Mississippi Today
Senate kills Mississippi ballot initiative without a vote
Senate kills Mississippi ballot initiative without a vote
The Senate on Thursday let a measure that would restore voters’ right to sidestep the Legislature and put measures on a statewide ballot die without taking a vote.
“After yesterday, I spoke to my colleagues and the colleagues I spoke to did not show enough support to do this this year,” said Senate Accountability Efficiency and Transparency Chairman John Polk, R-Hattiesburg. “… We have a representative form of government that has worked for a long time, and I know of no senator who will not accept constituents’ calls, emails or visits if they have an issue we need to deal with. I believe in our representative form of government, and voters every four years have the opportunity to change who represents them.”
Polk said there were too many differences between versions of the measure the Senate and House had passed to be ironed out in the final days of this year’s legislative session. Thursday was a deadline day for senators to take up the measure, and inaction killed the legislation.
Polk said that despite recent polling that shows strong voter support for reinstating the initiative process, he doesn’t believe the right to ballot initiative is top of mind for most Mississippians. He said he noticed this last week when he talked with constituents at a veterinarian’s office back home. They gave him a litany of issues they saw as important, Polk said.
“You know what was not on that list?” Polk said. “Ballot initiative.”
A similar measure died in the Legislature without a final vote last year, after the state Supreme Court in 2021 shot down the ballot initiative right Mississippi voters had for three decades.
Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann, who oversees the Senate, initially declined comment after the Senate adjourned Thursday, indicating he was busy and “not right now.” Polk, speaking to media, said that Hosemann had been “very vocal in wanting a ballot initiative” but lets his chairman make their own decisions.
Hosemann later sent out a written statement: “I have consistently said I am in favor of an initiative process in Mississippi. I trust the voters of the state, both in who they elect to office and on policy matters. A number of Republicans in the Senate have a different opinion on the initiative issue. This is the legislative process and we will continue that process.”
But many political observers and supporters of restoring the initiative had questioned Hosemann’s support for it, given he assigned the measure to Polk’s committee again this year after Polk had publicly voiced misgivings about reinstating ballot initiative.
READ MORE:Is ballot initiative a ‘take your picture off the wall’ issue for lawmakers?
Many Mississippians were angry when the state’s high court stripped voters of this right in 2021. This was in a ruling on a medical marijuana initiative voters had overwhelmingly passed, taking matters in hand after lawmakers had dallied for years on the issue. Legislative leaders were quick at the time with vows they would restore this right to voters, fix the legal glitches that prompted the Supreme Court to rule it invalid. Many lawmakers said they support the right.
Rep. Zakiya Summers, D-Jackson, said she was stunned to hear the Senate let the measure die Thursday without inviting more debate with the House on a compromise version. She disagrees with Polk about it not being a big issue with voters.
“My constituents think it’s necessary,” Summers said. “… People have issues they believe we are not addressing or listening to them on, like early voting, Medicaid expansion. Those are issues Mississippians are concerned about and when we don’t bring them to the forefront because of politics, they need to have this right to address them. Now we have to wait another year to do this.”
READ MORE:Bill restoring ballot initiative remains alive, though some say it ‘stifles’ Mississippi voters
The House and Senate versions of the measure, which would have required ratification by voters in November, differed. But both would have greatly restricted voters’ right to ballot initiative compared to the process that had been in place since 1992. Many supporters of restoring the right have been angered about legislative leaders’ proposals to date. In the House, most Democrats despite supporting restoration of the right voted “present” on the House version they found it so restrictive.
The Senate position on the initiative would require the signatures of at least 240,000 registered voters to place an issue on a statewide ballot. The House version would require about 106,000, nearer the previous threshold required for the last 30 years.
Under both proposals, the Legislature by a simple majority vote could change or repeal an initiative approved by the electorate. Unlike the previous process voters had for decades, voters could only pass or change state laws, not the state constitution.
Polk said he “could not get close to” agreeing on the lower number of signatures in the House proposal, and doubted the House would agree to his higher threshold. He said the House also had made a change he found untenable that he just noticed in recent days: It removed a prohibition on using a ballot initiative to change Mississippi’s position as a “right to work” state, which generally keeps labor unions weak in such states.
“That was disturbing to me,” Polk said.
A recentMississippi Today/Siena College pollshows Mississippi voters across the spectrum want their right to put issues directly on a statewide ballot restored.
The poll showed 72% favor reinstating ballot initiative, with 12% opposed and 16% either don’t know or have no opinion. Restoring the right garnered a large majority among Democrats, Republicans, independents and across all demographic, geographic and income lines.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Lackey family members show value of education
As children during the 1950s, Hilliard Lackey and Lillian Troupe often had to skip school to pick cotton with their sharecropping parents.
They grew up together in the small north Mississippi town of Marks, both raised by devoutly Christian families.
Marks has struggled with poverty for generations, and problems were compounded by Mississippi’s history of underfunding public education for Black students. Schools remained segregated, and both said it was common for Black children around them to drop out or miss school so they could work in the fields.
“That was the life we knew, the life we inherited,” Hilliard Lackey said.
Hilliard and Lillian met as classmates in sixth grade, started dating in high school and married in 1966. Despite the challenges of the time, their parents and church leaders encouraged them to be ambitious and succeed.
Today, several members of the Lackey family have doctoral degrees: Hilliard and Lillian Lackey; their daughters, Tahirih Lackey and Dr. Katrina Davis; the couple’s daughter-in-law, Tracy Knight Lackey; and his stepbrother and sister-in-law, Dr. Robert Long and Vanessa Rogers Long.

