Mississippi Today
How a business consultant with a history of domestic violence allegations took over the Delta State music department

CLEVELAND — It was the fourth day of classes at Delta State University last fall when the dean of the College of Arts and Sciences, Ellen Green, asked the music department to not hate her forever.
The 12 faculty members had just experienced one of the most tragic things to ever happen at the tiny college in the Mississippi Delta. Their department chair, Karen Fosheim, had been beaten to death in her home. Her stepson, then 14 years old, confessed to killing her.
It was on Green to hire a new chair for the grieving department. That day in August, she said she’d finally settled on someone to do it: Kent Wessinger, Ph.D.
A self-proclaimed “people scientist,” Wessinger has been called by one professional development group the “world’s foremost authority on workforce trends and solutions.” The tagline for his consulting company, the Florida-based Retention Partners, which focuses on millennials in the workforce, is “attract, engage and retain.”
He had been the headmaster of a missionary school in Jamaica, a program coordinator at the University of the Virgin Islands, and a visiting faculty member in entrepreneurship at a university in Belize, where in 2018 or so he says he struck up a friendship with Andy Novobilski, who’d go on to become Delta State’s provost. Novobilski announced in August that he was stepping down.
But Wessinger was not a musician. He was not even a tenured faculty member at Delta State or any university. According to his LinkedIn profile, he had never run a university department.
Green acknowledged it was “highly unusual.” That’s why the university planned for Wessinger to have a co-chair, a music faculty member who he’d simultaneously train to eventually take over full leadership of the department.
“He is a people person,” Green said, according to a recording of the meeting. “He is very likable. I found him to be — how do I put this? He likes building relationships. He understands what we do is all based on relationships.”
Despite Wessinger’s professed leadership expertise, his year helping lead the embattled music department did not raise morale or build bonds between faculty and students, but rather further grieved faculty who already feared for the department’s future, according to interviews with more than 16 faculty and current and former students. Multiple people asked not to be named, fearing retaliation.
Wessinger’s legacy in the department goes beyond personal or professional disagreements. He has been accused of domestic violence — a fact that, once uncovered, didn’t sit well with faculty still rattled by Fosheim’s killing.
His appointment raises a crucial question: Did Delta bring in the right person to lead its respected music department, and did it do enough — or anything — to vet him? And, if it did know about the past claims against Wessinger, what was Delta State’s responsibility to inform its faculty and students after the trauma they had suffered?
For some faculty, Wessinger’s decisions as department chair — made with the administration’s support — were possibly career-ending. He was involved in an attempted firing of the tenured band director, Erik Richards, a decision that a university committee recommended be overturned. He recommended denying tenure to an award-winning vocal teacher, Jamie Dahman, based in part on what Wessinger admitted, in his denial letter, was speculation.
A third faculty member who asked to not be named was reprimanded by the dean for unacceptable conduct and saying Wessinger had been accused of domestic violence, which the dean called “defamatory,” according to a letter the faculty member sent to Human Resources.
Students were also affected by the seeming disarray. In at least one instance, Wessinger took standard student complaints to human resources instead of following the typical process in higher education: To run them up the academic chain.
“The entire music department and the faculty were already mourning Dr. Fosheim, and now I feel like it’s just been constantly going downhill ever since she died,” said Lexie Johnson, a fifth-year music education major. “We just can’t catch a break.”
For his part, Wessinger says that every decision he made was for the students and in consultation with Julia Thorn, his co-chair. After granting an interview to Mississippi Today in July, he stopped discussing matters related to the university, claiming Delta State had instructed him and other administrators to “have no further contact with the press.”
“All of those decisions were made out of one single spirit and that spirit was for the students,” he said in July. “We don’t want this department to die.”
Delta State declined to comment on a majority of Mississippi Today’s inquiries, responding only to three questions a spokesperson said were not about “confidential personnel matters.”
Wessinger’s controversial handling of the department comes as Delta State is experiencing an employee retention problem. Since 2018, it has lost 46 faculty members, more than any other public university in the state, according to data from the Institutions of Higher Learning. Last school year, multiple departments were helmed by interim chairs, though music was the only one where an interim wasn’t an expert in its speciality.
And IHL recently cited one music degree for producing few graduates, putting it at risk of shutting down.
“If it doesn’t work with Dr. Wessinger, it’s four months, okay?” Green told the faculty. “This is very, very temporary.”
The Heartbeat of the Department
Like much at Delta State, the music department has seen better days.
Its building, Zeigel Hall, which sits on the campus’ historic quadrangle, in recent years has been plagued by asbestos and a faulty elevator that’s known to trap students for hours at a time.
