Mississippi Today
Days after Rankin’s ‘Goon Squad’ tortured two men, supervisors gave the sheriff a pay boost
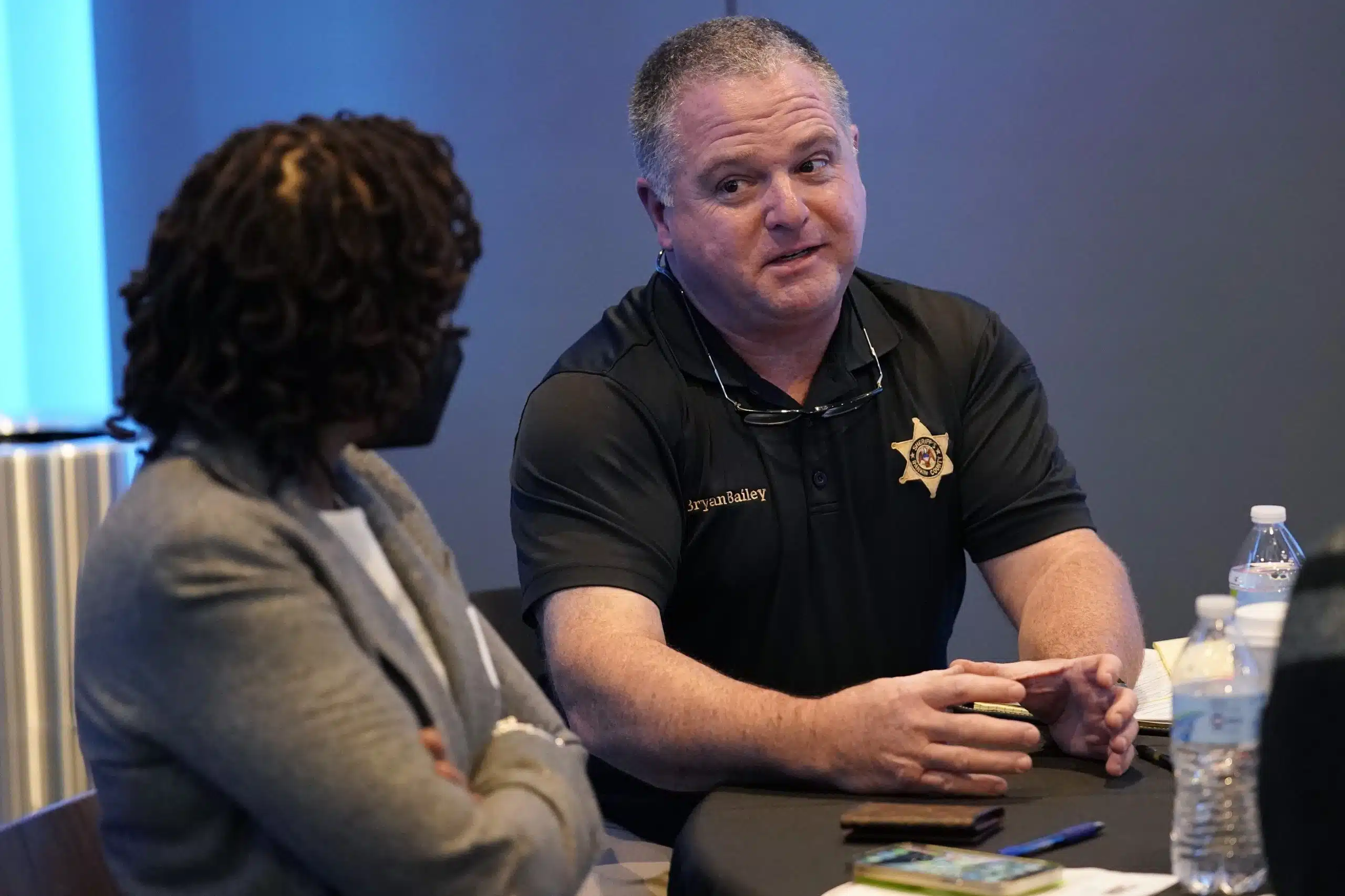

A dozen days after five Rankin County deputies known as the “Goon Squad” tortured, tased and sexually abused two Black men, the Rankin County Board of Supervisors gave Sheriff Bryan Bailey a $21,059 raise.
