Mississippi Today
Gov. Tate Reeves refuses to answer question about returning campaign donations tied to welfare scandal

RAYMOND — Gov. Tate Reeves refused to answer a question Wednesday about why he has not fulfilled a pledge to give away campaign donations from people who have pleaded guilty to multiple state charges involving Mississippi’s massive welfare scandal.
The first-term Republican governor running for reelection told reporters at a Hinds County event that he will eventually donate at least $6,000 that he received from Nancy and Zach New, two central figures in the scandal, to a charity once the ongoing criminal and civil cases involving how federal welfare funds were misspent have concluded.
But Reeves, at the same event, ignored a question from Mississippi Today seeking to clarify why, exactly, he’s waiting for the litigation to conclude to return the funds when the News pleaded guilty to multiple criminal charges at the federal and state levels more than a year ago.
“… You don’t get to follow around and ask the governor questions,” Reeves said in a tirade about Mississippi Today, refusing to answer the original question and several follow-ups.
Note: Audio of Reeves’ full response can be found at the bottom of this article.
In April 2022, the News brokered a plea deal with federal and state prosecutors, where the two defendants pleaded guilty to counts of bribing a public official, fraud against the government and wire fraud in exchange for cooperating with federal investigators.
The ongoing investigations by state and federal officials are unlikely to change the News’ guilty status.
The impetus for lingering questions about their donations to the governor stems from a 2020 press conference Reeves conducted, where he promised to place the contributions in a separate bank account from his primary campaign accounts.
But Reeves admitted on Wednesday that he had not transferred that money into a separate account, and it remains stowed away in his campaign coffers that total more than $9 million.
“It currently continues to be in the same account,” Reeves said in response to a WJTV reporter’s question. “We have probably five or six different accounts situated through Friends of Tate Reeves as well as Tate for Governor, and those monies, $9,000 or somewhere in that range, will be refunded at the appropriate time.”
The News also pleaded guilty to separate federal charges that involved bilking millions in taxpayer funds for their now-shuttered private school — the same private school Reeves showcased in a 2019 campaign ad.
Reeves’ campaign has reused the 2019 campaign footage in recent ads for his current bid for the Governor’s Mansion.
The governor on Wednesday criticized the press for asking why he would continue using footage from a school previously operated by people who have pleaded guilty to several crimes. Still, he ultimately said his campaign decided to include the video because it made for “a good picture.”
