Mississippi Today
Feds give Greenville grant for primary care clinic as Delta faces loss of health care services
Feds give Greenville grant for primary care clinic as Delta faces loss of health care services

Local leadership in the Delta says the region’s crumbling health system has been abandoned by the state – so they’re figuring out how to fix it on their own with the help of federal funds.
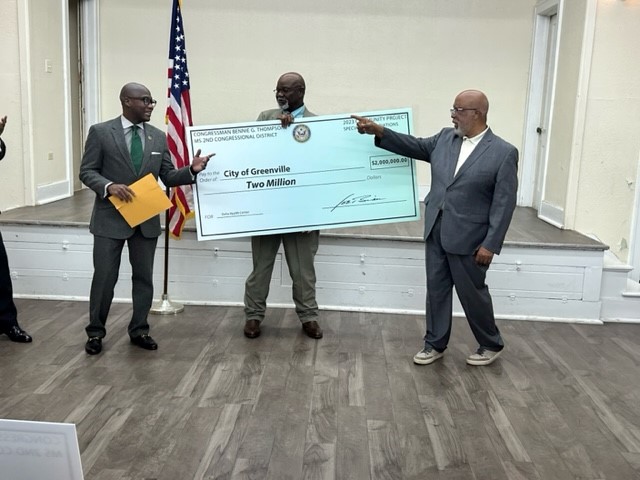
Greenville’s mayor and a local health clinic say they’re working to give people in the Delta better access to doctors and primary care, as hospitals around them shutter and strip back specialty care. As a result, the city of Greenville received $2 million in federal funds to construct a new health clinic in partnership with the Delta Health Center.
“This is a bottom-up action in response to the state’s failure to act,” said Greenville Mayor Errick Simmons. “We went straight to the solution, and we will continue to do these types of projects to make sure our folks get the health care they need.”
Simmons accepted a symbolic check from U.S. Congressman Bennie Thompson who helped secure the funds from a House spending bill earmarked for community projects during a Tuesday press conference. Thompson announced close to $18.8 million in federal funds for his district, which covers much of Western Mississippi.
“A lot of you have heard of the trouble that health care is having in the Delta,” Thompson said during the press conference. “Our governor, for some reason, doesn’t want to help.”
Thompson was referring to Gov. Tate Reeve’s firm stance against Medicaid expansion, despite a mounting statewide hospital crisis. New data from mid-January shows that 38% of Mississippi hospitals are at risk of closing. Of the 28 rural hospitals at risk of closing, 19 are at risk of shuttering immediately.

Mississippi news — direct to your inbox.
Reeves’ office did not immediately respond to a request for comment from Mississippi Today.
Greenwood Leflore Hospital recently shuttered its labor and delivery unit, primary care clinic and reduced other services. Delta Health-The Medical Center in Greenville also closed its neonatal intensive care unit and cardiac rehabilitation department last year.
Simmons said he applied for the grant last year because he feared the Delta would continue to lose access to doctors. Already, he said, there is only one pediatrician for every 4,000 children in the region.
He hopes other cities may copy his approach to help fund sorely needed primary care options to lessen the burden on the hospital system, which continues to struggle against massive staffing shortages.
“I think the Biden-Harris administration has a wealth of opportunities to begin grabbing pockets of money, working from local government to federal government, providing better access to quality health care to the folks that deeply need it,” Simmons said.
Delta Health Center CEO John Fairman said the new facility is projected to cost about $10 million to construct. He said he is in conversations with other funding sources and hopes to break ground on the new building before the end of the year.
The vision is for the clinic to better make use of telehealth options to connect rural residents who may not have internet access in their homes with specialists virtually. A nurse or a physician assistant would be in the room in person, too, helping facilitate care.
“Then they can make an assessment for intervention and as to whether or not they need to arrange transport to get to a specialist (in person),” Fairman said. “Once we get a better understanding of the data, we can have a specialist where the most acute cases are (scheduled weekly in person).”
The new clinic would also have a pharmacy open until 11 p.m. – most Delta pharmacies close at 6 p.m.
Fairman said the future of health care in the Delta needs to be collaborative, and he’s already in discussion with county hospitals on how to better partner. The Delta continues to be among the unhealthiest parts of the state with high percentages of uninsured residents. Fairman and Simmons want better health care intervention to prevent hospital visits.
