Deryn Davidson
Deryn Davidson, Colorado State University
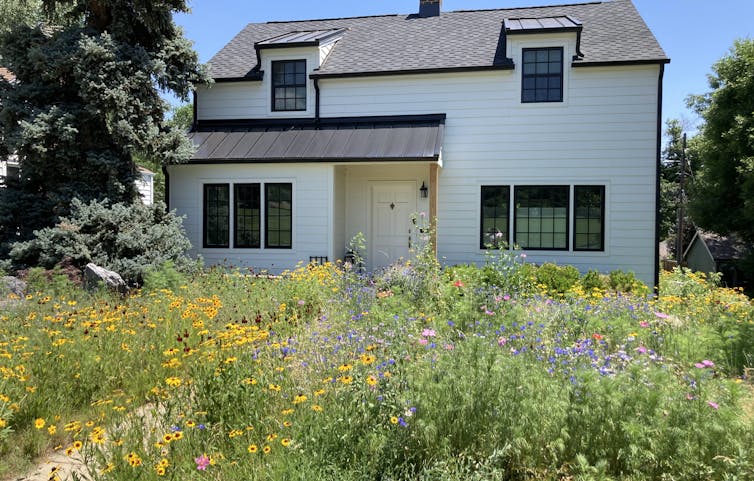
If you’ve spent any time in the gardening corners of social media lately, you’ve likely come across a trend called “chaos gardening.”
The name alone is eye-catching – equal parts fun, rebellious and slightly alarming. Picture someone tossing random seeds into bare soil, watering once or twice, and ending up with a backyard jungle of blooms. No rows, no color coordination, no spacing charts. Just sprinkle and hope for the best.
As a sustainable landscape specialist at Colorado State University Extension, I think a lot about how to help people make designed landscapes more sustainable. Occasionally, a new trend like this one crops up claiming to be the silver bullet of gardening – supposedly it saves water, saves the bees and requires no maintenance.
But what is chaos gardening, really? And does it work? As with most viral trends, the answer is: sometimes.
What chaos gardening is and isn’t
At its core, chaos gardening is the practice of mixing a wide variety of seeds, often including leftover packets, wildflower mixes, or cut flower favorites, and scattering them over a planting area with minimal planning.
The goal is to create a dense, colorful garden that surprises you with its variety. For many, it’s a low-pressure, joyful way to experiment.
But chaos gardening isn’t the same as ecological restoration, pollinator meadow planting or native prairie establishment. Unlike chaos gardening, all of these techniques rely on careful species selection, site prep and long-term management.
Chaos gardening is a bit like making soup from everything in your pantry – it might be delicious, but there are no guarantees.
Chaos gardening’s appeal
One reason chaos gardening may be catching on is because it sidesteps the rules of garden design. A traditional landscape design approach is effective and appropriate for many settings, but it is a time investment and can feel intimidating. Design elements and principles, and matching color schemes, don’t fit everyone’s style or skill set.
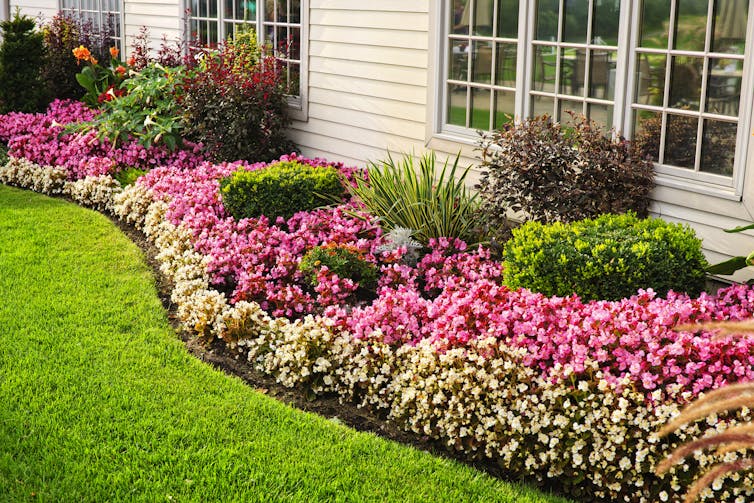

Elenathewise/iStock via Getty Images Plus
Even the apparently relaxed layers of blooms and informal charm of an English cottage garden actually result from careful planning. Chaos gardening, by contrast, lets go of control. It offers a playful, forgiving entry point into growing things. In a way, chaos gardening is an antidote to the pressure of perfection, especially the kind found in highly curated, formal landscapes.