On Feb. 6, supervisors officially appointed him director of the Safe Room, a task he has carried out for years.
This means Bailey, a Republican incumbent unopposed in the Nov. 7 election, now earns $140,059 — what appears to be the highest pay for a Mississippi sheriff. It’s far more than the $122,160 salary Gov. Tate Reeves collects.
State Rep. Becky Currie, R-Brookhaven, said she believes the bonus circumvented the will of the state Legislature, which capped sheriffs’ salaries in counties of more than 100,000 population at $119,000. “We had just given sheriffs a big raise,” she said. “It’s just not right.”
The state’s legislative watchdog told her the raise was legal, but she said she still thinks the act “takes advantage of the taxpayers. I’m shocked the board of supervisors went along with it.”
Greta Kemp Martin, the Democratic candidate for Mississippi attorney general, said Sheriff Bailey has “proven himself to be unfit for the job” and should resign.
In addition to the Goon Squad’s actions, she pointed to reporting by The New York Times and Mississippi Today, which revealed the sheriff repeatedly used grand jury subpoenas to gather the text messages and phone call logs of his married girlfriend and a man he suspected she was seeing.
Before giving Bailey the raise, Rankin County supervisors sought an attorney general’s opinion, wanting to know if the sheriff could also be paid “for overseeing the FEMA safe room,” another name for the county’s severe weather shelter.
A written opinion from the attorney general’s office, which isn’t legally binding, concluded state law limiting the sheriff’s salary “would not apply to the compensation for his or her second job.”
What Rankin County officials didn’t mention to the attorney general’s office was that the sheriff had been in charge of the Safe Room for years.
The 16,400-square-foot facility hosts far more events and parties than storm evacuations. Most of the Rankin County policies for the Safe Room, built at a cost of $2.8 million to taxpayers, center on how groups can use the room for events ($50 an hour, plus a $250 deposit).
“Event themes must be approved by the Rankin County Sheriff and-or his designee and must be consistent with promoting community culture, recreation and education,” the policies read. “The Rankin County Sheriff’s Department accepts cash, checks and purchase orders made payable to Rankin County.”
U.S. Rep. Bennie Thompson, D-Miss., past chairman of the House Committee on Homeland Security, noted that the position over the Safe Room is usually held by a county’s emergency management director rather than a sheriff.
Brian Adam serves as emergency management director for Hancock County, which has five shelters. When those shelters open to the public, the Red Cross operates them, he said.
He doesn’t know of any sheriffs who manage shelters.
Asked why the Rankin County sheriff was getting paid now for a task he had done for years, Craig Slay, an attorney for the supervisors, responded that Bailey undertook that responsibility “voluntarily” and it “does not fall within his duties as Sheriff.”
While Bailey’s pay has skyrocketed, the number of employees at the Rankin County Sheriff’s Department is falling.
Current and former deputies say morale is plummeting, and more than two dozen people have left the office in recent months. They say they feel they lack the support of the sheriff, who said from now on, he had to “verify” their work.
After Rankin County Undersheriff Paul Holley resigned Oct. 2, Bailey sent out an email asking those in the office to “be patient during this transition. I have always tried to be a good leader but have my shortcomings. …
“I want to recover all that has been taken from us, especially our name and reputation. I cannot do it alone. I need our team to do it. If we all do our part and do our job, we can regain what was stolen from us.”
Weeks after five deputies and a Richland police officer pleaded guilty to torturing two Black men and planting a gun and drugs on them, citizens from the community appeared before the county supervisors.
“Those who are supposed to protect and serve have been serving out a brand of justice that is outside the boundaries of human dignity and decency,” resident Joe Brazeal told supervisors. “How long do you really think this has really been going on in our county?”
Someone in the audience answered, “Decades.”
Brazeal called for an investigation “going back as far back and as long ago as these officers who were carrying a badge.”
He asked the supervisors, “How many are incarcerated now or have been banished from this county because of planted evidence? This is your responsibility. Some of you were on watch.”
Supervisor Steve Gaines responded that the deputies’ crimes surprised him. “I’m sorry this happened,” he said. “I believe the sheriff is sorry this happened. Let’s respect our law enforcement and not let a few bad apples ruin everything.”
In response to those calling for Bailey’s resignation, Slay told the crowd that when people called on supervisors to remove the sheriff, those calls should go to the governor.
