Mississippi Today
Democrats finalize hospital crisis plan, blast Republicans for inaction
Democrats finalize hospital crisis plan, blast Republicans for inaction
Note: This article was first published in Mississippi Today’s weekly legislative newsletter. Subscribe to our free newsletter for exclusive early access to legislative analyses and up-to-date information about what’s happening under the Capitol dome.
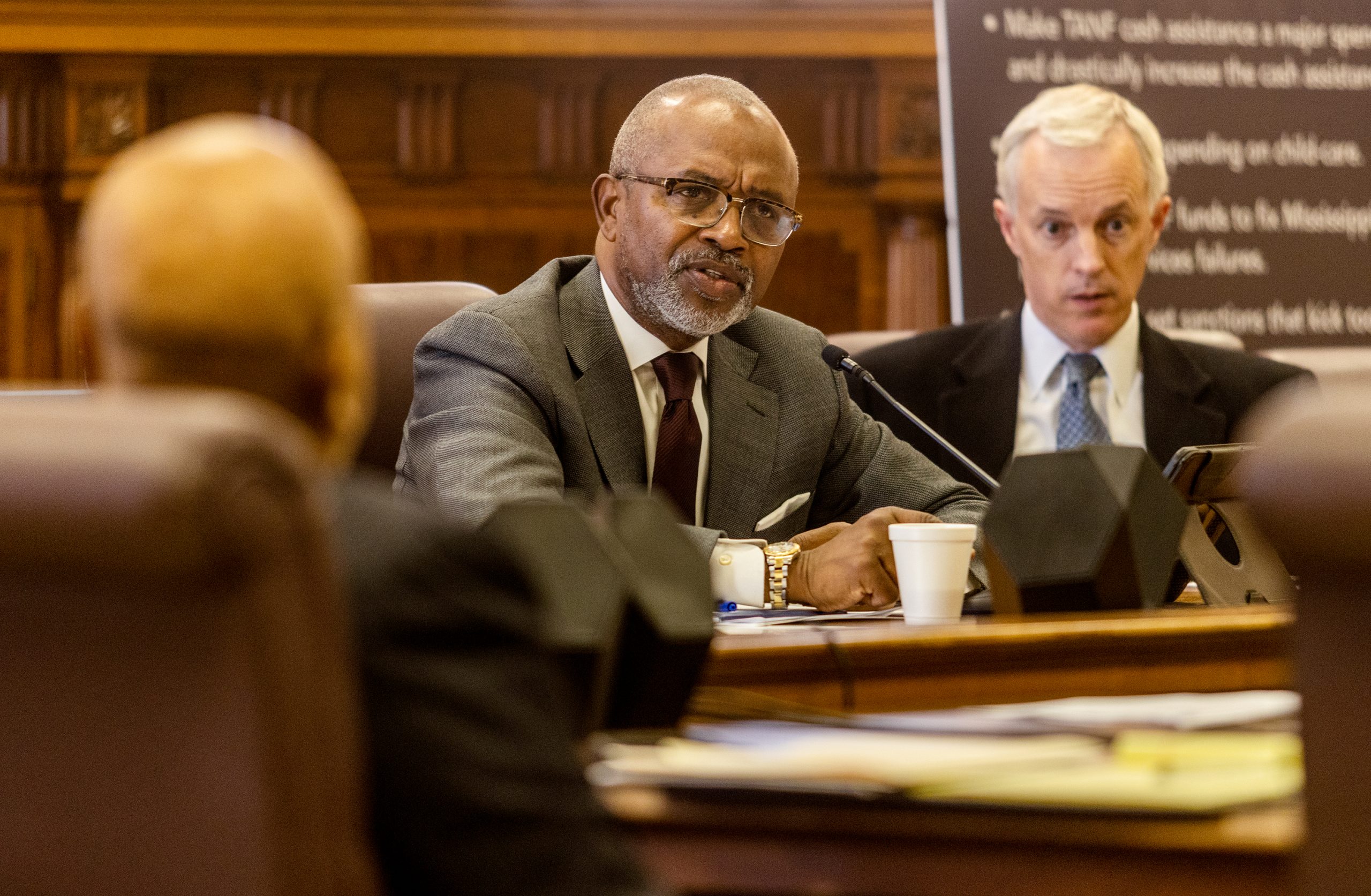
Democratic legislative leaders will propose a plan this week to address a problem they say most of their Republican counterparts won’t even fully acknowledge: the Mississippi hospital crisis.
