Mississippi Today
Gov. Tate Reeves’ lonely last stand against Medicaid expansion
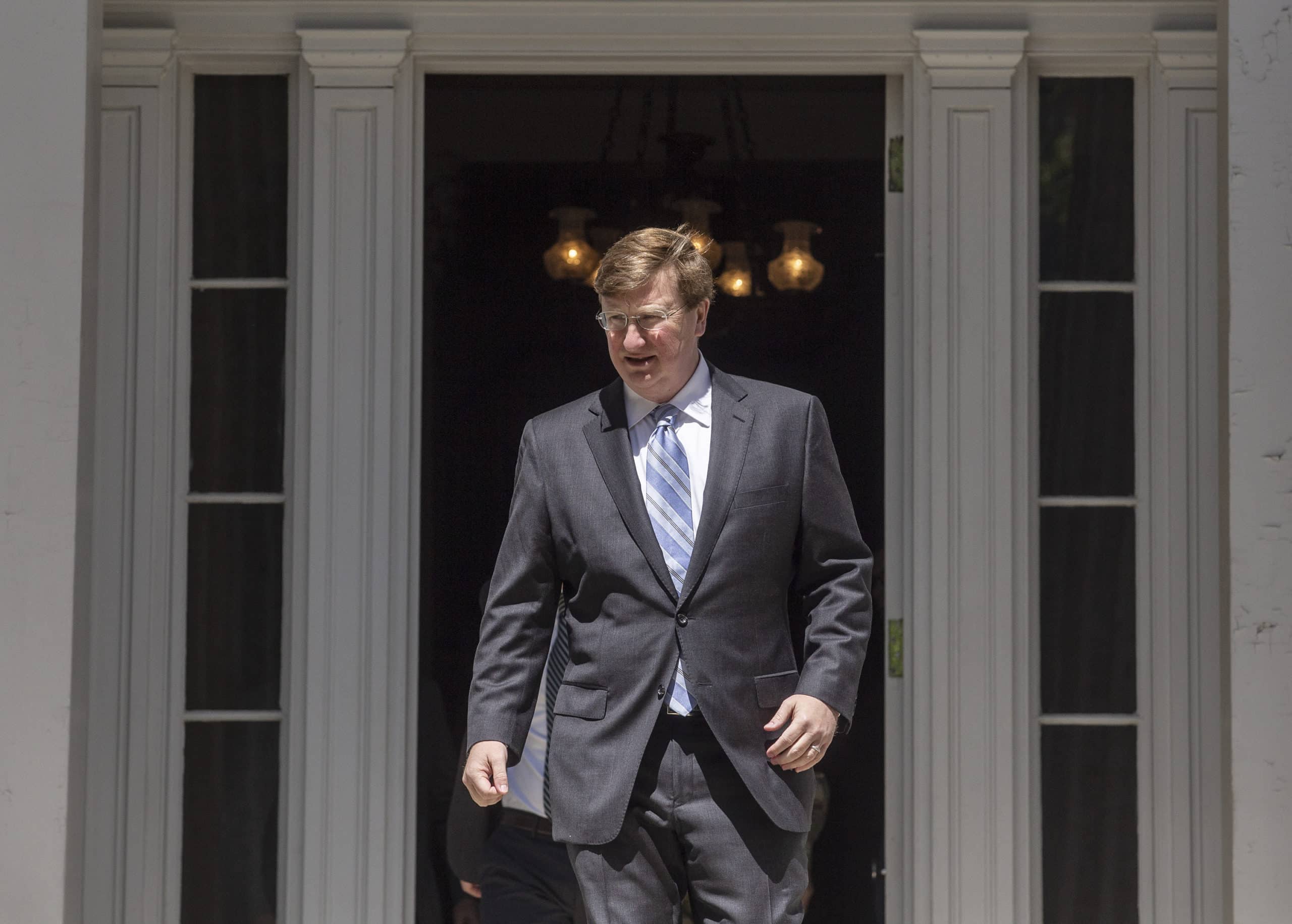

One year ago, Gov. Tate Reeves continued his years of steadfast defiance against Medicaid expansion and delivered a plea to his fellow Republican legislative leaders.
“Don't simply cave under the pressure of Democrats and their allies in the media who are pushing for the expansion of Obamacare, welfare, and socialized medicine,” Reeves said in his January 2023 State of the State address. “You have my word that if you stand up to the left's push for endless government-run healthcare, I will stand with you.”