The instruments are aging. The enrollment has shrunk. The band used to be renowned for producing band directors, but nowadays, students go to other schools, seeking the pomp of a traveling SEC game or the bravado of the Sonic Boom of the South.

In the midst of this challenge was Karen Fosheim. She was, students and faculty say, the heartbeat of the department. A pianist who became chair in 2016, she had a preternatural ability for knowing what was going on in the department at all times, many said, attending every concert and remembering the names of every student.
She was also skilled at uniting people, the chair’s most important role, recalled Mary Lenn Buchanan, Fosheim’s close friend and a retired Delta State music professor.
This was important because musicians have notorious egos. And there was already a rift in the music department. In 2019, Richards, the band director, received tenure despite opposition from some music faculty. The disagreement had dogged Zeigel Hall ever since.
But Fosheim commanded respect, Buchanan said, by always telling the truth.
“Unless Karen needed to tell someone they were pretty and they really weren’t, she did not lie,” Buchanan said.
Fosheim also directed that straightforwardness toward Delta State’s administration, especially during the pandemic, which may not have endeared her to them. By last summer, a rumor was circulating that Fosheim was going to be replaced.
The week of June 14, 2022, Fosheim didn’t show up for a scheduled work performance.
That day, concerned faculty asked the university police to request a wellness check on her home in Boyle, a small town just south of Cleveland. Her husband was out of state, and though Fosheim had been responding to texts, the replies were strange, unlike her.
Worried that Fosheim’s stepson, Alseny Camara, who is Black, would feel unsafe around police, two faculty members drove over that afternoon. They walked through the home with a detective. It was freezing inside and smelled.
Fosheim’s bedroom door was locked. The officer said he could get in via a window. As he removed the screen and peered through the glass, he saw a body prone on the floor.
That’s when Camara ran, according to testimony from a Bolivar County sheriff’s deputy during an August circuit court hearing. Deputies using K-9s found him shortly after 9:30 p.m., hiding in the woods near Fosheim’s home.
At the precinct, Camara confessed to killing his stepmom with an aluminum baseball bat. He was upset Fosheim, who was 57, had scolded him for trying to get out of his shift at a pet motel, according to the court hearing. He admitted he had impersonated her over text.
Jamie Dahman, then an assistant professor of music, had checked on Camara that day while Fosheim was still considered missing.
It still haunts Dahman that while he was talking to Camara, Fosheim was dead on the floor of her bedroom. It “sat with me for a long time,” he said, “and it still kind of gives me chills.”
As school was about to start two months later, the chair’s office was still full of Fosheim’s things: Half-finished crochet projects, potted plants, Nerf guns and foam darts, a picture of her stepson. Her voice was still on the answering machine. Her university memorial service still had to be planned.
If that weren’t enough, the Institutions of Higher Learning Board of Trustees had suddenly fired the president, William LaForge, sparking fears of budget cuts across the cash-strapped university.
And the music faculty still hadn’t heard from the administration about who would lead the department. The lack of leadership was becoming a problem. An important lock in the building wasn’t working. A new sound engineer needed to be hired.
Frustrated, Dahman sent an email to the department. He cc’d the dean, Green, and the provost, Novobilski. Since Novobilski, whose background is in business, came to Delta State in 2021, he had earned a reputation as a stickler for the hierarchy of academia.
The email got their attention. On Friday, Aug. 12, Green and Novobilski met with faculty.
A recording of the department meeting, the first without Fosheim, shows it was tense from the start. Voices were strained and shaky. Their anxiety stemmed from the stakes: Chairs have immense power in a department. Everyone wanted to trust that whoever took the role would be on their side. But faculty were worried administration, particularly Novobilski, had already come up with a plan for the role without them.

When Novobilski began the meeting, he seemed to confirm that fear by noting he had in fact been working to replace Fosheim. He acknowledged he should have called a meeting over the summer.
Dahman loudly interrupted him: “May I ask why we weren’t informed of what was going on?”
Then, a back-and-forth ensued. Novobilski told Dahman to take a deep breath.
It ended when Green asked if other faculty wanted to speak. One teared up explaining that he would have felt guilty volunteering for the vacant role. Another said that without Fosheim, the atmosphere in the department felt more toxic than ever.
Finally, Novobilski intimated he thought the department could benefit from someone outside “the music community” given its history of division.
“I have someone in mind, I’ll be honest with you,” Novobilski said. “This is someone I have worked with. … He has a lot of experience working with conflict resolution, mediation and he brings a lot of experience working with different groups of people, plus he’s a listener.”
This person, Novobilski said, did have administrative experience at the “college level.” But his specialty was business.
Dahman groaned.