“I presume that the fact that those videos were shot over five years ago, and for whatever reason, I guess whoever did the editing decided that it was a good picture,” Reeves said. “And that’s the reason they put it in the campaign ad.”
Democratic gubernatorial candidate Brandon Presley has continued to attack the governor for his connections to people caught up in the scandal and for failing to adequately provide oversight to the state’s welfare agency during the eight years he served as lieutenant governor.
Presley again criticized Reeves at a campaign event in Tupelo on Thursday, though the governor has not been charged with any crime and has denied taking any part in the scandal.
Note: Click below to listen to the audio of the May 31 interview with Gov. Tate Reeves. WJTV senior political reporter Richard Lake and Mississippi Today’s Taylor Vance were the two reporters asking questions.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
PSC moves toward placing Holly Springs utility into receivership
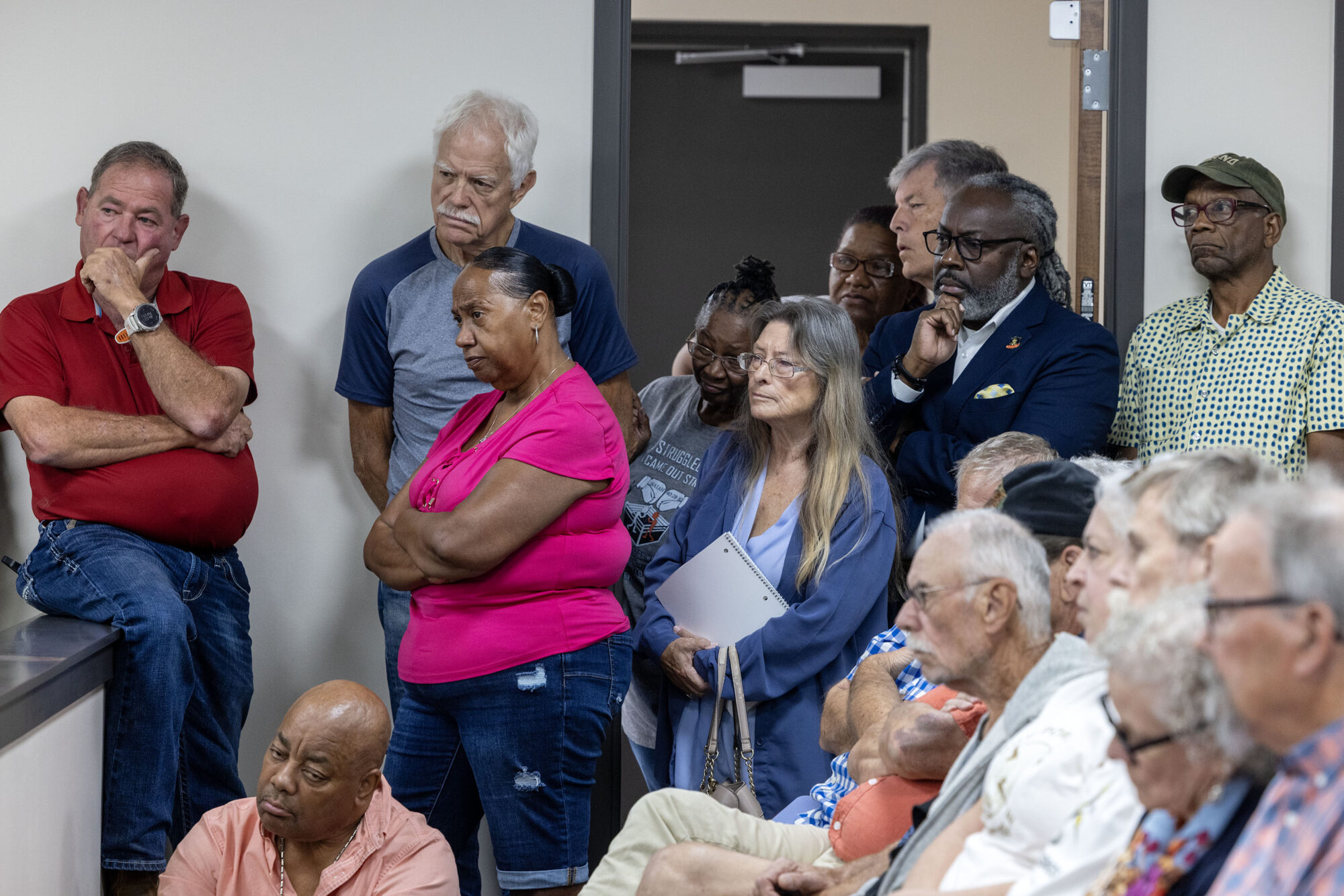
NEW ALBANY — After five hours in a courtroom where attendees struggled to find standing room, the Mississippi Public Service Commission voted to petition a judge to put the Holly Springs Utility Department into a receivership.
The PSC held the hearing Thursday about a half hour drive west from Holly Springs in New Albany, known as “The Fair and Friendly City.” Throughout the proceedings, members of the PSC, its consultants and Holly Springs officials emphasized there was no precedent for what was going on.
The city of Holly Springs has provided electricity through a contract with the Tennessee Valley Authority since 1935. It serves about 12,000 customers, most of whom live outside the city limits. While current and past city officials say the utility’s issues are a result of financial negligence over many years, the service failures hit a boiling point during a 2023 ice storm where customers saw outages that lasted roughly two weeks as well as power surges that broke their appliances.
Those living in the service area say those issues still occur periodically, in addition to infrequent and inaccurate billing.
“I moved to Marshall County in 2020 as a place for retirement for my husband and I, and it’s been a nightmare for five years,” customer Monica Wright told the PSC at Thursday’s hearing. “We’ve replaced every electronic device we own, every appliance, our well pump and our septic pumps. It has financially broke us.
“We’re living on prayers and promises, and we need your help today.”

Another customer, Roscoe Sitgger of Michigan City, said he recently received a series of monthly bills between $500 and $600.
Following a scathing July report by Silverpoint Consulting that found Holly Springs is “incapable” of running the utility, the three-member PSC voted unanimously on Thursday to determine the city isn’t providing “reasonably adequate service” to its customers. That language comes from a 2024 state bill that gave the commission authority to investigate the utility.