State health officials have warned lawmakers that 38 rural hospitals across the state are in danger of imminent closure because of budget problems. Some of those hospitals are larger regional care centers, such as Greenwood Leflore Hospital.
Even the large metro hospitals are understaffed and struggling to provide adequate care due to rising costs. Physicians and other health care leaders are sounding the alarm about the entire state’s ability to maintain a reliable system of care.
Given the growing urgency of the crisis, Democratic leaders under the dome say they can’t wait around for their Republican counterparts to propose solutions.
“I feel silly trying to explain to (Republicans) why we need to do something about this quickly when the need is right there smacking them in the face every single day,” said Rep. Robert Johnson, the House Democratic leader. “These people have the best possible access to the best possible information about the state, and they’re ignoring it. They’re running away from the problem. The house is fully on fire right now, but it’s fine because Republicans say it’s not really burning.
“I don’t know what they’re waiting on, but this crisis needs to be addressed right now,” Johnson continued. “I don’t know where their plan is, but we have one.”
That plan, shared with Mississippi Today before legislation is filed in coming days, has two key components:
- A bill that would appropriate $150 million as a “lifeline” to rural hospitals. The state would send cash directly to the hospitals to help temporarily balance their budgets and fund health care services. Public hospitals that can demonstrate financial hardship would apply for grants from the new fund, which would be administered by the Department of Finance and Administration. This proposal would flow from several funding sources: $135 million from American Rescue Plan Act funds lawmakers haven’t yet spent; $13 million from the state’s Health Care Expendable Fund; and $2 million from the BP settlement fund.
- Several bills that would expand Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, as 39 other states have done. Numerous economists say Medicaid expansion would provide $1 billion in new revenue to the state and help hospitals better cover the rising costs of providing care to poor, working Mississippians. Many Democrats have filed bills to expand Medicaid for more than 10 years, but GOP leaders at the Capitol have deeply dug their heels in opposition to it, claiming without proof that the state cannot afford it and writing it off as a liberal policy of former President Barack Obama.
READ MORE: Mississippi leaving more than $1 billion per year on table by rejecting Medicaid expansion
Rep. John Hines, who authored the rural hospital lifeline bill, said the first bill is intended to help hospitals temporarily until Medicaid expansion, the more long-term solution, is passed. Johnson, who has fought for Medicaid expansion for several years, panned the legislative Republicans who have blocked it.
“The Black man who was president is far enough removed now for Republicans to wake up and realize that every single Mississippian — white, Black, Democrat, Republican — is losing money and might lose out on critical care because of this crisis,” Johnson said. “We’re leaving $1 billion on the table every year while our hospitals close and people die. It’s as simple as that.”
The Republican leaders at the Capitol, House Speaker Philip Gunn and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann, are at odds about how to meet the moment. And in the early days of the session, no Republican appears eager to move quickly to pass a hospital crisis fix.
Gunn, who along with Gov. Tate Reeves is directly responsible for the state’s resistance to Medicaid expansion, proposed in December a one-time, $50-$70 million appropriation for hospitals this year. That was panned by critics and even inspired a statewide newspaper column that bluntly asked: “Will closed hospitals be Gunn’s legacy, too?”
Hosemann, to his credit, has been the one Republican leader who has directly acknowledged the hospital crisis. In December, he said he sought solutions to the crisis “not just for next year, but for the next generation.” He floated several ideas, including expanding a Medicaid program for new mothers — an effort he successfully led in the Senate last year but was killed by Gunn and the House — and increasing Medicaid reimbursements to struggling hospitals.
Hosemann has long been one of few Republican leaders open to discussion of Medicaid expansion, but he said last month it’s not likely lawmakers will tackle that issue this year. He also said it’s not a cure-all.
“I don’t think that’s the answer,” Hosemann said in December. “Even if we had that expansion, (Greenwood Leflore) would not make it, it would still be short.”
After just the first week of the legislative session, key lawmakers and legislative observers are already repeating the refrain: “Don’t expect anything major to gain steam this year because it’s an election year.” Indeed, all 174 legislative seats and all eight statewide offices are up for grabs this November.
But that logic isn’t sitting well with Johnson and other Democratic leaders, particularly as the Mississippi hospital crisis worsens by the day.
