Mississippi Today
Mississippi River cruises in flux a decade after industry’s return
A decade after the Mississippi River’s overnight cruise industry’s comeback, the three companies running the river are expanding itineraries, adjusting their fleets to meet fluctuating demand and eyeing new customer bases, all while river towns make moves to support the industry’s return to the waterway.
For a few hours on a balmy evening just before Memorial Day, hundreds of cruise-goers sprawled across Tunica, Mississippi. Some crossed the gangway and made a right for a Mississippi River museum; others headed inland for a brief stop at the casinos that put the area on the map.
They’re passengers on the American Queen, making a final pitstop on a seven-day cruise that started in New Orleans. In Tunica, a town with about 1,000 people, river cruises bring a significant customer base to the area, and it’s one of many river towns welcoming the business of overnight cruises.
When the American Queen docks at Greenbelt Park in Memphis the next morning — one of 94 boats set to dock in the city this year, up from 57 dockings five years ago — many of the 300-odd passengers headed out to explore the city.
The cruise company estimates that each passenger spends about $135 per day at port.
Visit Natchez in a 2019 benefit-cost analysis determined total direct benefits for the Natchez River Cruise Docking Facility Project would be $167,726,440 vs. a project cost of $10,186,124.
Between the three overnight cruise lines on the Mississippi River — American Queen Voyages, American Cruise Lines and, as of last year, Viking — the industry has an estimated $100 million annual economic impact in Memphis, according to Kevin Kane, president and CEO of Memphis Tourism. That figure has tripled since 2016, according to the Memphis River Parks Partnership, a nonprofit that manages 250 acres of riverfront parkland.
Kane said the cruises’ affluent customer bases present a lot of opportunity for the city. The cruises attract a crowd who are mostly retired, wealthy and well-traveled. Many employees on board the American Queen described their audience as older people who have already been on river cruises and want to check the Mississippi River off their lists.
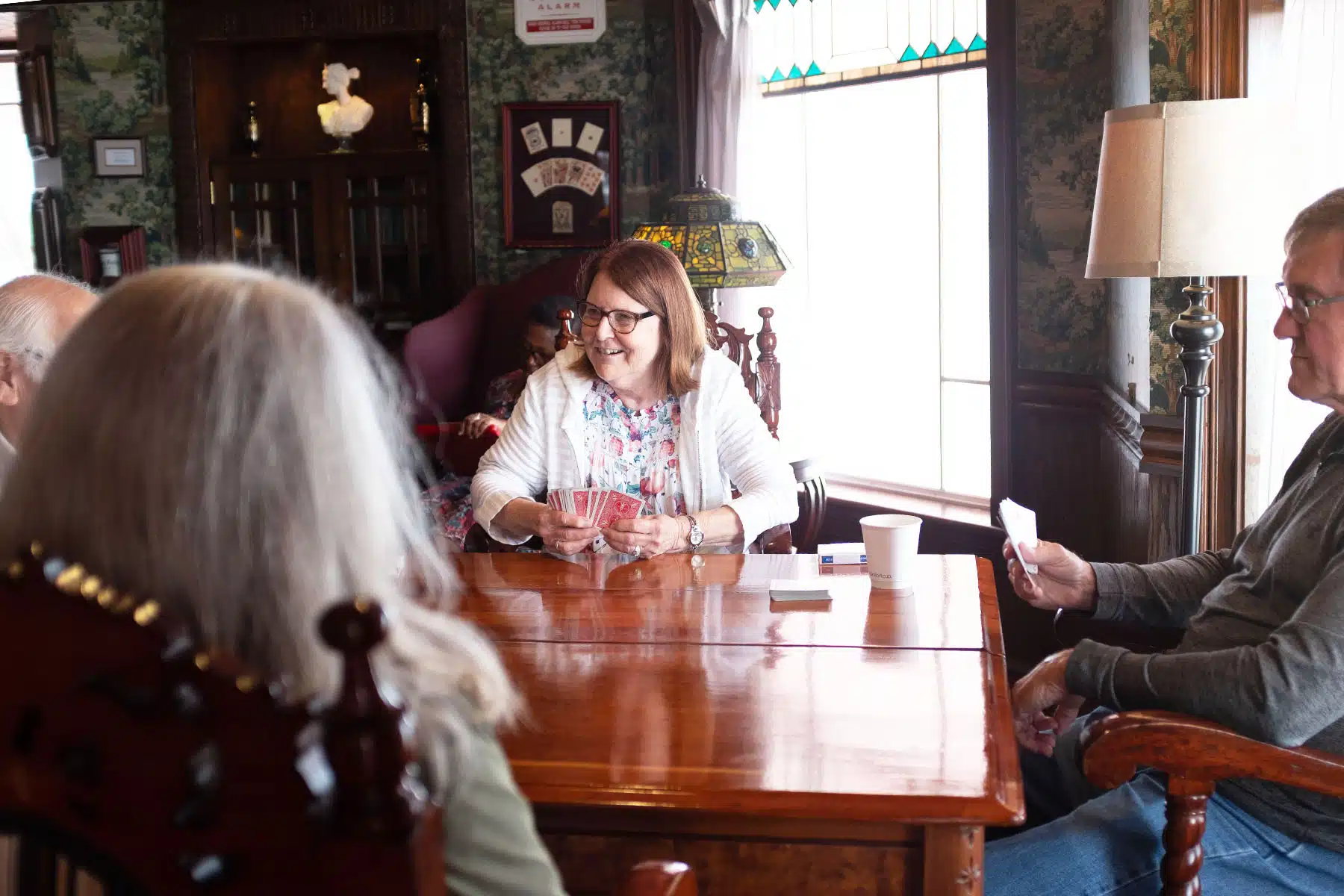