Faculty barely trusted a colleague to take the job — let alone a non-musician. One faculty member protested that he thought the department could make it work with an internal hire. Josh Armstrong, then the faculty senate president, said “this definitely feels much more like here’s your new boss, and here you go.”
If faculty weren’t happy with Wessinger by the end of the semester, Novobilski conceded, “we’ll put him to work doing something else.”
But his mind seemed made up. Wessinger would be on campus by the end of August.
‘People Crisis’
About eight years ago, Wessinger set out on a mission to understand the relationship between millennials and organizational structures.
Ever since, the 59-year old Georgia native says he’s been trying to help Fortune 500 companies, churches, regional banks, rotary clubs and insurance companies — that is, “anyone who would listen” to him — solve their workforce crisis.
“I’m not just about identifying the problem,” he says in a January 2022 YouTube video titled “People crisis.” “I want to be the guy who helps you to understand what’s going on but also provides sustainable solutions for you.”
When faculty scanned his LinkedIn, Wessinger appeared impressive at first. He was a keynote speaker at more than 30 conferences a year, the author of three books and the creator of a proprietary database on millennials. His companies had ambitious names — Create2Elevate, Generational Forces, Retention Partners.
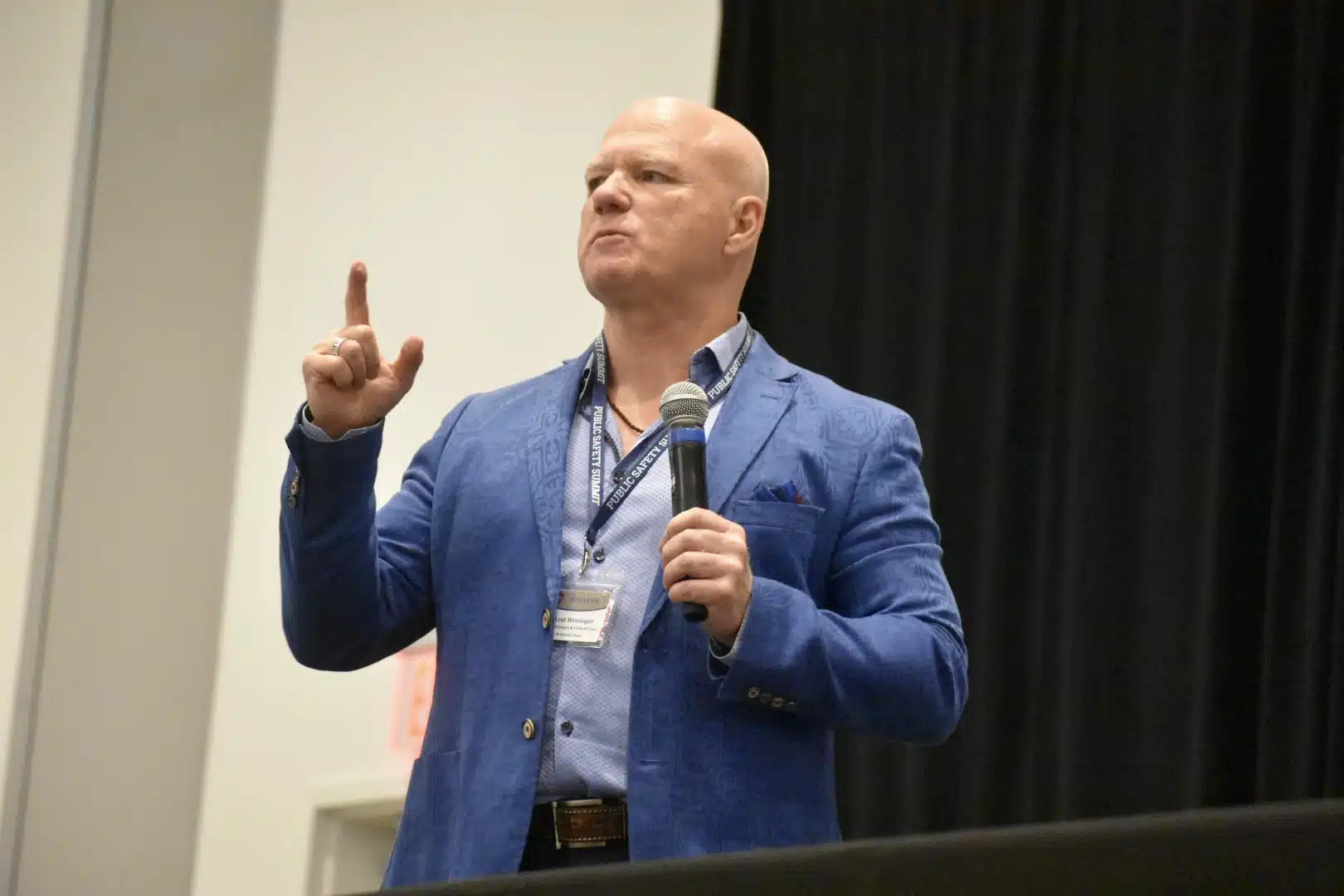

After a closer look, faculty didn’t understand how an accomplished business consultant had time to uproot to the Mississippi Delta.