“We need other ways to offer care after hours so people are not crowding up the emergency room, and we’re preserving trauma centers and emergency rooms for the people who really need that,” Fairman said.
Medicaid expansion would mean between 200,000 and 300,000 more Mississippians would have access to health insurance and hospitals would have an easier time being reimbursed for care rendered. More than 15 state bills that would have expanded Medicaid to provide coverage to the working poor died earlier this month without any debate or vote in the House or Senate.
“Had Mississppi accepted the expansion nine years ago, they would have accrued about $14 billion dollars that would go toward health care,” Thompson said. “But somehow they think people don’t need that.”
Simmons has little faith in the state stepping up to support what his community needs. He hopes more mayors are emboldened to think creatively.
“An unhealthy child cannot go to school to learn; an unhealthy adult cannot work,” Simmons said. “This is a way for us to begin addressing an epic state failure.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Mississippi prepares for another execution
The Mississippi Supreme Court has set the execution of a man who kidnapped and murdered a 20-year-old community college student in north Mississippi 30 years ago.
Charles Ray Crawford, 59, is set to be executed Oct. 15 at the Mississippi State Penitentiary at Parchman, after multiple requests by the attorney general’s office.
Eight justices joined the majority opinion to set the execution, concluding that Crawford has exhausted all state and federal legal remedies. Mississippi Supreme Court Justice T. Kenneth Griffis Jr. wrote the Friday opinion. Justice David Sullivan did not participate.
However, Kristy Noble with the Mississippi Office of Capital Post-Conviction Counsel released a statement saying it will file another appeal with the U.S. Supreme Court.
“”Mr. Crawford’s inexperienced trial counsel conceded his guilt to the jury — against Mr.
Crawford’s timely and repeated objections,” Noble said in the statement. “Mr. Crawford told his counsel to pursue a not guilty verdict. Counsel did just the opposite, which is precisely what the U.S. Supreme Court says counsel cannot do,” Noble said in the statement.
“A trial like Mr. Crawford’s – one where counsel concedes guilt over his client’s express wishes – is essentially no trial at all.”
Last fall, Crawford’s attorneys asked the court not to set an execution date because he hadn’t exhausted appeal efforts in federal court to challenge a rape conviction that is not tied to his death sentence. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court declined to take up Crawford’s case.
A similar delay occurred a decade ago, when the AG’s office asked the court to reset Crawford’s execution date, but that was denied because efforts to appeal his unrelated rape conviction were still pending.
After each unsuccessful filing, the attorney general’s office asked the Mississippi Supreme Court to set Crawford’s execution date.
On Friday, the court also denied Crawford’s third petition for post-conviction relief and a request for oral argument. It accepted the state’s motion to dismiss the petition. Seven justices concurred and Justice Leslie King concurred in result only. Again, Justice Sullivan did not participate.
Crawford was convicted and sentenced to death in Lafayette County for the 1993 rape and murder of North Mississippi Community College student Kristy Ray.
Days before he was set to go to trial on separate aggravated assault and rape charges, he kidnapped Ray from her parents’ Tippah County home, leaving ransom notes. Crawford took Ray to an abandoned barn where he stabbed her, and his DNA was found on her, indicating he sexually assaulted her, according to court records.
Crawford told police he had blackouts and only remembered parts of the crime, but not killing Ray. Later he admitted “he must of killed her” and led police to Ray’s body, according to court records.
At his 1994 trial he presented an insanity defense, including that he suffered from psychogenic amnesia – periods of time lapse without memory. Medical experts who provided rebuttal testimony said Crawford didn’t have psychogenic amnesia and didn’t show evidence of bipolar illness.
The last person executed in Mississippi was Richard Jordan in June, previously the state’s oldest and longest serving person on death row.
There are 36 people on death row, according to records from the Mississippi Department of Corrections.
Update 9/15/25: This story has been updated to include a response from the Mississippi Office of Capital Post-Conviction Counsel
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Mississippi prepares for another execution appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Centrist
The article presents a factual and balanced account of the legal proceedings surrounding a scheduled execution in Mississippi. It includes perspectives from both the state’s attorney general’s office and the defense counsel, without using emotionally charged language or advocating for a particular political stance. The focus on legal details and court decisions reflects a neutral, informative approach typical of centrist reporting.