Pew Research Center found that as of 2023, about 26% of all Black Americans 25 and older have a bachelor’s degree or higher, and 11% have advanced degrees. In Mississippi, 18.5% of Black residents have a bachelor’s degree or higher.
Hilliard Lackey is a longtime professor of urban higher education and lifelong learning at Jackson State University. He attended what was then called Jackson State College, earning his bachelor’s in history and political science, pre-law track, in 1965. (It became Jackson State University in 1974.)
Hilliard Lackey – who later earned a master’s degree in educational administration, an education specialist degree in the same topic, and a doctorate in higher education administration – was the first in his family to go to college.
“I left home and came to a whole new city, a whole new environment. It’s a college,” he said, looking back on the experience. “And I was astounded, and scared, and frightened and bewildered.”

Lillian, then still named Troupe, attended Coahoma Community College before transferring to what was then called Alcorn Agricultural and Mechanical College – since 1974, Alcorn State University. She graduated from Alcorn with a bachelor’s in business education in 1966 and earned a masters in education administration from Jackson State in 1974.
She was still living and working in Marks during community college.
“I went to Coahoma … rode the school bus, came home, got out of my clothes, went to the field, picked cotton,” she said. “And so I picked my way out of the cotton field to Alcorn.”

In June, West Coast Bible College & Seminary awarded Lillian Lackey an honorary doctorate for her years of community service.
Two of Hilliard and Lillian Lackey’s four children have doctorates. Davis has a medical degree and is a urogynecologist. Tahirih Lackey has a doctorate in civil environmental engineering and is a research hydraulic engineer at the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Research and Development Center.

Both sisters say their parents’ emphasis on education and success and their religious faith influenced their career paths.
Davis recounted that every Sunday, each member of the family stood in front of the fireplace and discussed what they’d done that week to achieve their goals. She and her siblings attended a variety of academic and athletic summer programs before and during college.
Hilliard and Lillian Lackey converted from Christianity to the Baha’i faith as adults. They raised their children “essentially as Christian Baha’is,” according to Hilliard Lackey, and let them choose what religion to follow when they were 15 years old.
“They pretty much told us, ‘Whatever you want to be, you can be, and we’ll be there to help you,’” Davis said.
“I would recognize that my parents, they were always helping other people. Like, throughout my whole life they demonstrated those concepts,” Tahirih Lackey said.

“None of us thought we had any barriers,” Davis said. “If there were barriers, they were from our own mental blocks.”
Hilliard Lackey’s stepbrother, Dr. Robert Long, is a dentist in Clarksdale. Long also credits his upbringing for his success, saying his parents raised him and his siblings with a strong work ethic and Christian values.
“They instilled in us that nobody is going to give you anything, nobody is obligated to give you anything,” Long said.
Long grew up in a small rural town in Quitman County, 15 miles from Marks. He had a similar upbringing to Hilliard Lackey. His parents encouraged him to get an education.
He attended Earlham College, where he majored in biology and found a mentor who inspired him to become a dentist.
He described his undergraduate experience as a “culture shock” and an “academic shock.” He chose to persevere through the challenges.
“I knew I could go home,” he said, “but I didn’t want to go home.”
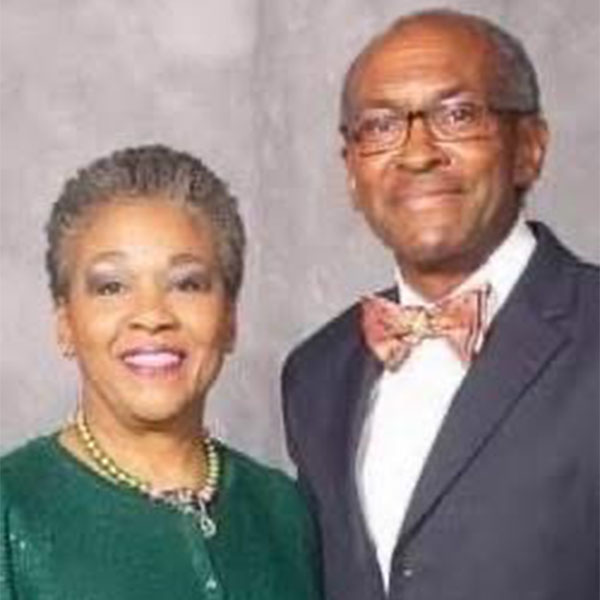

Vanessa Rogers Long grew up in a middle-class family in the small community of Memphis, Mississippi, and, like most of her family, has lived a life dedicated to service.
She was the first Black hospital administrator for the Mississippi Department of Corrections. She founded Mississippi Delta Connection, which is part of Links Inc. She also mentors teens on service and leadership skills. She has received several honors, including having her sorority, Alpha Kappa Alpha, dedicate a bench to her at her alma mater, LeMoyne-Owen College.
“Service is what I do,” she said.
Hilliard and Lillian Lackey are also deeply involved in community service, including their “Lackey Scholars” program inspired by a former teacher. Hillard Lackey estimates they’ve helped more than 500 high school students from Quitman County attend and graduate from Jackson State since 1967. In addition, they mentor dozens of students from Quitman County’s Madison Shannon Palmer High School to act as role models for their peers and the community.