The bill gives a pathway for temporarily removing the utility’s control from the city, allowing the PSC to petition a chancery judge to place the department into the hands of a third party. The PSC voted unanimously to do just that.

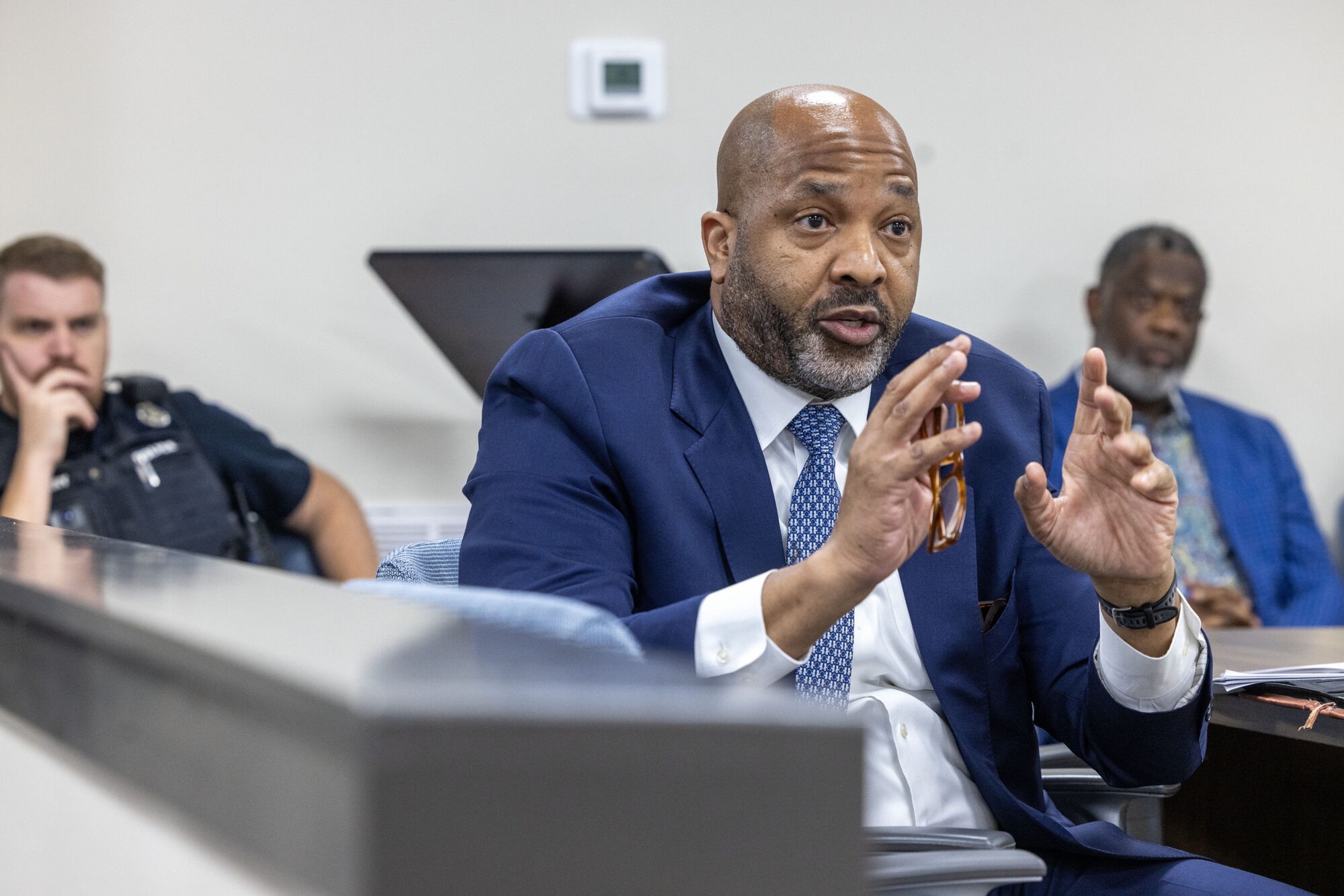
Thursday’s hearing gave the commission its first chance to direct official questions at Holly Springs representatives. Newly elected Mayor Charles Terry, utility General Manager Wayne Jones and City Attorney John Keith Perry fielded an array of criticism from the PSC. In his rebuttal, Perry suggested that any solution — whether a receivership or selling the utility — would take time to implement, and requested 24 months for the city to make incremental improvements. Audience members shouted, “No!” as Perry spoke.