Tickets for a seven-day Mississippi River cruise with American Queen Voyages start around $4,000, and their most expensive cabins cost about $10,000 per person. Caribbean cruises can cost as little as $500 because ocean cruise lines rely on a high volume of passengers; the biggest ocean liner can hold 7,600 passengers at maximum capacity, while the biggest Mississippi River vessel holds just over 400 guests.
Memphis is putting $36 million toward its docking infrastructure to accommodate more cruises — the most recent development in a contentious, and sometimes tumultuous, investment in river tourism. Currently, one boat can dock at Beale Street Landing at a time; after the planned expansion, which is expected to begin by year-end, it’ll accommodate two.
The city also accommodates riverboats a few miles upriver at Greenbelt Park, where crews have to tie off to trees on the riverbank. To refill water, they have to run a hose more than 100 feet to a hydrant on the street, there’s nowhere to offload trash and there’s no shaded area for passengers waiting on transportation. With the city’s planned renovation, a new dock at Greenbelt Park will allow three boats to dock simultaneously between the two sites.
The American Queen was originally slated to dock at Beale Street Landing on Memorial Day, but ongoing construction forced it to reroute to Greenbelt Park.
“The current docking situation at Greenbelt Park is sorely lacking and is not an acceptable arrival experience for passengers,” said George Abbott, director of external affairs for Memphis River Parks Partnership.
Abbott said the preference for Beale Street Landing creates competition over the most favorable dates to arrive and depart from Memphis.
“We really feel we’re only a couple years away from having one or multiple vessels docked here literally almost every day, year round,” Kane said.
Memphis is one of many Mississippi River cities bolstering its docking infrastructure to welcome more cruises, and the cruise companies have invested money in towns to gain preferred docking rights. Cruise lines are jockeying for prime spots as the number of boats docking has expanded in the decade since overnight cruises returned to the river.
But dock expansion in Memphis has been contentious from the jump. Plans to construct Beale Street Landing started in the early 2000s and dragged on through three mayoral administrations, nearly doubling its initial budget. In that time, Hurricane Katrina hit, the river’s overnight cruise industry collapsed, federal funds dried up and many questioned the investment.