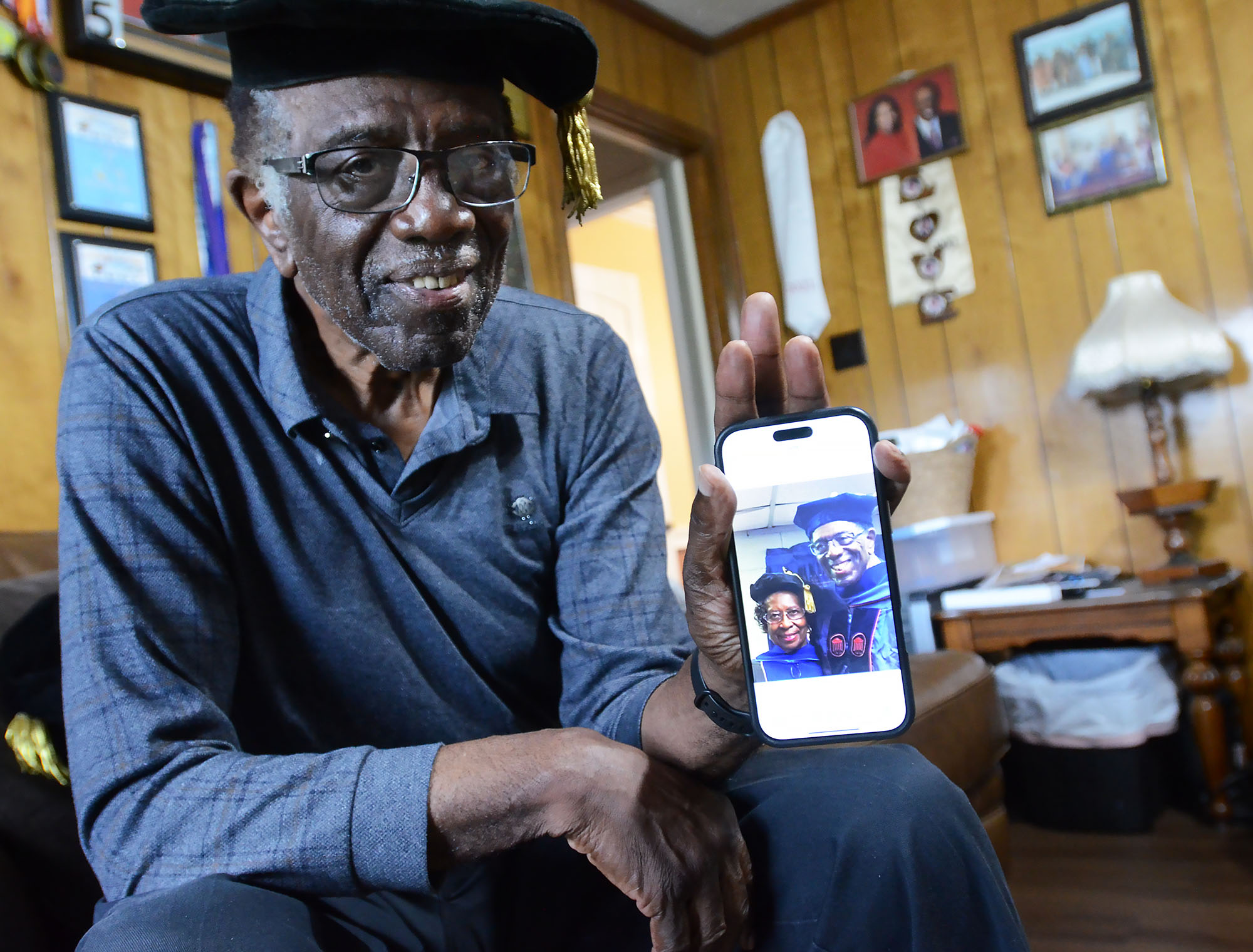

“That’s just been our thing, it’s always been,” Lillian Lackey said. “To help somebody, if they were hungry, if they were cold, if they were whatever.”
When asked what he would tell first-generation college students, Hilliard Lackey said: “Education is an equalizer. It gives an advantage to the disadvantaged. It levels the legacy playing field.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Lackey family members show value of education appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article emphasizes the value of education, community service, and overcoming historical racial and economic challenges, themes often highlighted in center-left discourse. It acknowledges systemic issues like underfunding of Black education in Mississippi while focusing on personal achievement and community upliftment without overt political partisanship. The tone is positive and supportive of education as a tool for social mobility, aligning with moderate progressive values but avoiding strong ideological language.
Mississippi Today
This superintendent took a failing Delta school district to a ‘B’ rating. Now, she’s leaving
INDIANOLA — The top of the Jeep was down, and Miskia Davis was behind the wheel, leading a parade through downtown Indianola.
It was 2019, just two years after the now 50-year-old Davis became superintendent of Sunflower County Consolidated School District. Back then, she wasn’t sure this moment would ever come.
She recalled feeling the first cool breeze of October as she waved at people who lined the street, smiling and celebrating.
But it had — the district’s first “C” rating, its first passing grade, and the community had shown up to a parade to celebrate the achievement. Generations of teachers and Sunflower County graduates stood on the sidewalk, proudly cheering the assembly of cars and students.
“It was … Oh my God,” Davis said. “My children were like, ‘We did something.’”
The work hadn’t been easy, but it had been worth it, Davis thought — the number crunching, the doubt and lukewarm welcome she felt from the community, the tough decisions she’d had to make.
Now, she’s ready to move on.
Daughter of the Delta
From starting kindergarten to subbing for elementary classes, Davis’ childhood and career in Sunflower County and her identity as a daughter of the Delta were her strengths in the classroom, she said.