There’s also the allure of ease. People want gardening to be simple. If chaos gardening brings more people into the joy and mess of growing things, I consider that a win in itself. Broader research has found that emotional connection and accessibility are major motivators for gardening, often more than environmental impact.
When does chaos gardening work?
The best outcomes from chaos gardening happen when the chaos has a few guardrails:
-
Choose plants with similar needs. Most successful chaos gardens rely on sun-loving annuals that grow quickly and bloom prolifically, like zinnias, cosmos, marigolds, snapdragons and sunflowers. These are also excellent cut flowers to use in bouquets, which makes them doubly rewarding.
-
Consider your region. A chaos garden that thrives in Colorado might flop in North Carolina. It is beneficial to select seed mixes or individual varieties suited to your area since factors like soil type and growing season length matter. Different plants have unique needs beyond just sun and water; soil pH, cold hardiness and other conditions can make a big difference.
-
Think about pollinators. Mixing in nectar- and pollen-rich flowers native to North America, such as black-eyed Susans, bee balm or coneflowers, provides valuable resources for native bees, butterflies, moths and other local pollinators. These species benefit even more if you plan your garden with phenology – that is, nature’s calendar – in mind. By maintaining blooms from early spring through late fall, you ensure a steady food supply throughout the growing season. Plus, a diverse plant palette supports greater pollinator abundance and diversity.
-
Prep your site. Even “chaos” needs a little order. Removing weeds, loosening the top layer of soil and watering regularly, especially during germination when seeds are sprouting, will dramatically improve your results. Successful seed germination requires direct seed-to-soil contact and consistent moisture; if seeds begin to grow and then dry out, many species will not survive.
When does chaos gardening not work?
There are a few key pitfalls to chaos gardening that often get left out of the online hype:
-
Wrong plant, wrong place. If your mix includes shade-loving plants and your garden is in full sun, or drought-tolerant plants whose seeds end up in a soggy low spot, they’ll struggle to grow.
-
Invasive species and misidentified natives. Some wildflower mixes, especially inexpensive or mass-market ones, claim to be native but actually contain non-native species that can spread beyond your garden and become invasive. While many non-natives are harmless, some spread quickly and disrupt natural ecosystems. Check seed labels carefully and choose regionally appropriate native or adapted species whenever possible.
-
Soil, sun and water still matter. Gardening is always a dialogue with place. Even if you’re embracing chaos, taking notes, observing how light moves through your space, and understanding your soil type will help you know your site better, and choose appropriate plants.
-
Maintenance is still a thing. Despite the “toss and walk away” aesthetic, chaos gardens still require care. Watering, weeding and eventually cutting back or removing spent annuals are all part of the cycle.
Beyond the hashtag
Beneath the chaos gardening memes, there’s something real happening: a growing interest in a freer, more intuitive way of gardening. And that’s worth paying attention to.
Once someone has success with a zinnia or cosmos, they may be inspired to try more gardening. They might start noticing which flowers the bees are visiting in their garden. They may discover native plants and pay attention to the soil they are tending, seeing how both are part of a larger, living system. A chaotic beginning can become something deeper.
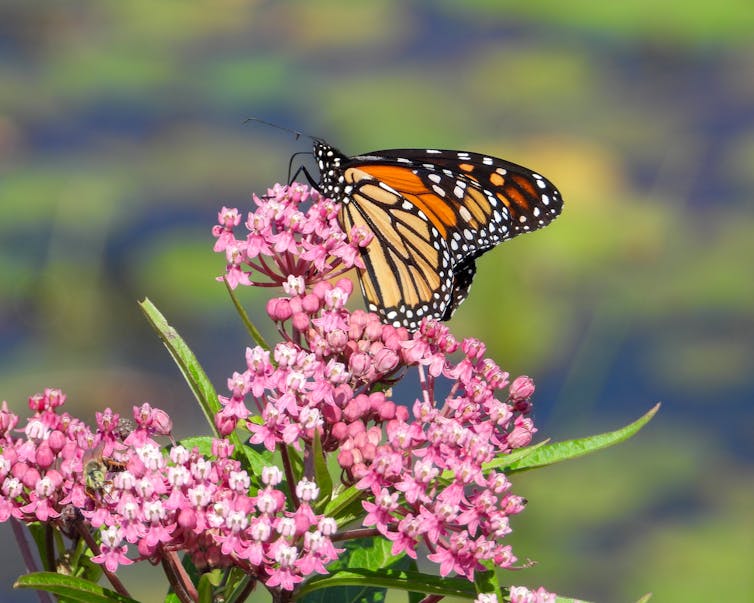

Brian Woolman/iStock via Getty Images Plus
Chaos gardening might not replace the structured borders of a manicured garden or a carefully curated pollinator patch, but it might get someone new into the garden. It might lower the stakes, invite experimentation and help people see beauty in abundance rather than control.