In 2001, the company that built the American Queen went bankrupt. It returned under different ownership but shuttered in 2008 alongside its only other competitor, just as Memphis broke ground on Beale Street Landing. For the first time in nearly two centuries, there was no overnight cruise on the Mississippi River.
Then, in 2012, a new company — now called American Queen Voyages — brought overnight cruises back to the Mississippi and headquartered in Memphis. It named Priscilla Presley the godmother of the American Queen, and after she christened it in Memphis, the boat set sail on its trip upriver, heralding another era of Mississippi River cruising.
Last year, Viking announced a cruise on the river, which signaled to many, including Kane, that overnight cruises on the Big Muddy are here to stay.
Captain Robert De Luca’s history with the American Queen dates back more than two decades, when he was second mate on the boat. He later piloted it before being promoted to captain, but after the industry collapsed in 2008, he left to pilot towboats instead.
When he returned to the American Queen last year after more than a decade away, he noticed changes in the customer base. During his welcome aboard, he asks first-timers to raise their hands; more hands go up today than did early in his career.
The number of passengers has changed, too. De Luca recalled times when there was a waitlist to ride the American Queen; as recently as 2016, the company reported 95% occupancy. On the lower Mississippi, De Luca said the boats tend to be about three-quarters full, but the numbers taper off on the upper river.
American Queen Voyages launched in 2012 with one boat. It later added two more to meet demand before retiring its smallest boat late last year.
“We were kind of competing against each other, almost, not filling up our own boats,” De Luca said of the company’s decision to retire its smallest boat. “When that business does hit, we’re ready.”
In late June 2023, the company announced plans to scrap its Great Lakes itineraries and sell the two boats it bought in 2019. The company characterized it as a move to refocus on its core river cruises. Its pivot away from the Great Lakes comes a year after Viking doubled its capacity in the region.
American Cruises Lines has five boats in its Mississippi River fleet, and three of those were added in the past three years. Its vessels are smaller, holding about half as many passengers as the American Queen — the biggest on the river by passenger capacity — and about half as many passengers as the Viking Mississippi — the biggest on the river by vessel size.
As American Cruise Lines expands the size of its fleet on the Mississippi, it’s also launching a 60-day cruise next fall. The $50,000 tour covers the Columbia and Snake Rivers in the West, followed by a cruise along the entire length of the Mississippi River and a final stint on the Hudson River, with flights included between the departure points.
As the two mainstays on the river adjust itineraries and fleets to meet fluctuating demand, Viking launched its first tours of the Mississippi River last September.
“Viking is a well-established cruise line, and they felt that they were really missing a strong opportunity for affluent travelers on river cruises,” Kane said.
But some of the businesses that have historically benefited from river tourism said that despite the upward trend since the industry returned in 2012, it hasn’t returned to pre-Hurricane Katrina levels.
Jay Schexnaydre, operations manager at the Laura Plantation, a stop included on two of the cruise lines’ itineraries between New Orleans and Baton Rouge, said the number of visitors from river cruises is lower than it was before the industry collapsed. When he started working at the Laura Plantation in 2001, he estimated that up to 150 cruise passengers would visit from each boat. Now, he places that number at 20 or 30 visitors, on average.
Schexnaydre has his own theories about why fewer cruise-goers turn up to the museum. Perhaps repeat passengers are opting to visit a different site this time around, or changing attitudes toward critical history drive fewer people to the Laura Plantation, which was the first of its kind in Louisiana to highlight the stories of enslaved people.
“It’s a certain kind of nostalgia for people who grew up with Tom Sawyer and Huckleberry Finn and the mighty Mississippi,” Schexnaydre said. “But the younger people — they don’t have that nostalgia for the river.”