“I grew up in Drew, poor and with two young parents,” Davis said. “We didn’t have elaborate meals, and when I went home, the lights may have been off. But it made me who I am, and these children were experiencing the same things I experienced as a child.”
So Davis was relatable. But as a young high school teacher at Ruleville Central High School, some of her students looked older than her and many were taller than she was. She was forced to learn how to command respect, too.
One particular child taught her an invaluable lesson. He was a star football player in her biology class, and he was failing the course by two points. He caused trouble in class and Davis was determined to fail him, despite more experienced teachers prodding her not to, to look past her own ego.
So Davis gave him another chance. She had him do extra work and spent hours talking to him. She learned why he behaved poorly in class — he was one of seven children to a young, single mother.
“He was angry at the world, and I just happened to be in the world,” she said. “It taught me the power of relationships. I think that’s the most important catalyst in transforming education.”
It was during that time that her superintendent “saw something” in her and pushed her to become a school leader. That kickstarted her journey in administration.
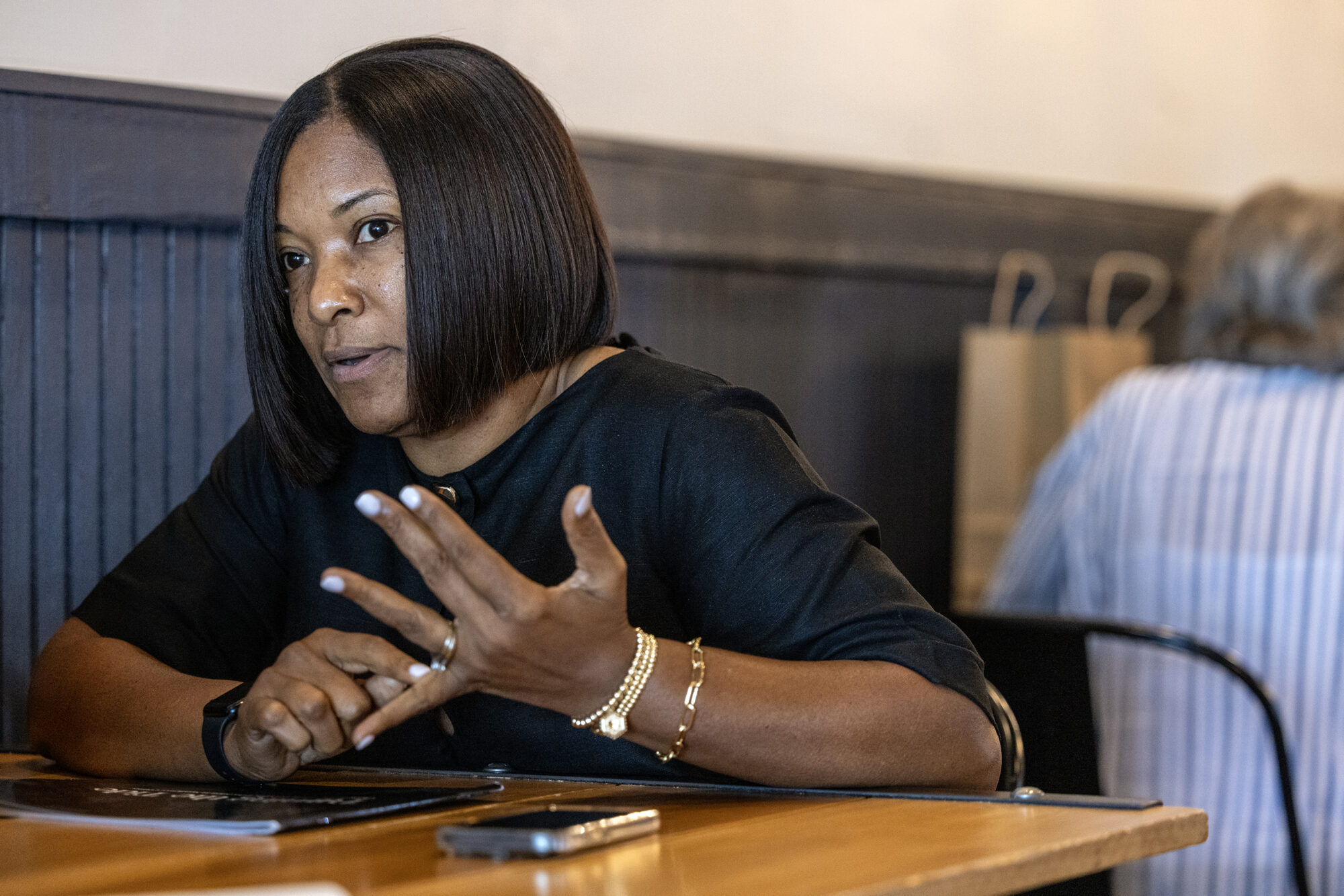

Davis soon learned she had a particular gift for turning failing schools around. Under her leadership as principal, Ruleville Middle School went from failing to an “A” letter grade in three years.
Her school improvement strategy began to take shape, similar to her teaching style. Davis was both a disciplinarian and someone to whom teachers and students could relate. She prioritized building strong relationships with teachers who were invested in their students. But she didn’t shy away from making controversial decisions, either. In Ruleville, she fired nearly all of the staff when she arrived.
But as Davis was gaining her footing as an administrator, Sunflower County School District was struggling.
After consistent failing grades resulted in the state takeovers of Indianola, Sunflower and Drew school districts, the Legislature decided to consolidate the three systems in 2012.