If that’s the entry point someone needs, then let the chaos begin.
Deryn Davidson, Sustainable Landscape State Specialist, Extension, Colorado State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Elenathewise/iStock via Getty Images Plus
Even the apparently relaxed layers of blooms and informal charm of an English cottage garden actually result from careful planning. Chaos gardening, by contrast, lets go of control. It offers a playful, forgiving entry point into growing things. In a way, chaos gardening is an antidote to the pressure of perfection, especially the kind found in highly curated, formal landscapes.
There’s also the allure of ease. People want gardening to be simple. If chaos gardening brings more people into the joy and mess of growing things, I consider that a win in itself. Broader research has found that emotional connection and accessibility are major motivators for gardening, often more than environmental impact.
When does chaos gardening work?
The best outcomes from chaos gardening happen when the chaos has a few guardrails:
-
Choose plants with similar needs. Most successful chaos gardens rely on sun-loving annuals that grow quickly and bloom prolifically, like zinnias, cosmos, marigolds, snapdragons and sunflowers. These are also excellent cut flowers to use in bouquets, which makes them doubly rewarding.
-
Consider your region. A chaos garden that thrives in Colorado might flop in North Carolina. It is beneficial to select seed mixes or individual varieties suited to your area since factors like soil type and growing season length matter. Different plants have unique needs beyond just sun and water; soil pH, cold hardiness and other conditions can make a big difference.
-
Think about pollinators. Mixing in nectar- and pollen-rich flowers native to North America, such as black-eyed Susans, bee balm or coneflowers, provides valuable resources for native bees, butterflies, moths and other local pollinators. These species benefit even more if you plan your garden with phenology – that is, nature’s calendar – in mind. By maintaining blooms from early spring through late fall, you ensure a steady food supply throughout the growing season. Plus, a diverse plant palette supports greater pollinator abundance and diversity.
-
Prep your site. Even “chaos” needs a little order. Removing weeds, loosening the top layer of soil and watering regularly, especially during germination when seeds are sprouting, will dramatically improve your results. Successful seed germination requires direct seed-to-soil contact and consistent moisture; if seeds begin to grow and then dry out, many species will not survive.
When does chaos gardening not work?
There are a few key pitfalls to chaos gardening that often get left out of the online hype:
-
Wrong plant, wrong place. If your mix includes shade-loving plants and your garden is in full sun, or drought-tolerant plants whose seeds end up in a soggy low spot, they’ll struggle to grow.
-
Invasive species and misidentified natives. Some wildflower mixes, especially inexpensive or mass-market ones, claim to be native but actually contain non-native species that can spread beyond your garden and become invasive. While many non-natives are harmless, some spread quickly and disrupt natural ecosystems. Check seed labels carefully and choose regionally appropriate native or adapted species whenever possible.
-
Soil, sun and water still matter. Gardening is always a dialogue with place. Even if you’re embracing chaos, taking notes, observing how light moves through your space, and understanding your soil type will help you know your site better, and choose appropriate plants.
-
Maintenance is still a thing. Despite the “toss and walk away” aesthetic, chaos gardens still require care. Watering, weeding and eventually cutting back or removing spent annuals are all part of the cycle.
Beyond the hashtag
Beneath the chaos gardening memes, there’s something real happening: a growing interest in a freer, more intuitive way of gardening. And that’s worth paying attention to.
Once someone has success with a zinnia or cosmos, they may be inspired to try more gardening. They might start noticing which flowers the bees are visiting in their garden. They may discover native plants and pay attention to the soil they are tending, seeing how both are part of a larger, living system. A chaotic beginning can become something deeper.

Brian Woolman/iStock via Getty Images Plus
Chaos gardening might not replace the structured borders of a manicured garden or a carefully curated pollinator patch, but it might get someone new into the garden. It might lower the stakes, invite experimentation and help people see beauty in abundance rather than control.
If that’s the entry point someone needs, then let the chaos begin.