Mississippi Today
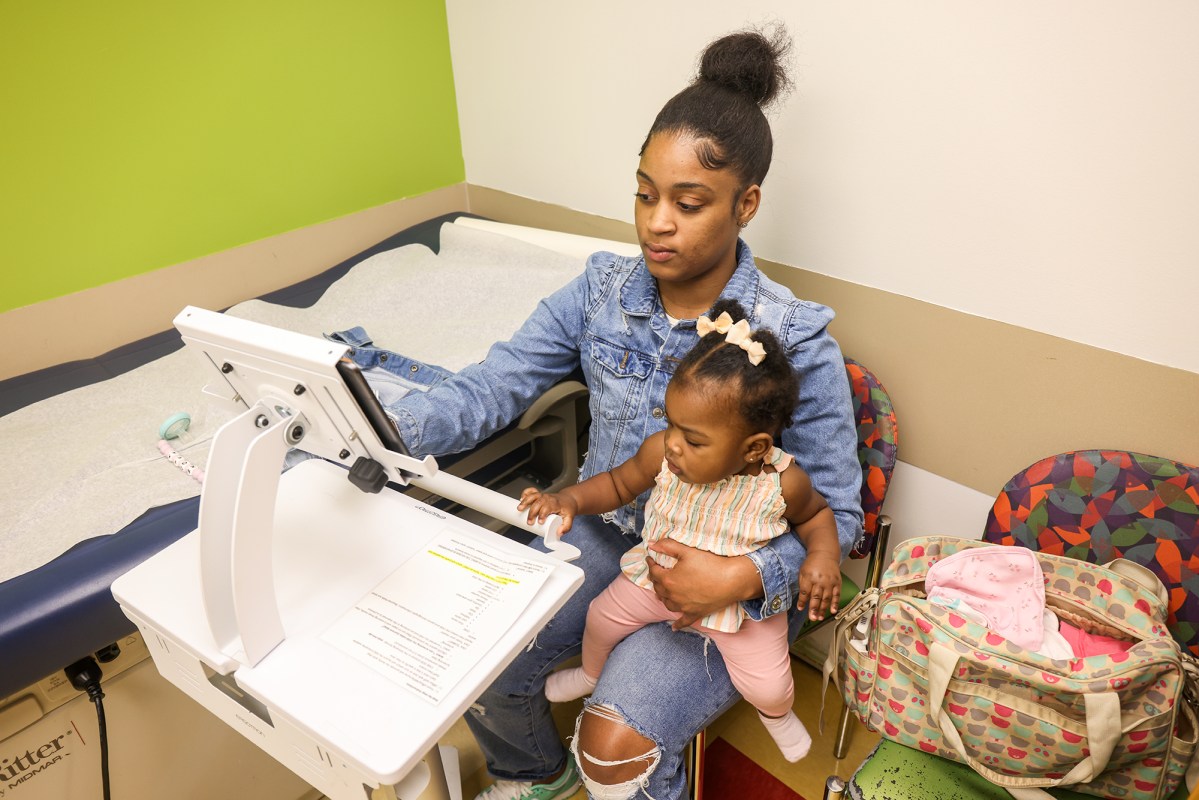
Mississippi moves from last to 33rd in developmental screenings of kids
Mississippi moves from last to 33rd in developmental screenings of kids
For years, Mississippi children were more likely to miss out on early childhood development screenings than anywhere else in the country.
But after a $17-million federal grant and the work of a state health childhood development project, Mississippi's early childhood screening rate shot up from dead-last to No. 33, according to ranking by the National Health Foundation. This means more children are receiving screenings designed to catch delays before they turn into serious problems later.
Dr. Susan Buttross, the University of Mississippi Medical Center's director of the child development clinic, called it an unprecedented improvement.
“But we're not done yet,” Buttross said.
Ultimately, most kids in Mississippi, and nationwide, still aren't being screened.
Despite the end to the five years of federal funding that created the project to grow the number of early childhood screenings – dubbed Mississippi Thrive! – Buttross and her team are continuing their work as the Early Childhood Development Coalition. Buttross, the director of the coalition, said she's garnered enough financial support to keep their work going while seeking more stable funding over the next year.
“Many times when we get grant money to work on a project, the work is done in a sort of silo fashion,” Buttross said. “The grant goes away and the work stops. But one of the benefits with this project was that part of the project was to really collaborate and work with other entities in the state.”
That means even with the official project over, the mission is still well alive.
That level of collaboration the project fostered, Buttross said, is what led Mississippi from having only 17% of children undergo developmental screenings in 2016 to 34.1% in the most recent data set available. At that rate, Mississippi is less than a single percentage point away from the national average.