District consolidation is a massive undertaking for any community, but especially for Sunflower County — smack dab in the middle of the Delta, an under-resourced region with a shrinking population, high poverty rates and a deep history of racial exploitation.
Davis arrived in 2014 to a school district that had lost hope — a district that she didn’t recognize.
All Sunflower knew was ‘failure’
Davis never wanted to be superintendent.
She spent three years working under the leader of the consolidated district. But when the superintendent was dismissed in 2017, Davis was appointed to the head role in an interim capacity. She got the job in January of 2018 without ever applying.
So with another state takeover looming, Davis went to work. The biggest challenge? The district and the community seemed resigned to failure.
“We had been failing so long, that’s all we knew,” she said. “No one was even sad.”
Early on, Davis visited a school to discuss recent test results. She was so struck by teachers’ apathy that she stopped the meeting midway and had them tear off a scrap of paper and write “yes” or “no” to a question: Did the teachers believe their school could ever be successful?
More than half said no.
“They were teaching my children,” Davis said, tearing up. “And they didn’t think they would ever be successful.”
Davis went to the school board to tell members that she wouldn’t be renewing many of those teachers’ contracts. That’s when she realized she didn’t just need to boost test scores — she needed to change attitudes.
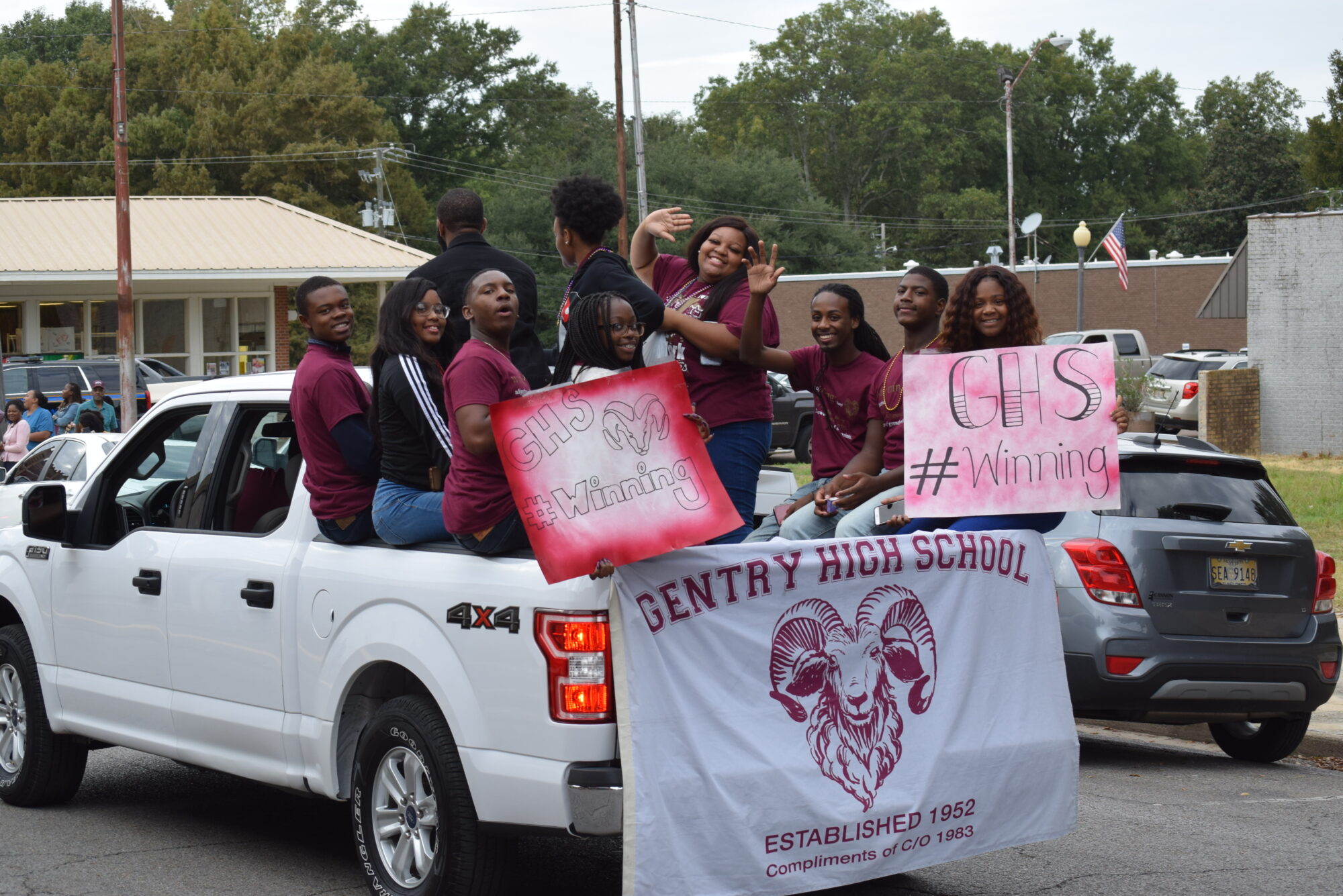
The hashtag #WINNING was born.
“We started to celebrate every little accomplishment,” Davis said. “We got T-shirts, shades, whatever. That was our mantra.”
Children received certificates for a week of perfect attendance. When students did well on benchmark assessments, teachers were ushered into the hallway to be celebrated by students and colleagues. Davis created the “Killin’ It” awards, given to students and teachers for meeting their testing benchmarks.