Later today, Reeves will again deliver his annual State of the State address. But this year, he will be standing mostly alone in that fight. It very well could be his final stand.
Much to the governor's chagrin, the very GOP legislative leaders he pleaded with last year are well underway this year in their push to pass Medicaid expansion — a policy that would have a profound effect on countless Mississippians, their families and their communities. Yes, there are a handful of anti-expansion Republicans in both the House and Senate, but whether Reeves can whip anywhere close to the number of votes needed to block it is in real question.
Medicaid expansion, which Republican Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann and Republican House Speaker Jason White are ushering this session, would provide health coverage to between 200,000 and 250,000 poor, working Mississippians and bring in more than $1 billion in additional federal funds to the state each year.
Proponents say the policy would save the lives and livelihoods of countless Mississippians and provide hospitals with a cash boon that could help them keep their doors open. Opponents such as Reeves have decried the policy as “welfare expansion” and, despite dozens of economic studies that say otherwise, maintain the state cannot afford the state match.
Last week, the two legislative leaders — and the Medicaid committee chairs they appointed — remained unmoved by Reeves' criticism about their pursuit of the policy.
“My position's been pretty clear on the fact that we were going to explore and look at Medicaid as it affects hard-working, low-income Mississippians,” House Speaker Jason White told Mississippi Today. “My ideas and thoughts about that haven't changed. He's the duly elected governor and he's certainly entitled to his opinions on that matter. I don't hold any of those against him. We just maybe here in the House have a different view of it.”
No matter how hard Reeves fights back, the GOP legislative leaders pushing an expansion plan this year are not caving to Democrats or the media. They are seeking to help Mississippians of all backgrounds who have long struggled to keep their families healthy. They are responding to small town hospital leaders and business owners who are begging for a life-saving shot in the arm. They are trying to create solutions for our state's dismal labor participation rate. They are modeling the success of 40 others states — including many GOP-controlled — where Medicaid expansion has unequivocally saved lives.
And, without question, many of the lawmakers know Medicaid expansion is a wildly popular public policy.
The vast majority of Mississippians want it. Business leaders want it, mayors want it, and hospital leaders want it. Republican voters want it, and Democratic voters want it. Big-time Republican donors want it. Health care organizations like the Mississippi State Medical Association, Mississippi Hospital Association, American Cancer Society, and the American Heart Association want it. A majority of legislative Republicans want it, and all legislative Democrats want it. The Republican lieutenant governor wants it, and the Republican speaker wants it.
But Tate Reeves doesn't. And his last-stand defiance could define his legacy.
The governor has more policy staffers inside the Capitol this year than in his first term, and whether they can convince enough GOP lawmakers to stand with the governor could become the biggest question of the 2024 legislative session.
If legislative leaders do advance and pass an expansion proposal as expected, Reeves could veto the bill. To override his veto would require a two-thirds vote of both the House and the Senate chambers. The mad scramble to whip and wrangle votes during those few days would be unmatched by any legislative moment of Reeves' governorship.
Many Capitol observers will be listening intently to the governor's State of the State speech Monday evening. Hosemann and White will be sitting closely behind the governor's podium, and how they respond to any renewed pleas or perhaps even attacks on their work will be very telling about the days and weeks to come.
To be sure, Reeves doesn't seem to have much support right now where it matters most. Tonight, at least in his opposition to Medicaid expansion, he'll be standing mostly alone.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Medical residents are increasingly avoiding states with abortion restrictions
Isabella Rosario Blum was wrapping up medical school and considering residency programs to become a family practice physician when she got some frank advice: If she wanted to be trained to provide abortions, she shouldn't stay in Arizona.
Blum turned to programs mostly in states where abortion access — and, by extension, abortion training — is likely to remain protected, like California, Colorado, and New Mexico. Arizona has enacted a law banning most abortions after 15 weeks.
“I would really like to have all the training possible,” she said, “so of course that would have still been a limitation.”
In June, she will start her residency at Swedish Cherry Hill hospital in Seattle.
According to new statistics from the Association of American Medical Colleges, for the second year in a row, students graduating from U.S. medical schools were less likely to apply this year for residency positions in states with abortion bans and other significant abortion restrictions.