Most notably, his experience in higher education was patchy. The administrative work Novobilski referenced at the Aug. 12 meeting appears to have primarily consisted of Wessinger setting up a satellite campus of the University of the Virgin Islands that offered remote classes, according to his LinkedIn.
They also discovered something particularly troubling. A 2012 opinion from the Supreme Court of the Virgin Islands in a divorce proceeding with an ex-wife, Robin Wessinger.
One line from the third page caught their eye: “The Motion stated that Kent ‘has been found to have committed repeated acts of domestic violence against [Robin] and was held in contempt of Court by [a Superior Court Magistrate] as a result of his continued violations of the January 20, 2010 Domestic Violence Restraining Order, which is in itself an act of Domestic Violence.”
This concerned faculty, who were still reeling from Fosheim’s death. It made many of them distrust Wessinger from the beginning.
Many students didn’t meet Wessinger until mid-October, almost two months into the semester, when he spoke to the recital class, according to an email.
Piper Gillam, a fifth-year music education major, said it “felt like a sales pitch.” Gillam said he called the students in the department, who were mainly born after 2000, “millennials.”
“In my head I was like, ‘I’m not a millennial. I’m Gen-Z,’” Gillam said. “And he was like, ‘and I know what you guys are thinking,’ and I was like, ‘OK, thank God, he’s gonna correct me,’ and he was like, ‘but you guys are millennials.’ So I googled it to see what age group am I, and it said Gen-Z, and I was like, alright, alright. I’m not trusting this man.”
Wessinger ran the music department like it was a business.
Faculty said he ignored their emails. But when they sought him out, they said he was hard to find in his office. Some meetings that Fosheim had scheduled months in advance now came with a few-hours notice from the department secretary. One faculty member said Wessinger neglected to notify them about a key deadline related to their tenure portfolio.
His lack of music knowledge was obvious, faculty said. He didn’t know what a “tone-row,” a basic composition method, was. He mispronounced the word “viola.”
“He said, ‘Vye-Ola,’” Richards recalled. “As in Davis.”
It didn’t make faculty feel like Wessinger was qualified to assess their work. In December, with evaluations around the corner, Green extended Wessinger’s part-time contract through the spring.
By then, faculty’s relationship with Wessinger had gotten so toxic, some started recording their interactions with him.
Wessinger seemed to have soured, too. According to sources close to Wessinger, and a text message sent on Oct. 18 by a faculty member to Wessinger’s co-chair, he started saying that Fosheim had left a “mess” in the department that he was going to “clean up.”

His prime target was Richards, the band director. A blunt and, by his own admission, polarizing figure in the department, Richards said he had questioned Wessinger when they first met. He wanted to know more about Wessinger’s dissertation on how limited opportunities for creativity in the Caribbean contributes to the region’s socio-economic crisis. It has several misspellings, including the name of a Haitian town.
Wessinger, according to sources close to him, talked openly about how he did not like Richards, who had other detractors as well.
On Feb. 22, Wessinger placed Richards on administrative leave pending an investigation into his “alleged contumacious conduct” – or as Webster’s dictionary defines it, “stubbornly disobedient” conduct.
About a month later, Lisa Giger, the human resources director, met with Richards’ wind ensemble class, according to a text message. She spent the session asking about the atmosphere of the class, multiple students said, and when they mentioned Richards, she had follow up questions.
Then on April 10, Richards received a letter from Novobilski: After a “thorough investigation by the Human Resources Department,” Richards was fired.
A university committee ultimately found that while Novobilski’s letter listed a slew of student and faculty complaints against Richards, only one had ever been formally documented. The previous administration had investigated and resolved that complaint in 2018-2019.
The thorough investigation, the committee wrote, seemed “one-sided,” but the committee couldn’t confirm that appearance because Richards was not allowed to ask any questions, which appears to be a violation of Delta State’s policies.
It is “completely outside of what is considered normal” for human resources to get involved in student complaints, said Daniel Durkin, a University of Mississippi professor and the president of the United Faculty Senate Association of Mississippi.
It is also “very unusual,” Durkin said, for someone like Wessinger who has not achieved tenure to evaluate applications for the prestigious distinction.
But that’s what Wessinger proceeded to do.
That spring, Dahman, the faculty member who was close to Fosheim, was considered for tenure. His application would become another piece of collateral damage in Wessinger’s drive to clean up the department.