“There is a great deal of data that shows children do better if they enter school healthy and ready to learn,” Buttross said. “The earlier you discover speech or language delay … and the earlier you correct them, the child is going to be way better off.”
The “Thrive!” project was a joint effort between the University of Mississippi Medical Center and the Social Science Research Center at Mississippi State University to educate pediatricians, nurse practitioners, social workers, childcare providers and parents on the importance of developmental screenings and how to conduct them.
The screenings are most commonly done by pediatric physicians. Ideally, doctors are checking with parents at their babies' 3, 18 and 30-month checkups. Physicians are working off a checklist of age-appropriate milestones from eye contact to leg kicks, according to Dr. Ruth Patterson, a pediatric specialist at UMMC in the coalition with Buttross.
“A screening does not make a diagnosis,” Patterson said. “But it discerns if a child is at risk for a developmental delay.”
Often, speech delays are tied to hearing problems – but without the screening questions, a parent might not realize their child isn't meeting the appropriate language benchmarks.
During the five-year project, Buttross, Patterson and others created a hands-on pilot program to show how much working directly physicians could improve screening rates and outcomes. The pilot focused on 31 physicians in six clinics between Jackson and the Gulf Coast.
The physicians who underwent that training improved their developmental screening rate to 85%.
“We went directly to these primary care provider offices to make sure we provided them with tools and training,” Patterson said. “We know the capability is there if the providers are provided with the right support.”
Some pediatricians in the state were trained years ago, and simply aren't aware of the latest screening methods and tools.
Ideally, the screenings take place in a doctor's office, said pediatric nurse practitioner Lauren Elliott.
“But we have engaged across communities, in whatever circles parents are in, we are trying to engage them,” Elliott said. “We have them complete a questionnaire to give them an idea.”
If parents find their child isn't meeting the benchmarks mentioned on the form, they're more likely to get into a doctor's office. But even those with the best intentions are likely to face barriers.
In Mississippi, many children don't have a primary care doctor. Some counties in the Delta don't have a single pediatrician, and parents don't have the means to travel far with their children for checkups. An urgent care or emergency room is handling a specific emergent health issue, not checking in on milestones.
Even if a physician screens a child, it may be difficult to get a referral to a specialist.
White children, insured children, children from an English-speaking household, or a higher-income home are all more likely to be screened, according to the National Health Foundation.
In Mississippi, federally funded child care centers called Head Start centers fill some of those gaps, completing 30% of the state's overall screenings despite comprising only 10% of the state's childcare center, according to a 2021 study by the Children's Foundation of Mississippi.
Despite the five-year project concluding, much of the work is just starting, according to the coalition.
The Legislature, Buttross said, allocated funds to support a fellowship to train early childhood specialists, something federal funds once covered. The $1.2 million appropriation to UMMC supported fellows who will graduate this June. The same funding was approved again this most recent session to train another eight fellows arriving in the coming academic year, though the bill has not yet been signed by the governor.
The “Thrive!” website is still active and a trove of information for both parents and physicians with support from the state's human services office.
All positive steps, Buttross said, but not enough.
“There has not been enough funding to our early intervention programs,” she said. “We fund it with far less dollars than any of the surrounding states.”
And it's the children who lose out without early intervention.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1961
MAY 20, 1961

A white mob of more than 300, including Klansmen, attacked Freedom Riders at the Greyhound Bus Station in Montgomery, Alabama. Future Congressman John Lewis was among them.
“An angry mob came out of nowhere, hundreds of people, with bricks and balls, chains,” Lewis recalled.
After beating on the riders, the mob turned on reporters and then Justice Department official John Seigenthaler, who was beaten unconscious and left in the street after helping two riders.
“Then they turned on my colleagues and started beating us and beat us so severely, we were left bloodied and unconscious in the streets of Montgomery,” Lewis recalled.
As the mob headed his way, Freedom Rider James Zwerg said he asked for God to be with him, and “I felt absolutely surrounded by love. I knew that whether I lived or died, I was going to be OK.”
The mob beat him so badly that his suit was soaked in blood.
“There was nothing particularly heroic in what I did,” he said. “If you want to talk about heroism, consider the Black man who probably saved my life. This man in coveralls, just off of work, happened to walk by as my beating was going on and said ‘Stop beating that kid. If you want to beat someone, beat me.' And they did. He was still unconscious when I left the hospital.”