They were just certificates, at the end of the day. But it led to a changed school culture, a renewed belief that they could succeed.
As an administrator, Davis leaned on what she knew worked as a teacher, relationship-building and strong discipline (she even sent her nephew to alternative school for fighting), and combined it with a data-driven approach and an eagle-eyed focus on testing.
She put an academic coach in every building, whose sole responsibility was supporting teachers.
Davis took teacher Dylan Jones out of the classroom and put him in the central office, where he was tasked with tracking district metrics.
Jones uncovered which consultants were working and which were uselessly costing the district millions. The district went from contracting with 30 firms to just four.
Jones also created an accountability system for teachers. With one click, Davis could see how each teacher’s students were performing, and she gave everyone access to the data. If teachers weren’t meeting their goals, Davis hosted regular meetings and had them explain — in front of everyone — what they needed to succeed.
Davis’ methods weren’t popular at first. Educators went to the school board and complained that the system was “punitive.” Some even quit. But Davis was steadfast and implored board members to see the work she and her team could do, if given the chance.
The district’s rating didn’t budge in 2018.
But in fall 2019, after Davis’ first full year as superintendent, Sunflower County Consolidated School District had earned its first “C” rating.
What happened after the first ‘C’
Those early years were difficult, Davis remembered, because she felt so isolated, just her and her team “in the trenches.”
She hosted community meetings, imploring local parents, leaders and business owners to support the district.
“They told me to come back when we were no longer failing,” Davis said.
So after that first “C,” when she started seeing the district’s hashtags on Facebook, when more people started coming to school events, when she started to get invited to speak at the local Rotary Club, it was bittersweet.
Teachers, too, took a while to come around. Their performance was being closely monitored through the accountability system, but soon they realized that Davis wasn’t giving them mandates outside of improving test scores. She gave them autonomy in their classrooms. Teachers had the final say on how to improve their students’ achievement. That kind of trust isn’t common, Sunflower County teachers told Mississippi Today.
It wasn’t until 2021, when voters passed a $31 million bond issue that would pay for major school renovations, that Davis felt the full support of the community.
Davis even won over Betty Petty, a local matriarch and fierce advocate for kids and parents.
“She has actually shown a presence at the schools, constantly meeting with teachers and making sure all children are learning,” Petty said. “We had community meetings where she would actually come out and listen to our concerns.”
Petty attended the ribbon-cutting ceremony at Gentry High School last July. Before renovations, plumbing problems caused flooding when it rained, so students had to wade through water to get from class to class. Davis said she’d never forget the sight of generations of Gentry graduates in the school atrium, looking around in wonder at the new facility.
“At first, I chose the community,” Davis said. “But eventually, the community chose me.”

The legacy she leaves behind
Strong schools make strong communities, but it can take time for results to show. Indianola Mayor Ken Featherstone hopes to see the dividends soon.
Featherstone took office four years ago, around the same time the district got its first “B” grade. It has maintained the grade ever since, the highest in the entire region.
He, like Davis, was reared in the Delta, but empathizes with her struggle garnering the support of a community deeply impacted by gun violence and low investment from state officials.
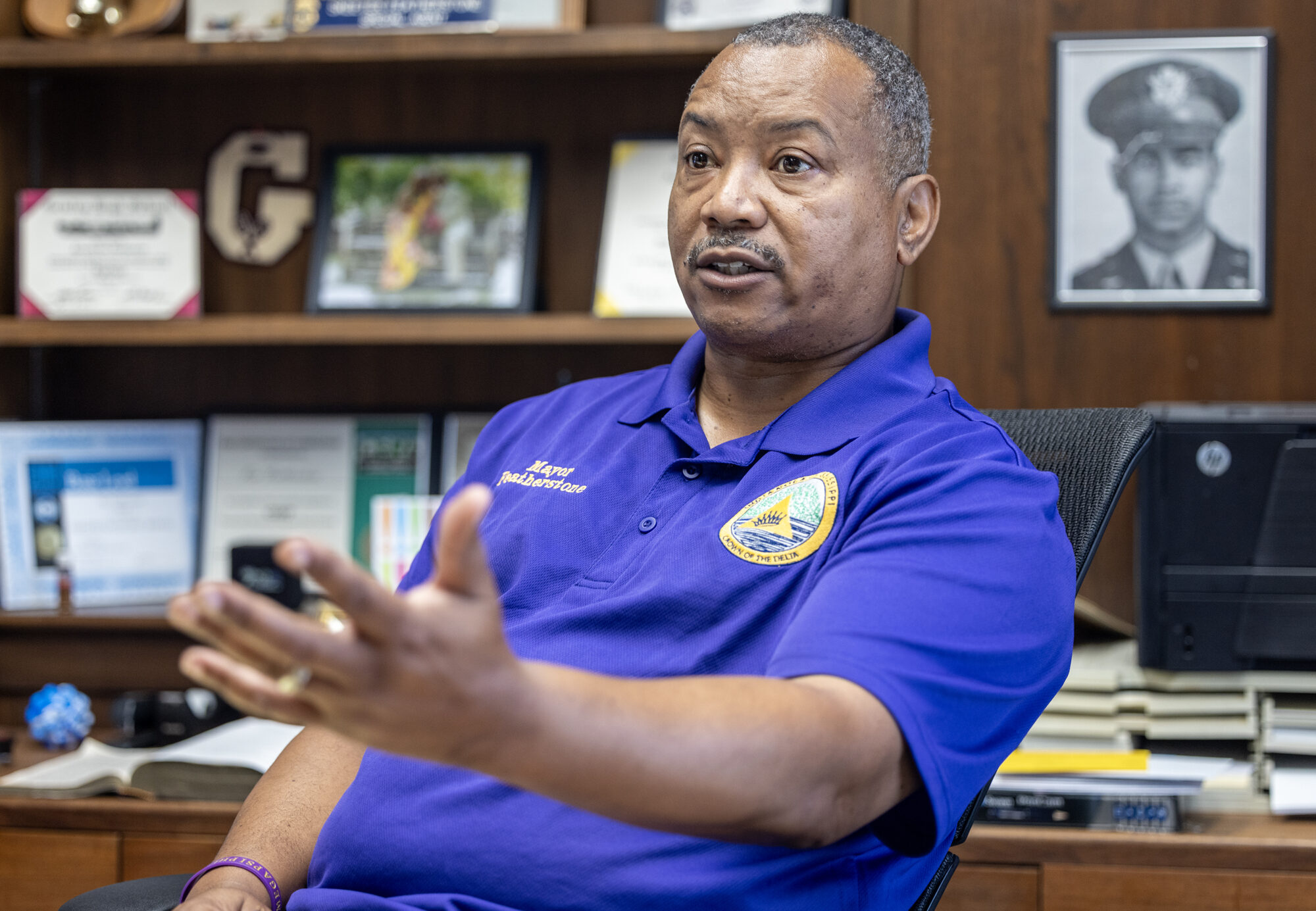

“People are very result-oriented,” he said, leaning back at his desk in city hall. “You till the soil, but it’s not until you start your seed breaking the ground do you see other people starting to water it. That’s just human nature.”
He’s hoping the district’s academic gains will be a boon for Indianola’s struggling economy.