Mississippi law gives the governor the power to remove a county elected official if he or she receives a petition of 30 percent or more of the qualified voters.
“This board does not have the power to remove any county elected official,” Slay told the audience.
Bailey, first elected a dozen years ago, has rejected calls to resign. At a press conference following the officers’ guilty pleas, he denied having any prior knowledge of the deputies’ actions or even the existence of the Goon Squad, despite the fact that challenge coins for the Goon Squad were stamped with the seal of the Rankin County Sheriff’s Department.
He blamed his deputies for lying to him. “The only thing I’m guilty of is trusting grown men that swore an oath to do their job correctly,” he said. “I’m guilty of that.”
Instead, he blamed others at his office. “The complaint has to come in,” he said. “The reports have to come in. Something has to come in that I’ve been notified. That’s what I’ve got supervisors for.”
In response to questions about the crimes carried out by his deputies, the sheriff told reporters, “The system works.”
He said investigators for the Mississippi Bureau of Investigation “came in. They saw the red flags. Today, we have five former deputies in jail because they [MBI] came in and did their job.”
Greta Kemp Martin, whose father serves as police chief for the town of Tishomingo, said if Bailey had taken full responsibility for what happened, she might feel differently.
“Kicking the can to his supervisors is cowardly,” she said. “This was more than roughing up someone. This was torture.”
Martin, whose grandfathers also worked in law enforcement, said what the Goon Squad did “puts good cops at risk, because it deflates the public trust.”
Ilyssa Daly examines the power of sheriffs’ offices in Mississippi as part of The Times’s Local Investigations Fellowship. Jerry Mitchell, co-founder of the Mississippi Center for Investigative Reporting that’s now part of Mississippi Today, is an investigative reporter who has examined civil rights-era cold murder cases in the state for more than 30 years.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Mississippi school superintendents indicted on fraud charges
The superintendents for Leake County and Hollandale school districts and a consultant have been indicted on four federal counts of conspiracy to commit embezzlement, theft and bribery.
According to the indictment, Earl Joe Nelson, while superintendent of Clarksdale Municipal School District and now Leake County School District, and Mario D. Willis, as superintendent of Hollandale School District, allegedly paid each other tens of thousands of dollars in school funds for consultant services that were never rendered from November 2021 until at least June 2023.
Additionally, the duo is accused of stealing U.S. Department of Education funds that were intended for their respective districts.
A St. Louis-based consultant and teacher, Moneka M. Smith-Taylor, has also been indicted on bribery charges in connection with the case. She allegedly received more than $250,000 from Willis for consulting services that were never provided over the course of two years.
She returned part of that money to Willis in the form of a cash kickback in return for the consulting contract, the indictment says.
A spokesperson for the Mississippi State Department of Education directed Mississippi Today to local school boards, who make personnel decisions for their respective districts, for comment.
The job status of the two superintendents is unclear. District officials could not be reached by presstime, but Willis is still listed as the superintendent of Hollandale School District and Nelson is still listed as the superintendent of Leake County School District in the state education department’s online directory.
It’s also unclear whether the defendants have a lawyer who could speak on their behalf.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Mississippi school superintendents indicted on fraud charges appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Centrist
The article reports on the indictment of two Mississippi school superintendents and a consultant on federal fraud charges in a straightforward, factual manner. It presents the legal allegations without editorializing or taking a stance. The language is neutral and focused on relaying verified information from the indictment and official sources, without suggesting guilt or innocence. There is no evident ideological framing or advocacy; rather, the piece sticks to reporting the details of the case and the status of the individuals involved. Thus, the article adheres to objective journalistic standards without discernible political bias.
Mississippi Today
Defendant in auditor’s ‘second largest’ embezzlement case in history goes free
Four years ago, agents from the state auditor’s office arrested Tunica nonprofit operator Mardis Jones in what the office trumpeted as the second-largest embezzlement case in its history and demanded Jones return over $1 million to the state.
The charges accused Jones of stealing $750,000 from a home rehabilitation program he was supposed to be administering while turning away needy rural residents living in crumbling houses.
But his defense attorney attacked holes in the case, and last month, a local jury found Jones not guilty of the criminal charges. Now, the state has made no indication it will bring a civil case to try to claw back the money from him.