Dahman, a vocal teacher who researches Bulgarian art song, had lots of reasons to be confident. In seven years of teaching at Delta State, he had never received a low mark on his annual evaluations, according to his tenure application. He’d earned a Mississippi Humanities Council Teaching Award in 2019. His students were accepted into graduate programs, won national competitions and sang in churches and funeral homes.
And chance was on his side. Most people who apply for tenure at Delta State end up getting it, according to an analysis of IHL data.
That’s why when Dahman was offered an extension on his tenure application in the fall, he did not accept it. In retrospect, he wonders if he should have. Dahman had received a verbal reprimand after his behavior at the Aug. 12 meeting, then he was put on a performance improvement plan in December. The plan required him to demonstrate “collegiality” with students, faculty, administration and campus visitors.
In late January, the department’s tenure committee, a panel of Dahman’s peers, recommended that Dahman receive tenure, and raised only minor concerns.
Then in mid-February, Wessinger recommended Dahman be denied on the basis of his teaching and collegiality, speculating there were more “violations” than the committee knew of. Two days later, Green, the dean, also recommended denial, claiming Dahman had “aggressively pounded the table” during the Aug. 12 meeting, an allegation that is not substantiated by the recording.
Dahman was devastated and angry.
His feelings spilled into his annual evaluation with Wessinger and Thorn in March. Wessinger began by asking if he could record due to the “environment” in the department, not knowing Dahman was recording as well.
Then, Wessinger revealed that he had recently taken Dahman’s students to HR and told them Dahman was on a performance improvement plan, something meant to be confidential. The students had complained about a remark Dahman had made in defense of his teaching — yet another issue that should have been resolved without HR.
Wessinger topped off the meeting by giving Dahman low marks for teaching and service. Dahman protested, but there was nothing he could do.
“This is my life, this is my livelihood, it’s how I support my children,” Dahman told them. “I feel like I’m being unfairly targeted because I snapped at the provost.”
Deconstructing hope
As the fall semester starts, many students and faculty say the music department is still struggling to get out of Wessinger’s shadow, even as he has moved on to lead a new department.
In June, Novobilski announced that Wessinger was going to be the interim chair of the Division of Management, Marketing and Business Administration.
Some faculty made a last-ditch effort to get rid of him. They sent an anonymous letter to Daniel Ennis, the new president of Delta State, summarizing their concerns with Wessinger — the adminstration’s decision to bring him on, his lack of music qualifications, the court document that said he had “committed repeated acts of domestic violence.”
Ennis didn’t respond to the letter, but even he has had to address the after-effects of decisions Wessinger had a hand in, like the hiring of Steven Hugley, the interim band director who made transphobic remarks on a podcast. Ennis also made the final call on Dahman’s tenure application, ultimately deciding to grant it.
A month later, Wessinger stood in a music room facing rows of empty risers for an interview with Mississippi Today. He talked about why he wanted to come to Delta State and how he had grown to care for it. Cleveland, he said, reminded him of the Virgin Islands — a place that needed help and where educational institutions are bastions of hope.
But some people had troubled him, deep in his soul.
“My personal issues have been accentuated to tear down and deconstruct the very opportunity that every student has here in this university,” he said, sweeping his hand out wide.
Wessinger acknowledged Fosheim’s killing had traumatized many faculty. But when he spoke about the anonymous letter, he grew agitated. He said it was full of “half truths, lies, manipulations.” He added that if Mississippi Today printed its reference to domestic violence, he was “not gonna be a happy camper.”
“We know who they are,” he said. “Anonymous, they’re not, and libel, they are.”
Yet Wessinger’s alleged past mistreatment of women goes beyond the restraining order that he violated in his divorce in the Virgin Islands, according to documents obtained by Mississippi Today.
Three other women across the U.S. have been granted restraining orders against him, all based on claims of domestic violence or mistreatment. In two of those cases, Mississippi Today confirmed through court records that Wessinger either sought or received a restraining order as well.
That was the case in Georgia, where a divorce was filed against Wessinger in 2016 in part on the basis of “fraud, cruel treatment,” which he denied. Affidavits submitted on behalf of his ex-wife, Laurie Higginbotham, allege that Wessinger wrote letters containing elaborate “false statements” that she had Huntington’s disease, and it was causing her to live in an altered state of reality.
In a phone call, Wessinger told Mississippi Today that every person who had accused him of domestic violence was “connected” and that he had believed at the time what he wrote in the letters about Higginbotham. He denied that he had ever mistreated or been violent toward a woman, adding that if he had, a judge would have taken away custody of his children.
“Attorneys will say anything in motions,” Wessinger said. “You’re reading a motion. You’re not reading the truth. You’re reading allegations. That doesn’t make it the truth.”