“We are in a crisis now,” responded Northern District Public Service Commissioner Chris Brown. “To try to turn the corner in incremental steps is going to be almost impossible.”

It’s unclear how much it would cost to fix the department’s long list of ailments. In 2023, TVPPA — a nonprofit that represents TVA’s local partners — estimated Holly Springs needs over $10 million just to restore its rights-of-way, and as much as $15 million to fix its substations. The department owes another $10 million in debt to TVA as well as its contractors, Brown said.
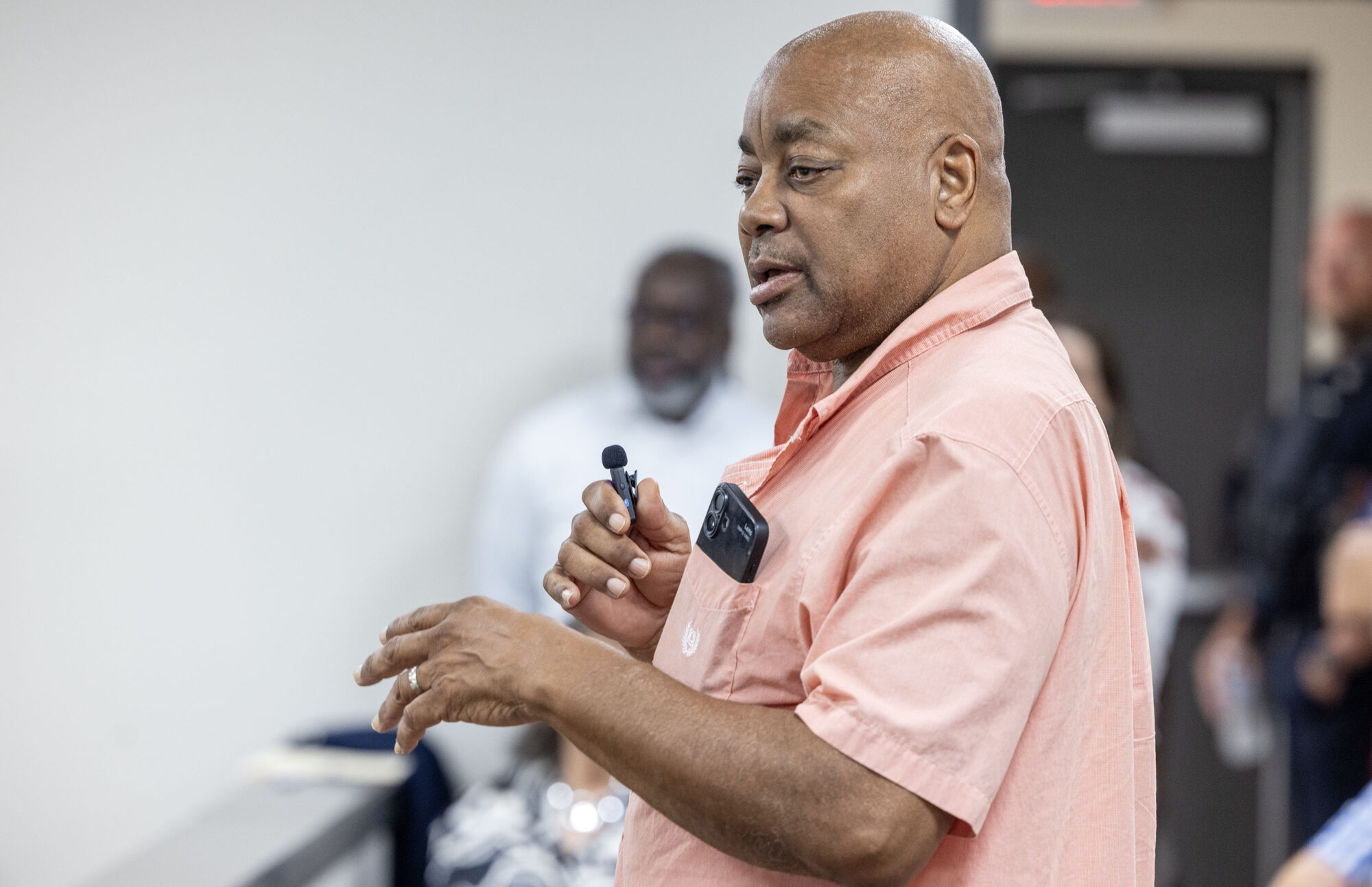
“The city is holding back the growth of the county,” said Republican Sen. Neil Whaley of Potts Camp, who passionately criticized the Holly Springs officials sitting a few feet away. “You’ve got to do better, you’ve got to realize you’re holding these people hostage, and it’s not right and it’s not fair… They are being represented by people who do not care about them as long as the bill is paid.”