Since the Supreme Court in 2022 overturned the constitutional right to an abortion, state fights over abortion access have created plenty of uncertainty for pregnant patients and their doctors. But that uncertainty has also bled into the world of medical education, forcing some new doctors to factor state abortion laws into their decisions about where to begin their careers.
Fourteen states, primarily in the Midwest and South, have banned nearly all abortions. The new analysis by the AAMC — a preliminary copy of which was exclusively reviewed by KFF Health News before its public release — found that the number of applicants to residency programs in states with near-total abortion bans declined by 4.2%, compared with a 0.6% drop in states where abortion remains legal.
Notably, the AAMC's findings illuminate the broader problems abortion bans can create for a state's medical community, particularly in an era of provider shortages: The organization tracked a larger decrease in interest in residencies in states with abortion restrictions not only among those in specialties most likely to treat pregnant patients, like OB-GYNs and emergency room doctors, but also among aspiring doctors in other specialties.
“It should be concerning for states with severe restrictions on reproductive rights that so many new physicians — across specialties — are choosing to apply to other states for training instead,” wrote Atul Grover, executive director of the AAMC's Research and Action Institute.
The AAMC analysis found the number of applicants to OB-GYN residency programs in abortion ban states dropped by 6.7%, compared with a 0.4% increase in states where abortion remains legal. For internal medicine, the drop observed in abortion ban states was over five times as much as in states where abortion is legal.
In its analysis, the AAMC said an ongoing decline in interest in ban states among new doctors ultimately “may negatively affect access to care in those states.”
Jack Resneck Jr., immediate past president of the American Medical Association, said the data demonstrates yet another consequence of the post-Roe v. Wade era.
The AAMC analysis notes that even in states with abortion bans, residency programs are filling their positions — mostly because there are more graduating medical students in the U.S. and abroad than there are residency slots.
Still, Resneck said, “we're extraordinarily worried.” For example, physicians without adequate abortion training may not be able to manage miscarriages, ectopic pregnancies, or potential complications such as infection or hemorrhaging that could stem from pregnancy loss.
Those who work with students and residents say their observations support the AAMC's findings. “People don't want to go to a place where evidence-based practice and human rights in general are curtailed,” said Beverly Gray, an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Duke University School of Medicine.
Abortion in North Carolina is banned in nearly all cases after 12 weeks. Women who experience unexpected complications or discover their baby has potentially fatal birth defects later in pregnancy may not be able to receive care there.
Gray said she worries that even though Duke is a highly sought training destination for medical residents, the abortion ban “impacts whether we have the best and brightest coming to North Carolina.”
Rohini Kousalya Siva will start her obstetrics and gynecology residency at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington, D.C., this year. She said she did not consider programs in states that have banned or severely restricted abortion, applying instead to programs in Maryland, New Hampshire, New York, and Washington, D.C.
“We're physicians,” said Kousalya Siva, who attended medical school in Virginia and was previously president of the American Medical Student Association. “We're supposed to be giving the best evidence-based care to our patients, and we can't do that if we haven't been given abortion training.”
Another consideration: Most graduating medical students are in their 20s, “the age when people are starting to think about putting down roots and starting families,” said Gray, who added that she is noticing many more students ask about politics during their residency interviews.
And because most young doctors make their careers in the state where they do their residencies, “people don't feel safe potentially having their own pregnancies living in those states” with severe restrictions, said Debra Stulberg, chair of the Department of Family Medicine at the University of Chicago.
Stulberg and others worry that this self-selection away from states with abortion restrictions will exacerbate the shortages of physicians in rural and underserved areas.
“The geographic misalignment between where the needs are and where people are choosing to go is really problematic,” she said. “We don't need people further concentrating in urban areas where there's already good access.”
After attending medical school in Tennessee, which has adopted one of the most sweeping abortion bans in the nation, Hannah Light-Olson will start her OB-GYN residency at the University of California-San Francisco this summer.
It was not an easy decision, she said. “I feel some guilt and sadness leaving a situation where I feel like I could be of some help,” she said. “I feel deeply indebted to the program that trained me, and to the patients of Tennessee.”
Light-Olson said some of her fellow students applied to programs in abortion ban states “because they think we need pro-choice providers in restrictive states now more than ever.” In fact, she said, she also applied to programs in ban states when she was confident the program had a way to provide abortion training.
