘sickle cell warrior’ and champion for blood donation, dies at 44