In determining next steps, Silverpoint Principal Stephanie Vavro told the PSC it may be hard to find someone willing to serve as receiver for the utility department, make significant investments and then hand the keys back to the city. The 2024 bill, Vavro said, doesn’t limit options to a receivership, and alternatives could include condemning the utility or finding a nearby utility to buy the service area.
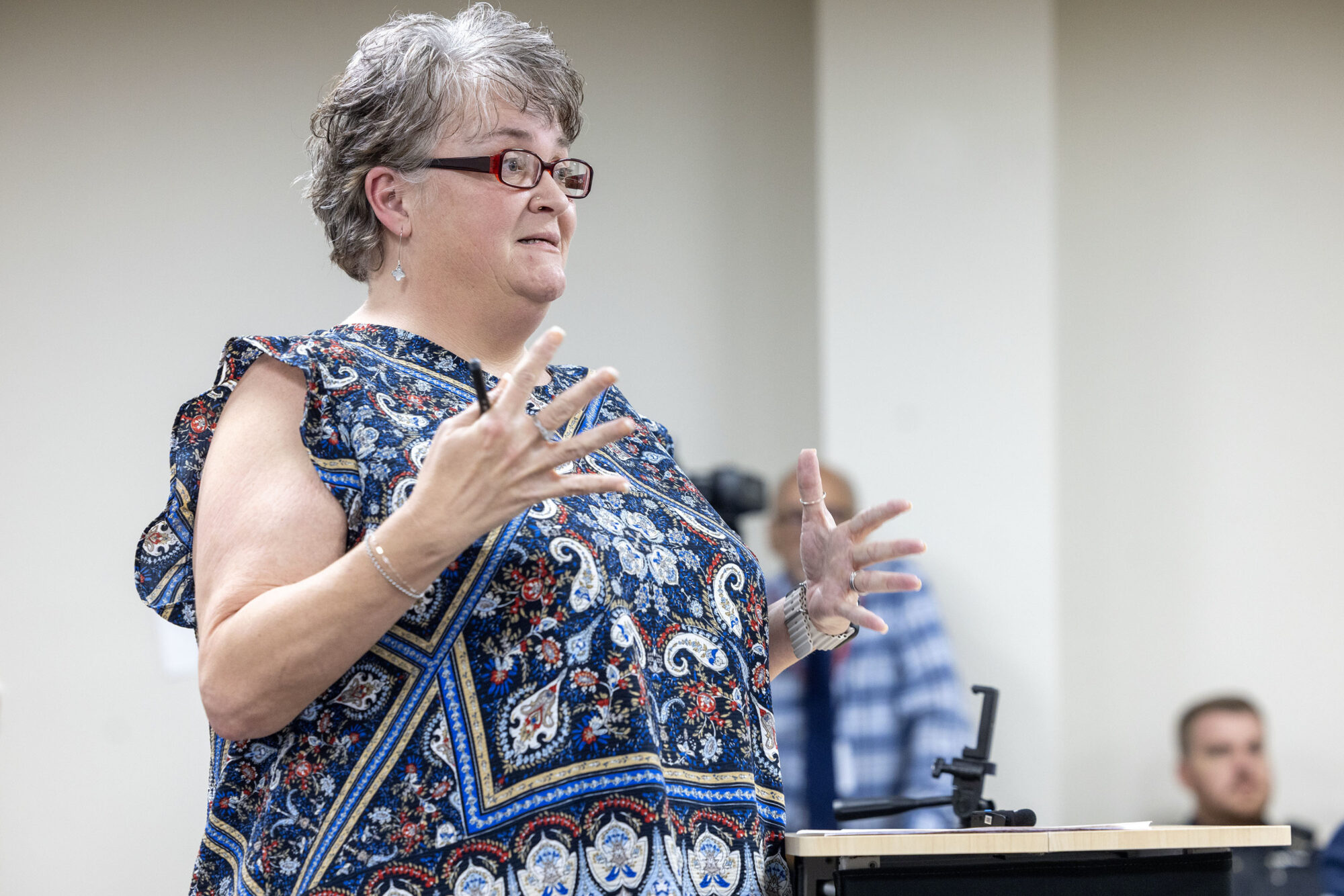

Answering questions from Central District Public Service Commissioner De’Keither Stamps, Vavro said it’s unclear how much the department is worth, adding an engineer’s study would be needed to come up with a number.