Mississippi Today
Presidents are taking longer to declare major natural disasters. For some, the wait is agonizing
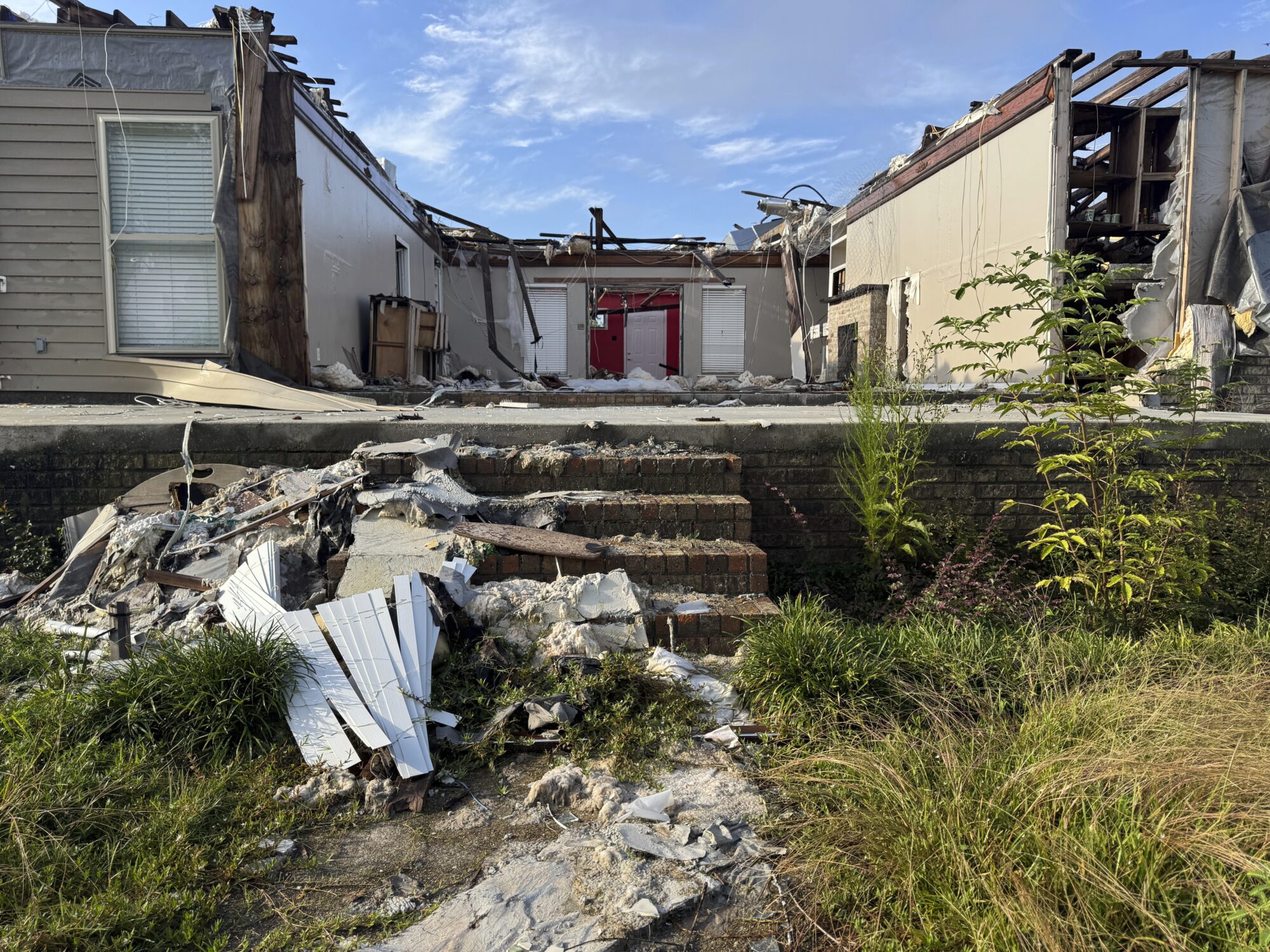
TYLERTOWN — As an ominous storm approached Buddy Anthony’s one-story brick home, he took shelter in his new Ford F-250 pickup parked under a nearby carport.
Seconds later, a tornado tore apart Anthony’s home and damaged the truck while lifting it partly in the air. Anthony emerged unhurt. But he had to replace his vehicle with a used truck that became his home while waiting for President Donald Trump to issue a major disaster declaration so that federal money would be freed for individuals reeling from loss. That took weeks.