This story, the last in a three-part series, published in partnership with the Mississippi Center for Investigative Reporting, part of Mississippi Today, is a product of the Mississippi River Basin Ag & Water Desk, an independent reporting network based at the University of Missouri in partnership with Report for America, funded by the Walton Family Foundation.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Hospitals see danger in Medicaid spending cuts
Mississippi hospitals could lose up to $1 billion over the next decade under the sweeping, multitrillion-dollar tax and policy bill President Donald Trump signed into law last week, according to leaders at the Mississippi Hospital Association.
The leaders say the cuts could force some already-struggling rural hospitals to reduce services or close their doors.
The law includes the largest reduction in federal health and social safety net programs in history. It passed 218-214, with all Democrats voting against the measure and all but five Republicans voting for it.
In the short term, these cuts will make health care less accessible to poor Mississippians by making the eligibility requirements for Medicaid insurance stiffer, likely increasing people’s medical debt.
In the long run, the cuts could lead to worsening chronic health conditions such as diabetes and obesity for which Mississippi already leads the nation, and making private insurance more expensive for many people, experts say.
“We’ve got about a billion dollars that are potentially hanging in the balance over the next 10 years,” Mississippi Hospital Association President Richard Roberson said Wednesday during a panel discussion at his organization’s headquarters.
“If folks were being honest, the entire system depends on those rural hospitals,” he said.
Mississippi’s uninsured population could increase by 160,000 people as a combined result of the new law and the expiration of Biden-era enhanced subsidies that made marketplace insurance affordable – and which Trump is not expected to renew – according to KFF, a health policy research group.
That could make things even worse for those who are left on the marketplace plans.
“Younger, healthier people are going to leave the risk pool, and that’s going to mean it’s more expensive to insure the patients that remain,” said Lucy Dagneau, senior director of state and local campaigns at the American Cancer Society.
Among the biggest changes facing Medicaid-eligible patients are stiffer eligibility requirements, including proof of work. The new law requires able-bodied adults ages 19 to 64 to work, do community service or attend an educational program at least 80 hours a month to qualify for, or keep, Medicaid coverage and federal food aid.
Opponents say qualified recipients could be stripped of benefits if they lose a job or fail to complete paperwork attesting to their time commitment.
Georgia became the case study for work requirements with a program called Pathways to Coverage, which was touted as a conservative alternative to Medicaid expansion.
Ironically, the 54-year-old mechanic chosen by Georgia Gov. Brian Kemp to be the face of the program got so fed up with the work requirements he went from praising the program on television to saying “I’m done with it” after his benefits were allegedly cancelled twice due to red tape.
Roberson sent several letters to Mississippi’s congressional members in weeks leading up to the final vote on the sweeping federal legislation, sounding the alarm on what it would mean for hospitals and patients.
Among Roberson’s chief concerns is a change in the mechanism called state directed payments, which allows states to beef up Medicaid reimbursement rates – typically the lowest among insurance payors. The new law will reduce those enhanced rates to nearly as low as the Medicare rate, costing the state at least $500 million and putting rural hospitals in a bind, Roberson told Mississippi Today.
That change will happen over 10 years starting in 2028. That, in conjunction with the new law’s one-time payment program called the Rural Health Care Fund, means if the next few years look normal, it doesn’t mean Mississippi is safe, stakeholders warn.
“We’re going to have a sort of deceiving situation in Mississippi where we look a little flush with cash with the rural fund and the state directed payments in 2027 and 2028, and then all of a sudden our state directed payments start going down and that fund ends and then we’re going to start dipping,” said Leah Rupp Smith, vice president for policy and advocacy at the Mississippi Hospital Association.

Even with that buffer time, immediate changes are on the horizon for health care in Mississippi because of fear and uncertainty around ever-changing rules.
“Hospitals can’t budget when we have these one-off programs that start and stop and the rules change – and there’s a cost to administering a program like this,” Smith said.
Since hospitals are major employers – and they also provide a sense of safety for incoming businesses – their closure, especially in rural areas, affects not just patients but local economies and communities.