“This is quite literally a matter of life and death, and we seem to be the only people in this building united behind providing relief for hospitals and health care for all Mississippians,” said Sen. Derrick Simmons, the Democratic leader of the Senate. “We’re going to push Republicans hard on this. We aren’t elected for three years and a vacation to Jackson during election years.”
Simmons continued: “We’ve got a plan. Here it is. ‘No’ is no longer an acceptable answer from the Republicans standing in the way of addressing this issue. If you don’t like it, and you have a better idea, then let’s hear what the plan is.”
READ MORE: Mississippi Today’s full coverage of the 2023 legislative session
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
‘Will you trust us?’: JPS plan for stricter cellphone policy makes some parents anxious
Superintendent Errick Greene wanted to be very clear with the roughly 50 parents who attended Thursday night’s community listening session: Jackson Public Schools already has a policy banning students from using cellphones at school.
But the leadership of Mississippi’s third-largest school district has decided that a new approach is in order, citing a series of incidents in recent years involving students using their cellphones to bully others, organize fights or text their parents inaccurate information about violence happening at or near their school.
“To be clear, it’s not the majority of our scholars, but I can’t look at a class and know who’s gonna be bullying today, who’s gonna be scheduling a meetup to cut up today,” Greene said toward the end of the hour-long meeting held at the JPS board room. “I can’t look at a group of scholars and say, ‘OK, yeah, you’re the one, let me take your phone, the rest of you can keep it.’”
Under the rewritten policy, students who take their phone out of their backpacks during the instructional day will lose it for five days for the first infraction, 10 days for the second and 45 days for the third. Currently, the longest the school will hold a phone is 10 days.
The Jackson school board is expected to consider the new policy at its meeting next week and the district hopes to implement the change when the new school year starts later this month, said Sherwin Johnson, the district’s communications director.
Students also currently have the option to pay up to a $25 fine to get their phone back, but the district wants to rescind that aspect of the policy.
“We’ve discovered that’s not equitable,” said Larrisa Harris, the JPS general counsel. “Not everybody has the resources to come and pay the fine.”
Support for the new policy among the parents who spoke at the listening session varied, but all had questions. How will students access the internet on their laptops if the WiFi is spotty at their school and they need to use their cellphone hotspot? If students are required to keep their phones in their backpacks during lunch, how will teachers prevent stealing? How will JPS enforce the ban on using cellphones on the bus?
One mother said she watches her daughter’s location while she rides the bus to Jim Hill High School so she knows her daughter made it safely.
“If they can’t have it on the bus, who’s gonna enforce that?” she said. “I’m just gonna be real, the bus driver got to drive.”
A common theme among parents was anxiety at the prospect of losing direct contact with their kids in the event of an emergency. A Pew Research survey found that most adults, regardless of political affiliation, support cellphone bans in middle and high school classes. But those who don’t say it’s because their child can use their phone during emergencies.
“If something happened, will we get an automatic alert to notify us? Because a lot of the time we see things on social media first,” said Ashley McIntyre, a mother of three JPS students. She attended the meeting with her eldest daughter, Aaliyah, who recently graduated from Powell Middle School.
Though JPS does have an alert system for parents, McIntyre said she didn’t know if it existed. She cited a bomb threat at Powell last year that she found out about because Aaliyah texted her, not through a school alert.
“We didn’t know what was going on, and she texted me, ‘Mom, I’m scared,’ so I went up there,” McIntyre said. “So that puts us on edge.”
Aaliyah said she uses her phone to text her mom and watch TikTok, but she feels like her classmates use their phones to be popular or to fit in. When a fight happens, she said many students pull out their phones to record instead of trying to get an adult who can stop it. Then the videos end up on Instagram pages dedicated to posting fights in JPS.
“Once the principal found out about the fight pages, they came around looking inside our videos and camera rolls,” she said. “It happened to me last year. They thought I had a fight on my phone.”
Toward the end of the meeting, Laketia Marshall-Thomas, the assistant superintendent for high schools, took the mic to respond to one parent who said she was concerned that older students would not come to school if they knew their phone could be taken.
“What we have seen is, it’s the older students—” Marshall-Thomas began.
“They are the problem,” someone from the audience chimed in.
“We’re not saying they cannot have them,” she continued. “We know that they have after school activities and they need to communicate with their moms … but we have had major, major issues with cellphones and issues that have even resulted in criminal outcomes for our scholars, but most importantly, our students … have experienced a lot of learning loss.”