Faculty don’t know about the additional allegations against Wessinger, and it is unclear if Delta State’s administration knew before hiring him. The restraining orders may not have shown up on a background check since they are not public information or were hidden in court files.
Through a spokesperson, the president’s office declined to comment, citing personnel matters.
On Aug. 10, Ennis gave his first convocation.
“I’m here beside you to tackle the challenges we face, but today, put them aside and join me in celebrating what we do,” he said in his address.
Wessinger wasn’t there to hear it. He was in Florida, speaking to the CEO Council of Tampa Bay, giving a speech about solving the workforce crisis.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Judge: Felony disenfranchisement a factor in ruling on Mississippi Supreme Court districts
The large number of Mississippians with voting rights stripped for life because they committed a disenfranchising felony was a significant factor in a federal judge determining that current state Supreme Court districts dilute Black voting strength.
U.S. District Judge Sharion Aycock, who was appointed to the federal bench by George W. Bush, last week ruled that Mississippi’s Supreme Court districts violate the federal Voting Rights Act and that the state cannot use the same maps in future elections.
Mississippi law establishes three Supreme Court districts, commonly referred to as the northern, central and southern districts. Voters elect three judges from each to the nine-member court. These districts have not been redrawn since 1987.
READ MORE: Mississippians ask U.S. Supreme court to strike state’s Jim Crow-era felony voting ban
The main district at issue in the case is the central district, which comprises many parts of the majority-Black Delta and the majority-Black Jackson Metro Area.
Several civil rights legal organizations filed a lawsuit on behalf of Black citizens, candidates, and elected officials, arguing that the central district does not provide Black voters with a realistic chance to elect a candidate of their choice.
The state defended the districts arguing the map allows a fair chance for Black candidates. Aycock sided with the plaintiffs and is allowing the Legislature to redraw the districts.
The attorney general’s office could appeal the ruling to the U.S. 5th Circuit Court of Appeals. A spokesperson for the office stated that the office is reviewing Aycock’s decision, but did not confirm whether the office plans to appeal.
In her ruling, Aycock cited the testimony of William Cooper, the plaintiff’s demographic and redistricting expert, who estimated that 56,000 felons were unable to vote statewide based on a review of court records from 1994 to 2017. He estimated 60% of those were determined to be Black Mississippians.
Cooper testified that the high number of people who were disenfranchised contributed to the Black voting age population falling below 50% in the central district.
Attorneys from Attorney General Lynn Fitch’s office defended the state. They disputed Cooper’s calculations, but Aycock rejected their arguments.
The AG’s office also said Aycock should not put much weight on the number of disenfranchised people because the U.S. Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals previously ruled that Mississippi’s disenfranchisement system doesn’t violate the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment.
Aycock, however, distinguished between the appellate court’s ruling that the system did not have racial discriminatory intent and the current issue of the practice having a racially discriminatory impact.
“Notably, though, that decision addressed only whether there was discriminatory intent as required to prove an Equal Protection claim,” Aycock wrote. “The Fifth Circuit did not conclude that Mississippi’s felon disenfranchisement laws have no racially disparate impact.”
Mississippi has one of the harshest disenfranchisement systems in the nation and a convoluted method for restoring voting rights to people.
Other than receiving a pardon from the governor, the only way for someone to regain their voting rights is if two-thirds of legislators from both chambers at the Capitol, the highest threshold in the Legislature, agree to restore their suffrage.
Lawmakers only consider about a dozen or so suffrage restoration bills during the session, and they’re typically among the last items lawmakers take up before they adjourn for the year.
Under the Mississippi Constitution, people convicted of a list of 10 types of felonies lose their voting rights for life. Opinions from the Mississippi Attorney General’s Office have since expanded the list of specific disenfranchising felonies to 23.
The practice of stripping voting rights away from people for life is a holdover from the Jim Crow era. The framers of the 1890 Mississippi Constitution believed Black people were most likely to commit certain crimes.
Leaders in the state House have attempted to overhaul the system, but none have gained any significant traction in both chambers at the Capitol.
Last year, House Constitution Chairman Price Wallace, a Republican from Mendenhall, advocated a constitutional amendment that would have removed nonviolent offenses from the list of disenfranchising felonies, but he never brought it up for a vote in the House.
Wallace and House Elections Chairman Noah Sanford, a Republican from Collins, are leading a study committee on Sept. 11 to explore reforms to the felony suffrage system and other voting legislation.
Wallace previously said on an episode of Mississippi Today’s “The Other Side” podcast that he believes the state should tackle the issue because one of his core values, part of his upbringing, is giving people a second chance, especially once they’ve made up for a mistake.