U.S. Rep. Bennie Thompson is the only Democrat in Mississippi’s congressional delegation. He voted against the bill, while the state’s two Republican senators and three Republican House members voted for it. Thompson said in a statement that the new law does not bode well for the Delta, one of the poorest regions in the U.S.
“For my district, this means closed hospitals, nursing homes, families struggling to afford groceries, and educational opportunities deferred,” Thompson said. “Republicans’ priorities are very simple: tax cuts for (the) wealthy and nothing for the people who make this country work.”
While still colloquially referred to as the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, the name was changed by Democrats invoking a maneuver that has been used by lawmakers in both chambers to oppose a bill on principle.
“Democrats are forcing Republicans to delete their farcical bill name,” Senate Democratic Leader Charles Schumer of New York said in a statement. “Nothing about this bill is beautiful — it’s a betrayal to American families and it’s undeserving of such a stupid name.”
The law is expected to add at least $3.3 trillion to the nation’s debt over the next 10 years, according to the most recent estimate from the Congressional Budget Office.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Hospitals see danger in Medicaid spending cuts appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article reports on the negative impacts of a major federal tax and policy bill on Medicaid funding and rural hospitals in Mississippi. While it presents factual details and statements from stakeholders, the tone and framing emphasize the harmful consequences for vulnerable populations and health care access, aligning with concerns typically raised by center-left perspectives. The article highlights opposition by Democrats and critiques the bill’s priorities, particularly its effect on poor and rural communities, suggesting sympathy toward social safety net preservation. However, it maintains mostly factual reporting without overt partisan language, resulting in a moderate center-left bias.
Crooked Letter Sports Podcast
Podcast: The Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame Class of ’25
The MSHOF will induct eight new members on Aug 2. Rick Cleveland has covered them all and he and son Tyler talk about what makes them all special.
Stream all episodes here.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Podcast: The Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame Class of '25 appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Mississippi Today
‘You’re not going to be able to do that anymore’: Jackson police chief visits food kitchen to discuss new public sleeping, panhandling laws
Diners turned watchful eyes to the stage as Jackson Police Chief Joseph Wade took to the podium. He visited Stewpot Community Services during its daily free lunch hour Thursday to discuss new state laws, which took effect two days earlier, targeting Mississippians experiencing homelessness.
“I understand that you are going through some hard times right now. That’s why I’m here,” Wade said to the crowd. “I felt it was important to come out here and speak with you directly.”
Wade laid out the three bills that passed earlier this year: House Bill 1197, the “Safe Solicitation Act,” HB 1200, the “Real Property Owners Protection Act” and HB 1203, a bill that prohibits camping on public property.
“Sleeping and laying in public places, you’re not going to be able to do that anymore,” he said. “There’s a law that has been passed that you can’t just set up encampments on public or private properties where it’s a public nuisance, it’s a problem.”
The “Real Property Owners Protection Act,” authored by Rep. Brent Powell, R-Brandon, is a bill that expedites the process of removing squatters. The “Safe Solicitation Act,” authored by Rep. Shanda Yates, I-Jackson, requires a permit for panhandling and allows people to be charged with a misdemeanor if they violate this law. The offense is punishable by a fine not to exceed $300 and an offender could face up to six months in jail. Wade said he’s currently working with his legal department to determine the best strategy for creating and issuing permits.
“We’re going to navigate these legal challenges, get some interpretations, not only from our legal department, but the Attorney General’s office to ensure that we are doing it legally and lawfully, because I understand that these are citizens,” he said. “I understand that they deserve to be treated with respect, and I understand that we are going to do this without violating their constitutional rights.”
Wade said the Jackson Police Department is steadily fielding reports of squatters in abandoned properties and the law change gives officers new power to remove them more quickly. The added challenge? Figuring out what to do with a person’s belongings.
“These people are carrying around what they own, but we are not a repository for all of their stuff,” he said. “So, when we make that arrest, we’ve got to have a strategic plan as to what we do with their stuff.”
Wade said there needs to be a deeper conversation around the issues that lead someone to becoming homeless.