While the district leadership did not go into detail about the criminal incidents, several pointed to instances where students have texted their parents inaccurate information, such as an unsubstantiated rumor there was a gun during a fight at Callaway High School or that a shooting outside Whitten Middle School occurred on school property.
“Having phones actually creates far more chaos than they help anyone,” Greene said.
While cellphones have been banned to varying degrees in U.S. schools for decades, youth mental health concerns have renewed interest in more widespread bans across the country. Cellphone and social media usage among school-aged kids is linked to negative mental health outcomes and instances of cyberbullying, research shows.
At least 11 states restrict or ban cellphone use in schools. After Mississippi’s youth mental health task force recommended that all school districts implement policies that limited cellphone and social media usage in classrooms, a bill that would’ve required school boards to create cellphone policies died during the legislative session. Still, several Mississippi school districts have passed their own policies, including Marshall County and Madison County.
Another concern about the ban was a belief among a couple of speakers at the meeting that cellphones can help parents hold the district accountable for misdeeds it may want to hide.
“I just saw a video today. It was not in JPS, but it was a child being yelled at by the teacher and had he not recorded it, his momma would have never known that this sweet lady that they go to church with is degrading her child like that,” one mother said.
Statements like these prompted responses from teachers and other parents who urged the skeptical attendees to be more trusting or to make sure the district has updated contact information for them in case school officials need to reach parents during an emergency.
“I think we have to trust the people watching over our children,” said one of the few fathers who spoke. “When I grew up, what the teacher said was gold.”
One teacher asked the audience, “Will you trust us?”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post ‘Will you trust us?’: JPS plan for stricter cellphone policy makes some parents anxious appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Centrist
The article presents a balanced report on Jackson Public Schools’ proposed stricter cellphone policy without taking a clear ideological stance. It fairly conveys the perspectives of school officials emphasizing discipline and safety, alongside parental concerns about communication and emergency access. The tone remains neutral, focusing on factual details such as policy changes, reasons behind them, and community reactions. While it includes some skepticism from parents and responses from district staff, the language does not endorse or oppose either side. Overall, the coverage adheres to neutral, factual reporting by presenting multiple viewpoints without editorializing.
Mississippi Today
Hospitals see danger in Medicaid spending cuts
Mississippi hospitals could lose up to $1 billion over the next decade under the sweeping, multitrillion-dollar tax and policy bill President Donald Trump signed into law last week, according to leaders at the Mississippi Hospital Association.
The leaders say the cuts could force some already-struggling rural hospitals to reduce services or close their doors.
The law includes the largest reduction in federal health and social safety net programs in history. It passed 218-214, with all Democrats voting against the measure and all but five Republicans voting for it.
In the short term, these cuts will make health care less accessible to poor Mississippians by making the eligibility requirements for Medicaid insurance stiffer, likely increasing people’s medical debt.
In the long run, the cuts could lead to worsening chronic health conditions such as diabetes and obesity for which Mississippi already leads the nation, and making private insurance more expensive for many people, experts say.
“We’ve got about a billion dollars that are potentially hanging in the balance over the next 10 years,” Mississippi Hospital Association President Richard Roberson said Wednesday during a panel discussion at his organization’s headquarters.
“If folks were being honest, the entire system depends on those rural hospitals,” he said.
Mississippi’s uninsured population could increase by 160,000 people as a combined result of the new law and the expiration of Biden-era enhanced subsidies that made marketplace insurance affordable – and which Trump is not expected to renew – according to KFF, a health policy research group.
That could make things even worse for those who are left on the marketplace plans.
“Younger, healthier people are going to leave the risk pool, and that’s going to mean it’s more expensive to insure the patients that remain,” said Lucy Dagneau, senior director of state and local campaigns at the American Cancer Society.
Among the biggest changes facing Medicaid-eligible patients are stiffer eligibility requirements, including proof of work. The new law requires able-bodied adults ages 19 to 64 to work, do community service or attend an educational program at least 80 hours a month to qualify for, or keep, Medicaid coverage and federal food aid.
Opponents say qualified recipients could be stripped of benefits if they lose a job or fail to complete paperwork attesting to their time commitment.
Georgia became the case study for work requirements with a program called Pathways to Coverage, which was touted as a conservative alternative to Medicaid expansion.