“We’re seeing things slowly come to our area,” Featherstone said. “To get manufacturing jobs to come to our area, we have to improve our public school system. Directors and presidents of manufacturing plants … they need to know where their kids are going to attend school.”
Davis announced in October 2024 that she would be leaving the superintendent job at the end of the school year. Now, she travels the state, consulting with other districts on how to replicate what she did in Indianola, as a director of District and School Performance and Accountability for The Kirkland Group, an education consulting firm based in Ridgeland.
Her departure was a tough blow, Featherstone said, and leaves the district’s hard-fought success hanging in balance.
Petty and her network of parents are concerned, too.
“I don’t think any of us know what will happen moving forward,” she said.
Davis said there was no big epiphany. She just felt her mission was accomplished. She said she’s adamant that the district’s “best days are ahead,” under new superintendent James Johnson-Waldington.
Johnson-Waldington, who was most recently serving as superintendent of Greenwood Leflore Consolidated School District, is also Sunflower-grown, and he was Davis’ principal when she taught at Ruleville Central High School. He plans on employing strategies similar to Davis: holding teachers accountable and celebrating their achievements.
After all, if it’s working, why change it?
“I feel a good kind of pressure,” Johnson-Waldington said. “I like challenges, and this is a new challenge for me. I’m not taking a failing school district to success. This is about maintaining and growing, and I accept that challenge for the very reason that this is home. I’m going to work very hard to maintain what Miskia has done.”
Davis leaves behind a legacy, Featherstone said, that makes her hometown proud. He was in the crowd that day at the parade. He remembers the excitement, the pride.
“Older teachers were there, and you could see the look on their faces that they knew they had reared someone who threw the oar out to a sinking district and brought it back up,” he said.
“She made us see ourselves in a better light, and we can’t thank her enough.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post This superintendent took a failing Delta school district to a ‘B’ rating. Now, she’s leaving appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article presents a positive and detailed profile of an educational leader working to improve a struggling school district in a historically under-resourced and economically challenged region. The focus on community uplift, education reform, accountability, and addressing systemic challenges aligns with themes often emphasized by center-left perspectives. However, the article maintains a largely neutral and factual tone without overt political framing or partisan language, emphasizing pragmatic solutions and community collaboration rather than ideological positions.
Mississippi Today
Theology student’s ‘brain drains back home’ despite economics, safety concerns
Editor’s note: This Mississippi Today Ideas essay is published as part of our Brain Drain project, which seeks answers to why Mississippians move out of state. To read more about the project, click here.
Though I imagine I’ll never return, more often than not, my brain drains back to Mississippi. My whole adult life has been a journey up and down the Hudson River, from New York City to the Adirondacks, but inevitably, I find my thoughts leaking toward another river.
I grew up fearing being left behind in the Rapture, but in earnest, it feels like I’m the one who left everyone behind. I’m not proud of this, but I’m certainly not ashamed. I have roots in the Northeast now, and a life that isn’t easily transplanted elsewhere, especially to the Red Clay Hills of Neshoba County. Life took me from Mississippi, and life keeps me away.
I left Mississippi for New York in 2015, and I estimate that I’ve returned only 11 times. My sporadic trips home have been mostly because I’m consistently broke, but now it’s a combination of that and concerns for my safety.
My mother, also limited by finances and Mississippi’s minimum wage, has visited me twice in 10 years, once in the spring of 2016 and then when I graduated from Yale Divinity School in 2023.
I haven’t been back since I came out as a trans woman and began medically transitioning in the winter of 2024. I try not to be overwhelmed with guilt or grief for the imagined, shared life I don’t experience with my mother. Rather, I’ve learned to cherish what we do have.