“A lot of people that we’re running across that are homeless are also suffering from medical conditions, mental health issues, and they’re also suffering from drug addiction and substance abuse. We’ve got to have a strategic approach, but we also can’t log jam our jail down in Raymond,” Wade said.
He estimates that more than 800 people are currently incarcerated at the Raymond Detention Center, and any increase could strain the system as the laws continue to be enforced.
“I think there’s layers that we have to work through, there’s hurdles that we are going to overcome, but we’ve got to make sure that we do it and make sure that my team and JPD is consistent in how we enforce these laws,” Wade said.
Diners applauded Wade after he spoke, in between bites of fried chicken, salad, corn and 4th of July-themed packaged cakes. Wade offered to answer questions, but no one asked any.
Rev. Jill Buckley, executive director of Stewpot, said that the legislation is a good tool to address issues around homelessness and community needs. She doesn’t want to see people who are homeless be criminalized, but she also wants communities to be safe.
“I support people’s right to self determine, and we can’t impose our choices on other people, but there are some cases in which that impinges on community safety, and so to the extent that anyone who is camping or panhandling or squatting and is a danger to themselves and others, of course, I fully support that kind of law. I don’t support homelessness being criminalized as such,” Buckley said.

Many of the people Wade addressed while they ate Thursday said they have housing, don’t panhandle, and shouldn’t be directly impacted by the legislation. But Marcus Willis, 42, said it would make more sense if elected officials wanted to combat the negative impacts of homelessness that they help more people secure employment.
“There ain’t enough jobs,” said Willis, who was having lunch with his girlfriend Amber Ivy.
The two live in an apartment together nearby on Capitol Street, where Ivy landed after her mother, whom Ivy had been living with, suffered a stroke and lost the property. Similarly, Willis started coming to eat at Stewpot after his grandmother, whose house he used to visit for lunch, passed away.
Willis holds odd jobs – cutting grass, home and auto repair – so the income is inconsistent, and every opportunity for stable employment he said he’s found is outside of Jackson in the suburbs. The couple doesn’t have a car.
Making rent every month usually depends on their ability to find someone to help chip in, said Ivy, who is in recovery from substance abuse. She said she’s watched problems surrounding homelessness grow over the years in Jackson. Ivy grew up near Stewpot and has lived in various neighborhoods across the city – except for the times she moved out of state when things got too rough.
“There was just moments where I just had to leave,” Ivy said. “Sometimes if you hit a slump here, there’s almost no way for you to get out of it.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post 'You're not going to be able to do that anymore': Jackson police chief visits food kitchen to discuss new public sleeping, panhandling laws appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Right
This article primarily reports on new laws in Jackson, Mississippi, targeting public sleeping, panhandling, and squatting, focusing on statements by Police Chief Joseph Wade and community perspectives. The coverage presents the legislative measures—authored by Republican and independent lawmakers—with a tone that emphasizes law enforcement challenges and community safety, reflecting a conservative approach to homelessness as a public order issue. While it includes voices concerned about criminalization and the need for social support, the overall framing centers on law enforcement and property protection. The article maintains factual reporting without overt editorializing but leans slightly toward a center-right perspective by highlighting legal enforcement as a solution.
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
Real-life Uncle Sam's descendants live in Arkansas
-
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
'Big Beautiful Bill' already felt at Georgia state parks | FOX 5 News
-
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days ago
LOFT report uncovers what led to multi-million dollar budget shortfall
-
Local News6 days ago
Maroon Tide football duo commits to two different SEC Teams!
-
The Center Square4 days ago
Here are the violent criminals Judge Murphy tried to block from deportation | Massachusetts
-
News from the South - South Carolina News Feed7 days ago
South Carolina lawmakers react as House approves Trump’s sweeping economic package
-
News from the South - Texas News Feed6 days ago
Hill Country flooding: Here’s how to give and receive help
-
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed6 days ago
Raleigh caps Independence Day with fireworks show outside Lenovo Center