CNSA
Jeffrey Gillis-Davis, Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis
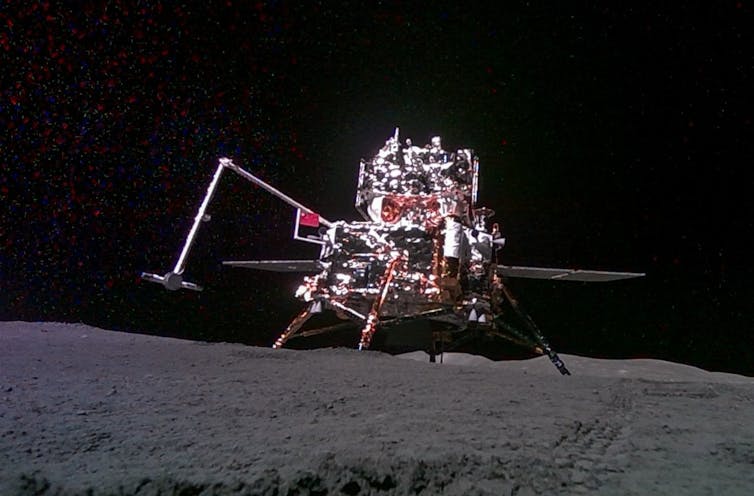
China achieved a historic feat by bringing back the first-ever sample from the lunar far side in June 2024. It’s moon lander, Chang’e 6, used a robotic scoop and drill to collect approximately 5 pounds (2 kilograms) of rocks and soil. These samples came back to Earth on June 25, 2024.
Chang’e 6 built off the accomplishments of two previous Chinese missions: Chang’e 4, which soft-landed on the far side of the Moon and used a rover to explore the surface, and Chang’e 5, which returned samples from the Moon’s near side.
Scientists expect the Chang’e 6 samples to deliver not only key geologic knowledge about the Moon but also improve their understanding of Earth and the solar system’s early history.
Lunar scientists like myself have been fascinated with the far side of the Moon since the Soviet Union’s Luna 3 mission in 1959, which revealed that the Moon’s far side looks very different from its near side.
The far side of the Moon
Because the same side of the Moon always faces toward Earth, you can see the far side only with spacecraft. The far side is not permanently dark – it alternates between two weeks of daylight and two weeks of night, just like any location on the Moon.
Images taken by spacecraft show that about a third of the Moon’s near-side surface is made up of dark, smooth plains, while only about 1% of the far side has these plains.
These dark plains were once volcanic lava flows, similar to those found on Earth in Hawaii, eastern Washington and India.
Images taken from lunar orbit tell researchers that these plains once had volcanic vents, cones, domes, collapsed pits and channels.
Only the Chang’e 4 and Chang’e 6 missions have landed on the lunar far side, while 25 spacecraft have successfully soft-landed on the near side. A landed mission on the far side is more difficult because mission control cannot directly see or talk with the spacecraft. So what’s needed is a second spacecraft to relay information between the lander and Earth. China used its orbiting satellite Queqiao-2, which was launched in March 2024.
Chang’e 6’s touchdown
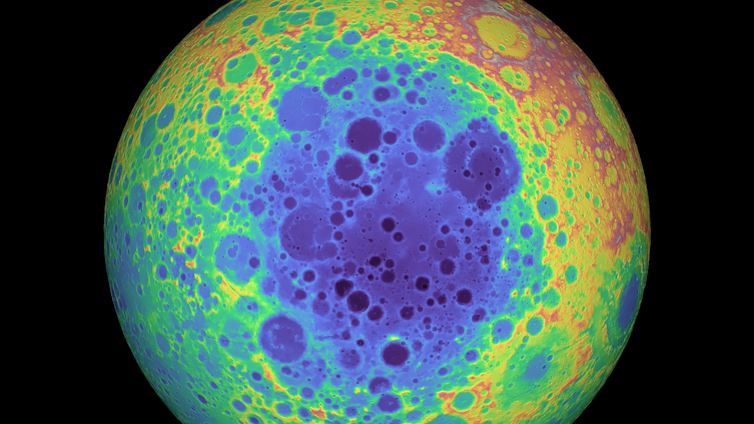
On June 6, 2024, Chang’e 6 landed within the colossal South Pole-Aitken basin, which is about 1,550 miles (2,500 km) wide and 5 miles (8 km) deep. It’s the solar system’s largest impact structure: a bowl-shaped feature formed when an asteroid collides with a body, causing an enormous explosion.