Ironically, the 54-year-old mechanic chosen by Georgia Gov. Brian Kemp to be the face of the program got so fed up with the work requirements he went from praising the program on television to saying “I’m done with it” after his benefits were allegedly cancelled twice due to red tape.
Roberson sent several letters to Mississippi’s congressional members in weeks leading up to the final vote on the sweeping federal legislation, sounding the alarm on what it would mean for hospitals and patients.
Among Roberson’s chief concerns is a change in the mechanism called state directed payments, which allows states to beef up Medicaid reimbursement rates – typically the lowest among insurance payors. The new law will reduce those enhanced rates to nearly as low as the Medicare rate, costing the state at least $500 million and putting rural hospitals in a bind, Roberson told Mississippi Today.
That change will happen over 10 years starting in 2028. That, in conjunction with the new law’s one-time payment program called the Rural Health Care Fund, means if the next few years look normal, it doesn’t mean Mississippi is safe, stakeholders warn.
“We’re going to have a sort of deceiving situation in Mississippi where we look a little flush with cash with the rural fund and the state directed payments in 2027 and 2028, and then all of a sudden our state directed payments start going down and that fund ends and then we’re going to start dipping,” said Leah Rupp Smith, vice president for policy and advocacy at the Mississippi Hospital Association.

Even with that buffer time, immediate changes are on the horizon for health care in Mississippi because of fear and uncertainty around ever-changing rules.
“Hospitals can’t budget when we have these one-off programs that start and stop and the rules change – and there’s a cost to administering a program like this,” Smith said.
Since hospitals are major employers – and they also provide a sense of safety for incoming businesses – their closure, especially in rural areas, affects not just patients but local economies and communities.
U.S. Rep. Bennie Thompson is the only Democrat in Mississippi’s congressional delegation. He voted against the bill, while the state’s two Republican senators and three Republican House members voted for it. Thompson said in a statement that the new law does not bode well for the Delta, one of the poorest regions in the U.S.
“For my district, this means closed hospitals, nursing homes, families struggling to afford groceries, and educational opportunities deferred,” Thompson said. “Republicans’ priorities are very simple: tax cuts for (the) wealthy and nothing for the people who make this country work.”
While still colloquially referred to as the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, the name was changed by Democrats invoking a maneuver that has been used by lawmakers in both chambers to oppose a bill on principle.
“Democrats are forcing Republicans to delete their farcical bill name,” Senate Democratic Leader Charles Schumer of New York said in a statement. “Nothing about this bill is beautiful — it’s a betrayal to American families and it’s undeserving of such a stupid name.”
The law is expected to add at least $3.3 trillion to the nation’s debt over the next 10 years, according to the most recent estimate from the Congressional Budget Office.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Hospitals see danger in Medicaid spending cuts appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article reports on the negative impacts of a major federal tax and policy bill on Medicaid funding and rural hospitals in Mississippi. While it presents factual details and statements from stakeholders, the tone and framing emphasize the harmful consequences for vulnerable populations and health care access, aligning with concerns typically raised by center-left perspectives. The article highlights opposition by Democrats and critiques the bill’s priorities, particularly its effect on poor and rural communities, suggesting sympathy toward social safety net preservation. However, it maintains mostly factual reporting without overt partisan language, resulting in a moderate center-left bias.
Crooked Letter Sports Podcast
Podcast: The Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame Class of ’25
The MSHOF will induct eight new members on Aug 2. Rick Cleveland has covered them all and he and son Tyler talk about what makes them all special.
Stream all episodes here.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Podcast: The Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame Class of '25 appeared first on mississippitoday.org
-
The Center Square6 days ago
Here are the violent criminals Judge Murphy tried to block from deportation | Massachusetts
-
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days ago
Woman arrested in Morgantown McDonald’s parking lot
-
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days ago
Cruising into Louisville: Viking cruise ship docks downtown on Ohio River
-
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed5 days ago
Learning loss after Helene in Western NC school districts
-
News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days ago
The six-year saga of two cannabis facility licenses
-
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days ago
Cell, no! After Two Years of Debate, Schools Get Months to Ban Phones
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed6 days ago
Arkansas and Oklahoma teams deploy to aid Texas floods
-
News from the South - South Carolina News Feed7 days ago
Keep your pets safe during hurricane season: experts share advice on go-bags and safe spaces