Terry, who reminded the PSC he’s only been Holly Springs’ mayor for just over 60 days, said there’s no way the city can afford the repair costs on its own. The city’s median income is about $47,000, roughly $8,000 less than the state’s as a whole.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post PSC moves toward placing Holly Springs utility into receivership appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Centrist
This article presents a factual and balanced account of the situation involving the Holly Springs Utility Department and the Mississippi Public Service Commission. It includes perspectives from various stakeholders, such as city officials, residents, and state commissioners, without showing clear favoritism or ideological slant. The focus is on the practical challenges and financial issues faced by the utility, reflecting a neutral stance aimed at informing readers rather than advocating a particular political viewpoint.
Mississippi Today
Brandon residents want answers, guarantees about data center
Residents of Brandon have raised concerns about the environmental impact and safety of a data center planned for their city.
AVAIO Digital, a Connecticut-based company, announced Aug. 19 that it plans to build a data center in Rankin County. While some celebrated the $6-billion investment and the over $20 million in annual tax revenue it would bring, other residents worry about the data center’s water and power consumption and possible pollution. The 600,000-square-foot facility is expected to be completed by 2027.
‘People genuinely just want answers’
When Nathan Rester first saw the news about the data center, he was immediately concerned. Rester grew up in Brandon and now lives there with his wife and toddler just a few miles from where the data center will be built.
READ MORE: Mississippi Marketplace: Another data center on the way
Rester had followed reports about the air pollution that people in and around Memphis have reported, a result of XAI constructing gas turbines without pollution controls normally used for such turbines. He didn’t want to see what was happening in Memphis happen in Brandon.
His wife, Larkyn Collier, made calls but found the answers unsatisfying.
“ No one could really give a straight answer on how it was being built, what sort of precautions were being taken, whether or not there had been any sort of consideration for utility costs or pollutants or anything like that,” Rester said
In response, Collier and Rester started a petition on change.org that now has over 430 signatures. The petition asks Rankin County leaders to guarantee the data center will not cause such problems. So far they have not received any communication from Rankin or Brandon government officials.
Rester is not completely opposed to the data center being built but he wants the government to guarantee it won’t bring utility bill hikes or pollution.
“ People genuinely just want answers and transparency here. And they want safeguards in place,” Rester said.
The AI boom comes to Mississippi
At their most basic level, data centers store computing equipment. They have been around since the 1940s and power things such as cloud storage. But with the boom in artificial intelligence investment, companies are rapidly constructing data centers across the globe.
The investment bank UBS estimates $375 billion will be spent globally on artificial intelligence in 2025. While this investment has fueled economic and technological growth, data centers have faced skepticism in the communities where they’re built, largely due to the amounts of energy and water they consume and possible pollution they emit.
Mississippi has two large-scale data center projects underway – Compass Datacenters in Meridian and Amazon in Madison County. Including the AVAIO data center, the three will add up to over $26 billion in new capital investment, an unprecedented amount for the state.
Cities and states are embracing data centers because of the potential economic growth, new taxes and innovation they bring.
“This investment is poised to create a lasting, positive impact on the city and the wider region,” Brandon Mayor Butch Lee said in a statement to Mississippi Today. “The project represents a major step forward for Brandon, bringing high-tech jobs and economic growth that will resonate throughout Rankin County and beyond.”
When the property is on the tax rolls and fully up and running, the ad valorem tax will bring in an estimated $23 million in new revenue according to Rankin First, the county’s economic development group. Most of it will go to the local school district.
“ These are not here today. And if we didn’t win this project, we would never see those,” said Garrett Wright, executive director of Rankin First, about tax revenue from the data center.
Rankin First, similar to many economic development groups, is not part of county government and is hired to attract new investment and cultivate existing businesses. It owns the land that the data center will be built on, which has been vacant for around 20 years.