NASA/GSFC/University of Arizona
Superimposed on top of South Pole-Aitkin is a slightly younger and much smaller impact structure called the Apollo basin, about 308 miles (492 km) in diameter.
Impact basins expose the Moon’s deep interior like a drill core. For instance, the impact that created the South Pole-Aitkin basin may have removed part of the Moon’s crust, exposing materials deep inside the Moon – up to 62 miles (100 km) down. The subsequent Apollo impact would have then removed even more material. So, the returned samples will likely contain some rocks that are different from those in the current sample collection.
Chang’e 6 landed here on some of the sparse, far-side volcanic deposits. Analyzing the composition of the volcanic rocks Chang’e 6 brought back might help researchers figure out why the near side has so many more volcanic deposits. Scientists will also be able to compare the ages of these far-side rocks with rocks from volcanic eruptions on the near side that took place about 3.9 to 3.2 billion years ago.
Measuring the rocks’ actual ages will help scientists refine other methods, such as crater counting, that are used to estimate the age of surface formations on planets.
Since planet surfaces accumulate more craters the longer they’re around, researchers can estimate a planetary surface’s age by comparing the number of craters they can count to those generated by a simulated model. But crater counting isn’t very accurate – having actual rock samples can help researchers figure out how to improve these methods.
Uncovering secrets from the Moon’s molten past
Researchers theorize that the Moon, along with some rocky planets, used to be almost completely molten. So for a brief period of time early in its history, the Moon was just lava with little or no solid rock.
Chang’e 6’s landing site could contain materials from the Moon’s mantle – the layer beneath its crust. These samples could help scientists understand how the Moon evolved from a magma ocean to having geologic layers – a solidified crust, mantle and core.
Data from these samples could also provide clues about Earth’s evolution in the last stages of planetary formation. Scientists predict that about 4 billion years ago, lots of asteroids and comets rained down on rocky planets like Earth. We call this period the “lunar cataclysm” period. Studying certain rocks from crater impacts on the Moon could help scientists learn more about this era.
Since the South Pole-Aitkin basin is the oldest well-preserved structure on the Moon, it could hold evidence about whether the number of basin-forming impacts occurred over a longer period of time, like 500 million years, or a shorter period, like 200 million years. Knowing the timescale would help gauge the intensity of impacts during the solar system’s formation.
A scientific gift from the far side
Extraterrestrial materials – such as samples from the Moon, Mars, asteroids and comets – are gifts that keep on giving.
Scientists will curate and maintain these samples in laboratories to keep them pristine. This process will distribute some of the precious samples for analyses with state-of-the-art equipment. The rest will be stored for future generations of scientists to explore new questions that emerge decades from now.
Science makes the most progress when scientists share ideas, data and samples. At the end of 2023, the China National Space Administration made the samples from Chang’e 5 available to a set of international researchers. I expect to see a similar sample-sharing program for the Chang’e 6 samples.
This sharing, however, doesn’t go both ways. NASA cannot directly share the samples they curate with Chinese researchers because of the Wolf Amendment, which bars NASA from using funds to collaborate with China on any programs.
China’s future lunar exploration plans include the Chang’e 7 and 8 missions, planned for 2026 and 2028, respectively. These missions will land at the south pole to search for water ice, carbon dioxide ice – also known as dry ice – and methane in an ice form. NASA’s recently canceled VIPER rover had similar goals. These missions will help China figure out where to put its International Lunar Research Station, which is planned for 2030.
Jeffrey Gillis-Davis, Research Professor of Physics, Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.