It’s strange to be who I am, mostly for her but also for me. She has learned to love me regardless of whether or not she understands what I’m doing. In her mind, if you go to college, you become a nurse or a lawyer. You settle down, probably in Jackson, maybe Oxford, most likely in my hometown of Philadelphia, and commute by car more than an hour to work. You probably see your mom weekly. She sees her grandkids as often as possible.
That is not how life turned out. We do talk on the phone. Sometimes we get into once-a-week phone call sprees, other times, I drop off for weeks, maybe a month, when I’m depressed.
When I come home, she picks me up from the airport and drives me back a few weeks later. We crack the windows, smoke cheap Mississippi cigarettes and try to cram 10 years of a strange-to-us mother-daughter relationship into a 90-minute ride to the airport in Jackson. Usually, we talk about suffering, death, sin, God, the end of the world, and what the hell I am doing with my life.
You go to college to get a job, to make more money than your parents and to buy a strange suburban-but-rural McMansion just beyond city limits where you start a family around the age of 25 at the latest.
According to my mother, I went to the University of Mississippi and got brainwashed. She tells me often that it’s like she doesn’t know who I am, and she’s mostly right. She hasn’t met anyone I’ve dated in person since high school. She hasn’t seen me in person since transitioning, and I changed my name to Romy. I explain my relationship with my family to friends, peers, new partners and congregations, always with an articulate sense of heartbreak that I’ve learned to intellectualize and package up in a story of “working-class origins,” single motherhood, a white Christian nationalist rural community and my stumbling through adulthood “refusing not to live by my values.”
I originally left Mississippi to be an AmeriCorps Vista volunteer in the Capital Region of New York. I’d never been there. I took a Greyhound from Memphis to New York City to Albany, New York with two large suitcases and a backpack. Several of my friends from college had moved to New York City, and their couches and shared beds provided a safe launching pad for more of us. I had also fallen in love with a fashion student turned designer that I met on a trip to the city the year prior. Though that romance flamed and flickered for many years and ultimately flamed out, my reason for staying in the North was the life I was increasingly stumbling into.
I went there because, at the time, I had an insatiable desire to live out my values and politics. After all, I was maybe one of two socialist public policy majors at the Trent Lott Leadership Institute at the University of Mississippi, and I didn’t want to be a lawyer, a lobbyist or a policy wonk.
I wanted to be poor and engage in building sustainable autonomous communities. I wanted to learn how to be a person who had no work/life distinction, but a vocation and calling.
Through AmeriCorps, I luckily found a small group of activists, urban homestead types, organizers and ex-social workers living together helping others at the margins and themselves start businesses and worker-cooperatives while struggling through mental health crises, and taking on an impossible but seemingly always plausible dream of a directly democratic community owned, operated and governed only by those who live there.
This was my first “job” out of college. It was my dream come true, and the most difficult thing I’d ever done. I burnt out pretty hard after two years, and probably made somewhere between $25,000 and $30,000 during that whole time. Since then, the most I’ve made in a year is my current PhD stipend of about $34,000.
I was, however, helped along by friends, colleagues and the activist communities that I was stumbling into. Through them, I was encouraged to go to Union Theological Seminary, land a job at a prestigious artist residency in the mountains, go to Yale Divinity School, discern that I was called to be a priest and come to know myself as a trans woman.
My life outside of Mississippi has been sustained solely by relationships that transgress the boundaries between work and life, co-workers and friends. I regularly reflect on and often worry about how fragile this all is, and if my own vocational and intellectual pursuits have been worth what I’ve left behind or never had.
I’m not sure I’ll ever know. However, I’ve managed to find profound meaning in it all so far, and it keeps me digging myself into this hole in which I will hopefully find what I am looking for, or dig my own damn grave.
Originally from Philadelphia, Romy Felder (she/her) is currently a PhD student at Union Theological Seminary. She is also pursuing the priesthood in the Episcopal Diocese of New York. She has a background in worker-cooperative development, community organizing, popular education and arts management. Romy lives cavalierly but contentedly in Brooklyn, New York.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Theology student's 'brain drains back home' despite economics, safety concerns appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Left-Leaning
This essay reflects a distinctly personal and ideological perspective rather than neutral reporting. The author frames Mississippi as economically limiting and socially unsafe, particularly for marginalized identities such as transgender individuals, while presenting Northern activist and academic communities in a sympathetic and aspirational light. References to socialism, worker-cooperatives, and critiques of conservative Mississippi culture suggest a worldview aligned with progressive or left-leaning politics. The tone is introspective and critical of traditional Southern expectations, while valorizing alternative, activist-driven lifestyles. As such, the piece is less about balanced reporting and more an expression of lived experience through a progressive lens.
-
News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days ago
Floridians lose tens of millions to romance scams
-
News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days ago
New Texas laws go into effect as school year starts
-
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
Final steel girders placed on new Gulf Shores bridge, completion on track
-
News from the South - West Virginia News Feed6 days ago
Religious exemption debate front and center amid new school year in WV
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed6 days ago
Trump, Zelenskyy exit White House talks hopeful about security guarantee for Ukraine
-
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
Despite federal shift, state health officials encourage COVID vaccines for pregnant women
-
News from the South - Tennessee News Feed7 days ago
Son hopes to get emergency visa following mother's death in East Tennessee
-
News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago
U.S. agriculture secretary announces end to subsidies for solar panels on farmland




















