Jones’ nonprofit Tunica County Housing Inc. secured a subcontract with the county through the North Delta Regional Housing Authority in 2014 to run the county’s home rehabilitation program funded with casino revenue. For his work, vetting applications and managing expenses, Jones earned $12,000 a month.
At the core of the criminal case were “strange money transfers” and a finding that several of the people whose applications for home rehab were approved allegedly never received any repairs to their homes. According to the auditor’s office, investigators found less than 20% of the nearly $2 million Jones’ nonprofit received went to the contractors working to rehab homes.
“Once again, an arm of government trusted a private organization to run a government program, and a large percentage of the program’s spending was flat out stolen,” State Auditor Shad White said in a press release after the arrest.
Attorney General Lynn Fitch echoed White, saying, “These funds – hundreds of thousands of dollars – were meant to help the elderly, handicapped, and poverty stricken. But the funds never got to the vulnerable citizens who needed it most.”
Jones’ lawyer Carlos Tanner explained to Mississippi Today that the program operated with an extreme backlog, and that “some of the people they were claiming didn’t get their houses done actually did” by the time the trial was held this year.
The program was poorly administered, Tanner said, meaning that even if a person’s application was approved and a rehab contract prepared, county officials could direct Jones to put someone else’s repair job ahead of his or hers.
“But just because it was run like a first weekend lemonade stand does not mean Mardis Jones stole money,” Tanner said.
Tanner said the investigators gathered paltry evidence, only looking at details that fit their narrative. While Jones did earn a large salary through his contract, Tanner said prosecutors never presented evidence that Jones converted money that was supposed to be used on home rehabilitation to his personal use.
Investigators got a warrant to seize Jones’ electronics, Tanner said, but “they never bothered to search it.”
“The two OSA (Office of the State Auditor) officials who were running the investigation, I questioned them about it during trial, and neither of them could tell me where the computer was, where the phone was, or what the contents were,” Tanner said.
Jacob Walters, a spokesperson for the auditor’s office, defended the way the investigators handled the case, saying, “The state auditor’s office is never going to turn a case we investigated over to a prosecutor unless we’re fully confident in the work that we did.”
At the time the auditor’s office announced the Jones arrest, it also said it delivered a demand letter ordering Jones to repay over $1 million, the money it alleged he stole plus interest and investigative expenses.
It’s up to the attorney general or local district attorney to decide how to prosecute auditor investigations, or in Jones’ case, what happens to the civil demand now that a jury found him not guilty in the criminal case.
When a person receives a demand alongside his or her arrest, regardless of what happens with criminal charges, the claw back can be enforced through civil litigation — much like the case against several defendants in a stunning Mississippi Department of Human Services fraud case, which began in 2020 and has yet to be resolved. Walters said the demand against Jones is still the office’s next-largest in history, second only to the welfare scandal.
The government might choose to pursue civil litigation, even if criminal prosecution is unsuccessful, because there is a lower burden of proof to win civil cases.
But the attorney general’s office told Mississippi Today last month that it had not received the Jones demand letter from the auditor, meaning it has nothing left to enforce.
Walters said the auditor’s office sent the letter along with the case file four years ago, but that with a turnover in attorneys prosecuting the case, the auditor had to resend the file last year. If the attorney general’s office no longer possesses the demand document, Walters said, “it’s an incredibly easy problem to resolve.”
“Just reach out to us with a single phone call or email and we can get it to you,” Walters said.
After the interview, the auditor’s office sent the demand letter by email, and the attorney general’s office confirmed it was received.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Defendant in auditor’s ‘second largest’ embezzlement case in history goes free appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Centrist
This article presents a factual and balanced account of the embezzlement case involving Mardis Jones without overt ideological framing. It reports statements from both government officials criticizing the alleged misconduct and the defense attorney’s rebuttals, highlighting weaknesses in the prosecution’s case. The tone remains neutral, avoiding partisan language or loaded terms. It focuses on the procedural aspects, jury verdict, and potential civil actions without advocating for a political viewpoint. The article provides context from multiple perspectives, adhering to objective reporting rather than promoting a specific ideological stance.
Mississippi Today
JPD called ICE on Miss. father, who faces deportation
Kerlin Moreno-Orellana is facing deportation over a misdemeanor charge that usually results in a fine. He was picked up by Immigration and Custom Enforcement agents on Thursday morning and transferred from the Raymond Detention Center to an ICE detention center in Louisiana.