AVAIO is eligible for the state’s data center tax incentive and fee in lieu of property tax. Companies pay a negotiated fee for a set period of time instead of the full property tax. The incentive is designed to encourage economic development. It requires sign off from the county board of supervisors, municipal authorities and Mississippi Development Authority, the state’s economic development agency.
It’s estimated AVAIO will create 60 direct jobs and the Amazon data center 300-400 direct jobs. While data centers create relatively few permanent, direct jobs they create additional jobs in the community. A McKinsey and Company report found that for every direct data center job, approximately 3.5 more jobs are created in the community.
Some residents on social media have wondered whether the data center will negatively impact traffic. Traffic and grade separation of the rail lines have been key conversations as Rankin County has grown. Rankin First acknowledged that AVAIO’s presence will increase traffic but they see it as an opportunity to push for long needed infrastructure improvements.
Rankin First and Brandon have been working with AVAIO for two years and says the company is coming to Brandon, in part, because of the thriving community.
“ The company wants to be a community partner. We see that they’re going to get involved with the local community,” said Regina Todd, assistant director of Rankin First.
Brandon residents want answers
Bailey Henry has lived in Brandon for over a decade. She said that when she read about the new data center on social media, she became concerned.
“ I’ve lived in Mississippi the majority of my life and I was raised to leave things better than you found it,” Henry said. “ And I just don’t think that Mississippi is going to be better off from this.”
Henry is worried about the pressure the data centers will put on the city’s infrastructure, pollution and power demands.
She describes the announcement as “ brief and nonchalant as all the explanations have been. From politicians to people who work for Entergy. It has just been, ‘This is what it is. It’s going to be great. Don’t ask any questions.’”
Henry has made calls to and left voicemails with multiple government offices and has not heard back from any of them.
She’s skeptical, but she hopes she’s wrong.
Brandon concerns echo nationwide conversation
The biggest concerns from residents nationwide over data centers has been potential pollution and increases in utility bills. Across the country, there are stories about data centers driving up energy rates, worsening water shortages, polluting the air and creating a constant noise.
AI data centers demand massive amounts of electricity and run constantly. The average AI data center uses as much electricity as 100,000 households, according to a report from the International Energy Agency.
Another concern is water usage. Data centers need to stay at a specific temperature, and water is one of the most efficient ways to cool the servers. The IEA report found that the average AI data center needs about 528,000 gallons of water every day. For communities that already have water concerns, data centers can exacerbate the problems.
Some communities have blamed the increased demand from data centers for rising electricity bills. While part of these costs may be due to general inflation or paying for infrastructure upgrades, some states are trying to monitor or regulate how households are affected.
A data center’s impact can vary based on the design of the center. But by their very nature they consume a lot of power.
“ AI chips are very power hungry. We’re building a lot of computing capacity, so we need to power all of this,” said Ahmed Saeed, a computer science assistant professor at Georgia Tech.
AVAIO promised “sustainable design,” including rainwater collection and solar panels that would “minimize power demands.” But it’s still unclear what, if any, impact the new data center will have on Rankin County residents.
“ Having clarity on the impact of data centers within the community where they’re building is important,” Saeed said. Saeed believes data centers are here to stay and are key for innovation. But he also thinks there’s a need for more government regulation.
“ They’re not necessarily a negative thing, but on the flip side, in order to make sure that they’re net positive it’s hard to ensure that without some regulation,” Saeed said.
Rankin County’s administrator declined to comment for this story. AVAIO and Brandon Water did not respond to requests for comment.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Brandon residents want answers, guarantees about data center appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article presents a balanced view but leans slightly center-left by emphasizing environmental concerns, community impact, and the need for government transparency and regulation regarding the data center project. It highlights residents’ worries about pollution, utility costs, and infrastructure strain, while also acknowledging economic benefits and job creation. The focus on environmental and social accountability alongside economic development aligns with a center-left perspective that values both growth and sustainability.
Mississippi Today
Democratic DA Scott Colom announces U.S. Senate run against Hyde-Smith
Scott Colom, a Democratic district attorney in north Mississippi, announced today that he will run for the U.S. Senate next year against incumbent Republican Cindy Hyde-Smith.
Colom’s entrance into the race is likely to spark a long and expensive battle for the seat, with both national parties expected to spend millions on the race in the Magnolia State.
Chuck Schumer, the Senate’s Democratic leader from New York, told the New York Times he wants to help elect a Democrat in Mississippi. But the Republican Party is almost certain to defend its ironclad grip on Mississippi, a state where both U.S. Senate seats have been held by the GOP since 1989.