To quell the violence, Attorney General Robert Kennedy sent in 450 federal marshals.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Podcast: The controversial day that Robert Kennedy came to the University of Mississippi
Retired U.S. Bankruptcy Judge Edward Ellington talks with Mississippi Today's Bobby Harrison and Geoff Pender about former U.S. Attorney General Robert Kennedy's speech at the University of Mississippi less than four years after the riots that occurred after the integration of the school. Ellington, who at the time headed the Ole Miss Speaker's Bureau as a law school student, recalls the controversy leading up to the speech.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
2024 Mississippi legislative session not good for private school voucher supporters
Despite a recent Mississippi Supreme Court ruling allowing $10 million in public money to be spent on private schools, 2024 has not been a good year for those supporting school vouchers.
School-choice supporters were hopeful during the 2024 legislative session, with new House Speaker Jason White at times indicating support for vouchers.
But the Legislature, which recently completed its session, did not pass any new voucher bills. In fact, it placed tighter restrictions on some of the limited laws the state has in place allowing public money to be spent on private schools.
Notably, the Legislature passed a bill that provides significantly more oversight of a program that provides a limited number of scholarships or vouchers for special-needs children to attend private schools.
Going forward, thanks to the new law, to receive the vouchers a parent must certify that their child will be attending a private school that offers the special needs educational services that will help the child. And the school must report information on the academic progress of the child receiving the funds.
Also, efforts to expand another state program that provides tax credits for the benefit of private schools was defeated. Legislation that would have expanded the tax credits offered by the Children's Promise Act from $8 million a year to $24 million to benefit private schools was defeated. Private schools are supposed to educate low income students and students with special needs to receive the benefit of the tax credits. The legislation expanding the Children's Promise Act was defeated after it was reported that no state agency knew how many students who fit into the categories of poverty and other specific needs were being educated in the schools receiving funds through the tax credits.
Interestingly, the Legislature did not expand the Children's Promise Act but also did not place more oversight on the private schools receiving the tax credit funds.
The bright spot for those supporting vouchers was the early May state Supreme Court ruling. But, in reality, the Supreme Court ruling was not as good for supporters of vouchers as it might appear on the surface.
The Supreme Court did not say in the ruling whether school vouchers are constitutional. Instead, the state's highest court ruled that the group that brought the lawsuit – Parents for Public Schools – did not have standing to pursue the legal action.
The Supreme Court justices did not give any indication that they were ready to say they were going to ignore the Mississippi Constitution's plain language that prohibits public funds from being provided “to any school that at the time of receiving such appropriation is not conducted as a free school.”
In addition to finding Parents for Public Schools did not have standing to bring the lawsuit, the court said another key reason for its ruling was the fact that the funds the private schools were receiving were federal, not state funds. The public funds at the center of the lawsuit were federal COVID-19 relief dollars.
Right or wrong, The court appeared to make a distinction between federal money and state general funds. And in reality, the circumstances are unique in that seldom does the state receive federal money with so few strings attached that it can be awarded to private schools.
The majority opinion written by Northern District Supreme Justice Robert Chamberlin and joined by six justices states, “These specific federal funds were never earmarked by either the federal government or the state for educational purposes, have not been commingled with state education funds, are not for educational purposes and therefore cannot be said to have harmed PPS (Parents for Public Schools) by taking finite government educational funding away from public schools.”
And Southern District Supreme Court Justice Dawn Beam, who joined the majority opinion, wrote separately “ to reiterate that we are not ruling on state funds but American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) funds … The ARPA funds were given to the state to be used in four possible ways, three of which were directly related to the COVID -19 health emergency and one of which was to make necessary investments in water, sewer or broadband infrastructure.”
Granted, many public school advocates lamented the decision, pointing out that federal funds are indeed public or taxpayer money and those federal funds could have been used to help struggling public schools.
Two justices – James Kitchens and Leslie King, both of the Central District, agreed with that argument.
But, importantly, a decidedly conservative-leaning Mississippi Supreme Court stopped far short – at least for the time being – of circumventing state constitutional language that plainly states that public funds are not to go to private schools.
And a decidedly conservative Mississippi Legislature chose not to expand voucher programs during the 2024 session.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
-
Our Mississippi Home7 days ago
Beat the Heat with Mississippi’s Best Waterparks
-
SuperTalk FM4 days ago
State auditor cracking down on Mississippians receiving unemployment benefits
-
Mississippi News Video6 days ago
Jackson has a gang problem
-
Kaiser Health News7 days ago
Medicaid ‘Unwinding’ Decried as Biased Against Disabled People
-
Local News3 days ago
Family files lawsuit after teen’s suicide in Harrison County Jail
-
Mississippi Today5 days ago
On this day in 1950
-
228Sports6 days ago
George County Pours Runs In 6A South State Title Victory At PRC
-
Local News Video5 days ago
In the Kitchen with J's Restaurant