“I felt like there was no perfect, 100% guarantee; we've seen how fast things can change,” she said. “I don't feel particularly confident that California and New York aren't going to be under threat, too.”
As a condition of a scholarship she received for medical school, Blum said, she will have to return to Arizona to practice, and it is unclear what abortion access will look like then. But she is worried about long-term impacts.
“Residents, if they can't get the training in the state, then they're probably less likely to settle down and work in the state as well,” she said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1928
MAY 9, 1928

Burl Toler was born in Memphis. The first Black official in any major sport in the U.S., he defeated prejudice at each turn.
In 1951, Toler starred for the legendary undefeated University of San Francisco Dons. Prejudice kept the integrated team from playing in the Gator Bowl, but the team found success anyway. Nine players went to the NFL, three of them later inducted into the Professional Football Hall of Fame. Their best player may have been Toler, who was drafted by Cleveland but suffered a severe knee injury in a college all-star game that ended his playing days.
Toler decided to make his way into professional football through officiating. The NFL hired him in 1965 — a year before Emmett Ashford became the first Black umpire in Major League Baseball and three years before Jackie White broke the color barrier in the NBA.
He rose above the racism he encountered, working as a head linesman and field judge for a quarter-century. He officiated Super Bowl XIV, where the Pittsburgh Steelers defeated the Los Angeles Rams in 1980. Two years later, he officiated the “Freezer Bowl,” where the Cincinnati Bengals defeated the San Diego Chargers in the AFC Championship Game. The game marked the coldest temperatures of any game in NFL history — minus 59 degrees wind chill — and Toler suffered frostbite.
In addition to his NFL work, he worked as an educator, becoming the first Black secondary school principal in the San Francisco district. He died in 2009. Two area schools and a hall on the University of San Francisco campus have been renamed in his honor. On Nov. 23, 2020, Toler was remembered again when the NFL had its first all-Black officiating crew.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
EPA absolves MDEQ, Health Department of discrimination in funding Jackson water
About a year and half ago, on the heels of Jackson's infamous water system failure, advocates and politicians from Mississippi began publicly questioning the funding mechanisms that are supposed to support such systems.
In October 2022, U.S. Reps. Bennie Thompson and Carolyn Maloney wrote Gov. Tate Reeves, grilling him over an apparent disparity in how federal infrastructure funds were allocated to Jackson versus other parts of the state.
Then days later, the Environmental Protection Agency's civil rights office opened an investigation into two state agencies — the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality and the Mississippi Department of Health — in response to the NAACP's claims of discrimination under Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Title VI prohibits discrimination — based on race, color or national origin — in providing federal assistance.
On Monday, though, the EPA announced it had ended the probe after finding no evidence the agencies had short-changed Jackson's water system. In its investigation, the EPA looked at the funding amounts and racial demographics of cities that received water funding from MDEQ and the Health Department and determined there was no correlation between the two factors.
“The evidence overwhelmingly shows that the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality did everything right,” MDEQ Executive Director Chris Wells said in a press release following the EPA's announcement.
The two agencies are in charge of disbursing funds from the EPA called “state revolving loan,” or SRF, funds, which are meant to help cities make infrastructure improvements. MDEQ handles SRF funds related to wastewater infrastructure, while the Health Department handles SRF funds for drinking water.
But the claims against the agencies were only part of the 2022 complaint the NAACP filed with the EPA. The federal agency did not address another complaint: The group also focused on the state Legislature, which has denied attempts in recent years by Jackson to raise money for its water system, such as creating a new 1% tax.
Click here for the EPA's full responses to MDEQ and Health Department.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
-
SuperTalk FM6 days ago
State approves $160M to expand Highway 7 to four lanes in Lafayette County
-
SuperTalk FM3 days ago
Legislation outlawing ‘squatted’ vehicles in Mississippi signed into law
-
228Sports2 days ago
PRC’s Bats Come Alive Late As Blue Devils Beat Picayune To Advance To 6A South State Title Series
-
Mississippi Today4 days ago
On this day in 1917
-
Mississippi News4 days ago
LCSO wants people aware of a scam circling the area
-
Mississippi News4 days ago
Winston Co. Sheriff’s Office investigates shooting at Dave’s Club
-
SuperTalk FM20 hours ago
Mississippi governor approves bill allowing electronic search warrants
-
Mississippi News1 day ago
Strong storms late Wednesday night – Home – WCBI TV