In an interview with Mississippi Today ahead of his announcement, Colom said he intends to cast Hyde-Smith’s voting record as prioritizing “D.C. politics” instead of hard-working Mississippians, including her vote for the “One Big Beautiful Bill” that slashed social safety net programs and provided tax cuts for the wealthy.
“Mississippi needs a senator who’s going to put Mississippi first,” Colom said.
But Colom faces an uphill battle. He’s a Democrat running in Mississippi, with one of the most reliably conservative electorates in the nation.
Mississippi last elected a Democrat to the U.S. Senate in 1982, when it reelected John Stennis. A majority of Mississippians have voted for the Republican nominee for president since 1980.
Still, Colom said he can crack the GOP’s stronghold in the state because he has experience with pitching moderate and progressive solutions to a more conservative electorate, as he did when he defeated long-serving incumbent Forrest Allgood, an independent, for district attorney in 2015.
“At the time, people didn’t think I could win the DA’s race,” Colom said.
A native of Columbus, Colom is the elected district attorney of the 16th Circuit Court District, which includes Lowndes, Oktibbeha, Clay and Noxubee counties. He is the first Black DA for the district.
He first won that election by casting his opponent as an incredibly harsh prosecutor who was more concerned with obtaining stiff sentences for convicted criminals than true rehabilitation. After Colom took office, he said he focused his office’s efforts on tackling violent crime and promoting alternative sentencing for nonviolent offenders.
“I have faith that the truth always sees through if you get the message out, speak with conviction and lead with your values,” Colom said. “That’s my plan. I want to speak with my values.”
For example, Colom said he would push for legislation that raises the nation’s minimum wage and exempts law enforcement officers and public school teachers from paying federal income taxes.
This may be the first time the two have competed head-to-head, but it will not be the first time Colom and Hyde-Smith have butted heads. Former President Joe Biden in 2023 nominated Colom to a vacant federal judicial seat in northern Mississippi, but Hyde-Smith thwarted the nomination.
Despite support for Colom from Roger Wicker, Mississippi’s senior U.S. senator, Hyde-Smith was able to block his nomination because of a longstanding tradition in the U.S. Senate that requires senators from a nominee’s home state to submit “blue slips” if they approve of the candidate.
Hyde-Smith never returned one of these slips for Colom. If both senators don’t submit a blue slip, the nominee typically does not advance to a confirmation hearing before the Senate Judiciary Committee.
Hyde-Smith, at her reelection launch last week, mentioned her opposition to Colom’s elevation to the federal bench.
“He thought he was going to be a federal judge, and I blocked him,” Hyde-Smith said to applause.
Colom is the first Democrat to announce his candidacy for the Senate seat. Ty Pinkins, an unsuccessful Democratic candidate for U.S. Senate in 2024, has declared he’s also running for the Senate again in 2026 as an independent.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Democratic DA Scott Colom announces U.S. Senate run against Hyde-Smith appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
The article presents a factual overview of Democratic candidate Scott Colom’s Senate run against Republican Cindy Hyde-Smith, highlighting Colom’s progressive policy positions such as raising the minimum wage and critiquing Hyde-Smith’s voting record on social safety net cuts. While it includes perspectives from both sides and contextualizes Mississippi’s conservative political landscape, the emphasis on Colom’s values and policy proposals, along with critical framing of Hyde-Smith’s record, suggests a slight lean toward a center-left viewpoint. The tone remains largely informative without overt partisan language.
-
Mississippi Today6 days ago
DEI, campus culture wars spark early battle between likely GOP rivals for governor in Mississippi
-
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed5 days ago
‘They broke us down’: New Orleans teachers, fired after Katrina, reflect on lives upended
-
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
Alabama state grocery tax to fall 1% on Monday
-
News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days ago
Missouri joins dozens of states in eliminating ‘luxury’ tax on diapers, period products
-
Mississippi Today4 days ago
Trump proposed getting rid of FEMA, but his review council seems focused on reforming the agency
-
News from the South - Tennessee News Feed4 days ago
Tennessee ranks near the top for ICE arrests
-
News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago
Alabama union leaders say they’re fighting for the state’s middle class
-
News from the South - South Carolina News Feed6 days ago
Warm and Mainly Dry Labor Day