“This issue is not a Republican or Democratic issue,” Wallace said. “It allows a woman or a man, whatever the case may be, the opportunity to have their voice heard in their local elections. Like I said, they’re out there working. They’re paying taxes just like you and me. And yet they can’t have a decision in who represents them in their local government.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Judge: Felony disenfranchisement a factor in ruling on Mississippi Supreme Court districts appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article presents a focus on voting rights and racial justice issues, highlighting the impact of felony disenfranchisement on Black voters in Mississippi. It emphasizes civil rights concerns and critiques longstanding policies rooted in the Jim Crow era, which aligns with center-left perspectives advocating for expanded voting access and systemic reform. The coverage is factual and includes viewpoints from multiple sides, but the framing and emphasis on racial disparities and voting rights restoration suggest a center-left leaning.
Mississippi Today
Jackson police chief steps down to take another job, national search to come
Jackson Police Department Chief Joseph Wade told the mayor last week he was choosing to retire after 29 years of service and two years at the helm of the force. Wade said he’d been given another job opportunity, which has yet to be announced.
His last day is Sept. 5.
Mayor John Horhn said he told Wade the officer would be crazy not to take the job — one that comes with less stress and more pay.
“His wife has been on his back, his blood pressure has been up,” Horhn said during Tuesday’s City Council meeting. “He has done a commendable job.”
Wade became chief during a period in which Jackson was called the murder capital of America. Under his tenure, Wade said crime has fallen markedly, including a roughly 45% reduction in homicides so far this year compared to the same period in 2024, the Clarion Ledger reported. He said he’s also increased JPD’s force by 37, for a total of 258 officers.
Wade said his biggest accomplishment is reestablishing trust. “We are no longer the laughing stock of the law enforcement community,” he said.
The chief’s departure comes less than two months after Horhn took office, replacing former Mayor Chokwe Antar Lumumba who originally appointed Wade, and on the heels of a spate of shootings that Wade said were driven by gangs of young men.
“I have received so many calls from the community: ‘Chief, please don’t leave us,'” Wade told the crowd in council chambers.
But Wade said he “would rather leave prematurely than overstay my welcome,” adding that the average tenure of a police chief is 2.5 years.
Wade said that last year he stood next to Jackson Councilman Kenny Stokes and told the media he was going to cut crime in half, “And what did I do? Cut it in half,” he said.
“What I’ve seen in our community in some situations is people want police, but they don’t want to be policed,” Wade said.
Hinds County Sheriff Tyree Jones will serve as interim police chief until the administration finds a replacement. Jones said he has not finalized a contract with the city, responding to a question about whether he will draw a salary from both agencies.
“I could think of no one better than the sheriff of Hinds County,” Horhn said, adding that the appointment is temporary.
Jones said during the meeting that his responsibility as sheriff will continue uninterrupted and that his goal within JPD is to ensure continued professionalism in the department.
“I extend my heartfelt gratitude to my dear friend and retired police chief Joe Wade,” Jones said. “Again, let me be clear, I have no aspirations to permanently hold the position.”
Horhn said there is precedence for the dual role that “Chief Sheriff Jones is about to embark upon,” citing former mayor Frank Melton’s hiring of Sheriff Malcolm McMillin.
The city has enlisted help from former U.S. Marshal George White and the former chief of the Mississippi Highway Patrol, Col. Charles Haynes, to lead the Law Enforcement Task Force that will conduct a nationwide search to fill the position. The administration expects that to take between 30 and 60 days, according to a city press release.
The release said the task force will also examine safety challenges in Jackson more broadly, such as youth crime, drug crimes, departmental needs and interagency coordination.
“I am grateful that Marshal White and Col. Haynes have agreed to lead this important effort. Their breadth of experience, commitment to public safety and deep understanding of law enforcement challenges will ensure the task force conducts a rigorous search for our next chief,” said Horhn. “I am confident they will help shape solutions that address the evolving needs of Jackson.”
The city said it would soon release details about the opportunity for the public to offer input on the process.
“Hinds County is all in for whatever we have to do to make Jackson and Hinds County the safest it can be,” Hinds County Supervisors President Robert Graham said during the meeting.
Wade, who hails from nearby Terry, graduated from JPD’s 23rd recruit class in 1995, rising from a police recruit and hitting every rung of the ladder on his way to chief. “I was homegrown,” he said.
Wade said he received “an amazing offer in a private sector at an amazing organization. Don’t ask me where. That will be released at the appropriate time.”
This story may be updated.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Jackson police chief steps down to take another job, national search to come appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Centrist
The article presents a straightforward news report on the resignation of a police chief, focusing on facts, quotes from officials, and crime statistics without evident ideological framing. It covers perspectives from multiple local government figures and avoids partisan language, reflecting a neutral, balanced tone typical of centrist reporting.