On June 16, Jackson police arrested Moreno-Orellana, a contractor, in south Jackson along with his employer Christy Parker, who was showing him one of the old properties she worked on. Both were charged with illegal dumping, but Parker claims they did not dump anything.
After detaining them, Jackson police called a local TV outlet, 16 WAPT News, to come shoot the scene of the arrest. Parker said they were kept in the police car for over an hour, waiting for the news crew. The WAPT newsroom explained that the Jackson police routinely asks them to cover arrests related to illegal dumping or other high profile cases, in order to “dissuade people.”
Once at the station, the Jackson Police Department called ICE on the 35-year-old father of four, who had worker authorization documents. He was kept in jail overnight, while Parker was released hours after their arrest.
“He didn’t do anything I didn’t do,” Parker said in an interview with Mississippi Today. “But because I’m white, I’m here?”
A municipal court ordered Moreno-Orellana’s release the day after, but ICE placed a detainer on him – a formal request to keep a non-citizen in custody for 48 hours, while the agency investigates. It is not an arrest warrant. However, a state law passed in 2016 mandates that all local law enforcement comply with ICE detainers placed on undocumented immigrants.
“What we are doing today is no different than what we’ve always operated when the detainer is sent by ICE to the jail,” said Hinds County Sheriff Tyree Jones. “Nothing has changed.”
While the Hinds County Sheriff’s Department has historically worked with ICE, Jackson police actively seeking out ICE to detain people is a fairly recent occurrence, said Mississippi-based immigration attorney Jeremy Litton. Jackson police did not respond to a request for comment.
ICE picked up Moreno-Orellana with hours left on his detainer, and he now faces deportation. ICE spokesperson Lindsay Williams said that Moreno-Orellana violated the conditions of a past bond agreement by being arrested for a new charge. He had already spent over a month in ICE custody in 2019, after getting arrested by park rangers for speeding and driving without a license.
Still, a minor misdemeanor charge – like illegal dumping – is normally insufficient for ICE to threaten to deport someone with worker authorization paperwork. Removal of a person with documentation is usually justified if the person is deemed a threat to public safety or national security.
“This does feel like a result of the elevated focus on deporting people from the Trump administration,” said Matt Steffey, professor at the Mississippi College School of Law.
Moreno-Orellana, who is from Honduras, has three boys and a girl, the youngest of whom is less than a year old. He has lived in Mississippi for over 16 years. Colleagues describe him as a valuable worker and a good friend.
“All he ever did was work and go home,” Parker said. “He was always willing to give somebody help.”
The possibility of his deportation is leaving his family in a precarious situation. Moreno-Orellana was the sole breadwinner of the family, and his wife worries about sustaining herself and their children without him.
“I’ve always dedicated myself to taking care of my kids at home, and he’s the one who brings food to the table,” his wife said in Spanish. “I’m afraid of staying, being without my children’s father. Not so much for me, but because they need him.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post JPD called ICE on Miss. father, who faces deportation appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article primarily reports on the actions of law enforcement and ICE with a focus on the human impact of deportation on a Mississippi family. While the reporting remains factual, the framing and choice of quotes highlight concerns about racial disparities, immigration enforcement policies, and potential overreach by authorities, suggesting a subtle critical tone toward current immigration enforcement practices. The article’s emphasis on the family’s hardship and the legal nuances involved positions it slightly left-of-center, sympathetic to immigrant rights and critical of aggressive ICE actions. However, it avoids overt ideological language, maintaining largely balanced coverage.
-
News from the South - Tennessee News Feed6 days ago
Thieves take thousands of dollars in equipment from Union County Soccer League
-
Mississippi Today4 days ago
Defendant in auditor’s ‘second largest’ embezzlement case in history goes free
-
News from the South - Texas News Feed6 days ago
Robert Nichols to retire from Texas Senate
-
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed6 days ago
3 lawsuits filed against CVS, Louisiana AG announces
-
News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days ago
Residents provide feedback in Kearney Street Corridor redevelopment meeting
-
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News 5 NOW at 12:30pm | June 24, 2025
-
The Conversation6 days ago
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory will help astronomers investigate dark matter, continuing the legacy of its pioneering namesake
-
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
DeSantis signs bill into law that ensures public access to Florida beaches | Florida