Mississippi Today
Bluesky blocks access in Mississippi, citing free speech and privacy concerns over state law
Mississippians can no longer access the Bluesky app after the social media platform blocked access to users in the state.
Bluesky said on Friday that it made the decision after the U.S. Supreme Court declined for now to block a Mississippi state law that the platform said limits free expression, invades people’s privacy and unfairly targets smaller social media companies. The state law, passed in 2024, requires users of websites and other digital services to verify their age.
“The Supreme Court’s recent decision leaves us facing a hard reality: comply with Mississippi’s age assurance law—and make every Mississippi Bluesky user hand over sensitive personal information and undergo age checks to access the site—or risk massive fines,” the company wrote in a statement. “The law would also require us to identify and track which users are children, unlike our approach in other regions. We think this law creates challenges that go beyond its child safety goals, and creates significant barriers that limit free speech and disproportionately harm smaller platforms and emerging technologies.”
Mississippi Attorney General Lynn Fitch, whose office defended the law, told the justices that age verification could help protect young people from “sexual abuse, trafficking, physical violence, sextortion and more,” activities that the First Amendment does not protect.
The age verification law added Mississippi to a list of Republican-led states where similar legal challenges are playing out.
NetChoice is challenging laws passed in Mississippi and other states that require social media users to verify their ages, and asked the Supreme Court to keep the measure on hold while a lawsuit plays out.
That came after a federal judge prevented the 2024 law from taking effect. But a three-judge panel of the 5th Circuit U.S. Court of Appeals ruled in July that the law could be enforced while the lawsuit proceeds.
On Aug. 14, the Supreme Court rejected an emergency appeal from a tech industry group representing major platforms such as Facebook, X and YouTube.
There were no noted dissents from the brief, unsigned order. Justice Brett Kavanaugh wrote that there’s a good chance NetChoice will eventually succeed in showing that the law is unconstitutional, but hadn’t shown it must be blocked while the lawsuit unfolds.
Bluesky grew after the 2024 presidential election. Many users of X, which is owned by Elon Musk, retreated from the platform in response to the billionaire’s strong support of Donald Trump.
In Bluesky’s statement explaining its decision to block access in Mississippi, the company said age verification systems “require substantial infrastructure and developer time investments, complex privacy protections, and ongoing compliance monitoring — costs that can easily overwhelm smaller providers.”
“This dynamic entrenches existing big tech platforms while stifling the innovation and competition that benefits users,” the company added.
Bluesky said it did follow other digital safety regulations, such as the United Kingdom’s Online Safety Act. Under that statute, age checks are required only for accessing certain content and features, and Bluesky does not track which users are under 18, the platform said:
“Mississippi’s law, by contrast, would block everyone from accessing the site—teens and adults—unless they hand over sensitive information, and once they do, the law in Mississippi requires Bluesky to keep track of which users are children.”
The Mississippi law, authored by Rep. Jill Ford, a Republican from Madison, is called the “Walker Montgomery Protecting Children Online Act,” named after a Mississippi teen who reportedly committed suicide after an overseas online predator threatened to blackmail him.
The Associated Press contributed to this report
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Bluesky blocks access in Mississippi, citing free speech and privacy concerns over state law appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
The content presents a perspective that emphasizes concerns about free speech, privacy, and the impact of government regulation on smaller tech companies, which aligns with a more progressive or liberal viewpoint on digital rights and corporate regulation. It critiques a Republican-led state law as potentially overreaching and harmful to innovation, while also acknowledging the law’s intent to protect children. The balanced presentation of both sides, with a slight emphasis on the tech platform’s viewpoint and civil liberties, suggests a center-left bias.
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
New I-55 bridge between Arkansas, Tennessee named after region’s three ‘Kings’
-
News from the South - Texas News Feed4 days ago
DEA agents uncover 'torture chamber,' buried drugs and bones at Kentucky home
-
News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days ago
Missouri settles lawsuit over prison isolation policies for people with HIV
-
News from the South - Virginia News Feed6 days ago
Erin: Tropical storm force winds 600 miles wide eases into Atlantic | North Carolina
-
Our Mississippi Home7 days ago
Vardaman: The Sweet Potato Capital Serving Up Love, Tradition, and Flavor at Sweet Potato Sweets
-
Local News6 days ago
Florida must stop expanding ‘Alligator Alcatraz’ immigration center, judge says
-
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed7 days ago
Hickory police face lawsuit over fatal shooting
-
The Center Square6 days ago
Georgia ICE arrests up 367 percent from 2021, making for ‘safer streets, open jobs | Georgia