“You wake up in the truck and look out the windshield and see nothing. That’s hard. That’s hard to swallow,” Anthony said.
Disaster survivors are having to wait longer to get aid from the federal government, according to a new Associated Press analysis of decades of data. On average, it took less than two weeks for a governor’s request for a presidential disaster declaration to be granted in the 1990s and early 2000s. That rose to about three weeks during the past decade under presidents from both major parties. It’s taking more than a month, on average, during Trump’s current term, the AP found.
The delays mean individuals must wait to receive federal aid for daily living expenses, temporary lodging and home repairs. Delays in disaster declarations also can hamper recovery efforts by local officials uncertain whether they will receive federal reimbursement for cleaning up debris and rebuilding infrastructure. The AP collaborated with Mississippi Today and Mississippi Free Press on the effects of these delays for this report.
“The message that I get in the delay, particularly for the individual assistance, is that the federal government has turned its back on its own people,” said Bob Griffin, dean of the College of Emergency Preparedness, Homeland Security and Cybersecurity at the University at Albany in New York. “It’s a fundamental shift in the position of this country.”
The wait for disaster aid has grown as Trump remakes government
The Federal Emergency Management Agency often consults immediately with communities to coordinate their initial disaster response. But direct payments to individuals, nonprofits and local governments must wait for a major disaster declaration from the president, who first must receive a request from a state, territory or tribe. Major disaster declarations are intended only for the most damaging events that are beyond the resources of states and local governments.
Trump has approved more than two dozen major disaster declarations since taking office in January, with an average wait of almost 34 days after a request. That ranged from a one-day turnaround after July’s deadly flash flooding in Texas to a 67-day wait after a request for aid because of a Michigan ice storm. The average wait is up from a 24-day delay during his first term and is nearly four times as long as the average for former Republican President George H.W. Bush, whose term from 1989-1993 coincided with the implementation of a new federal law setting parameters for disaster determinations.
The delays have grown over time, regardless of the party in power. Former Democratic President Joe Biden, in his last year in office, averaged 26 days to declare major disasters — longer than any year under former Democratic President Barack Obama.

FEMA did not respond to the AP’s questions about what factors are contributing to the trend.
Others familiar with FEMA noted that its process for assessing and documenting natural disasters has become more complex over time. Disasters have also become more frequent and intense because of climate change, which is mostly caused by the burning of fuels such as gas, coal and oil.
The wait for disaster declarations has spiked as Trump’s administration undertakes an ambitious makeover of the federal government that has shed thousands of workers and reexamined the role of FEMA. A recently published letter from current and former FEMA employees warned the cuts could become debilitating if faced with a large-enough disaster. The letter also lamented that the Trump administration has stopped maintaining or removed long-term planning tools focused on extreme weather and disasters.
Shortly after taking office, Trump floated the idea of “getting rid” of FEMA, asserting: “It’s very bureaucratic, and it’s very slow.”
FEMA’s acting chief suggested more recently that states should shoulder more responsibility for disaster recovery, though FEMA thus far has continued to cover three-fourths of the costs of public assistance to local governments, as required under federal law. FEMA pays the full cost of its individual assistance.
Former FEMA Administrator Pete Gaynor, who served during Trump’s first term, said the delay in issuing major disaster declarations likely is related to a renewed focus on making sure the federal government isn’t paying for things state and local governments could handle.
“I think they’re probably giving those requests more scrutiny,” Gaynor said. “And I think it’s probably the right thing to do, because I think the (disaster) declaration process has become the ‘easy button’ for states.”
The Associated Press on Monday received a statement from White House spokeswoman Abigail Jackson in response to a question about why it is taking longer to issue major natural disaster declarations:
“President Trump provides a more thorough review of disaster declaration requests than any Administration has before him. Gone are the days of rubber stamping FEMA recommendations – that’s not a bug, that’s a feature. Under prior Administrations, FEMA’s outsized role created a bloated bureaucracy that disincentivized state investment in their own resilience. President Trump is committed to right-sizing the Federal government while empowering state and local governments by enabling them to better understand, plan for, and ultimately address the needs of their citizens. The Trump Administration has expeditiously provided assistance to disasters while ensuring taxpayer dollars are spent wisely to supplement state actions, not replace them.”
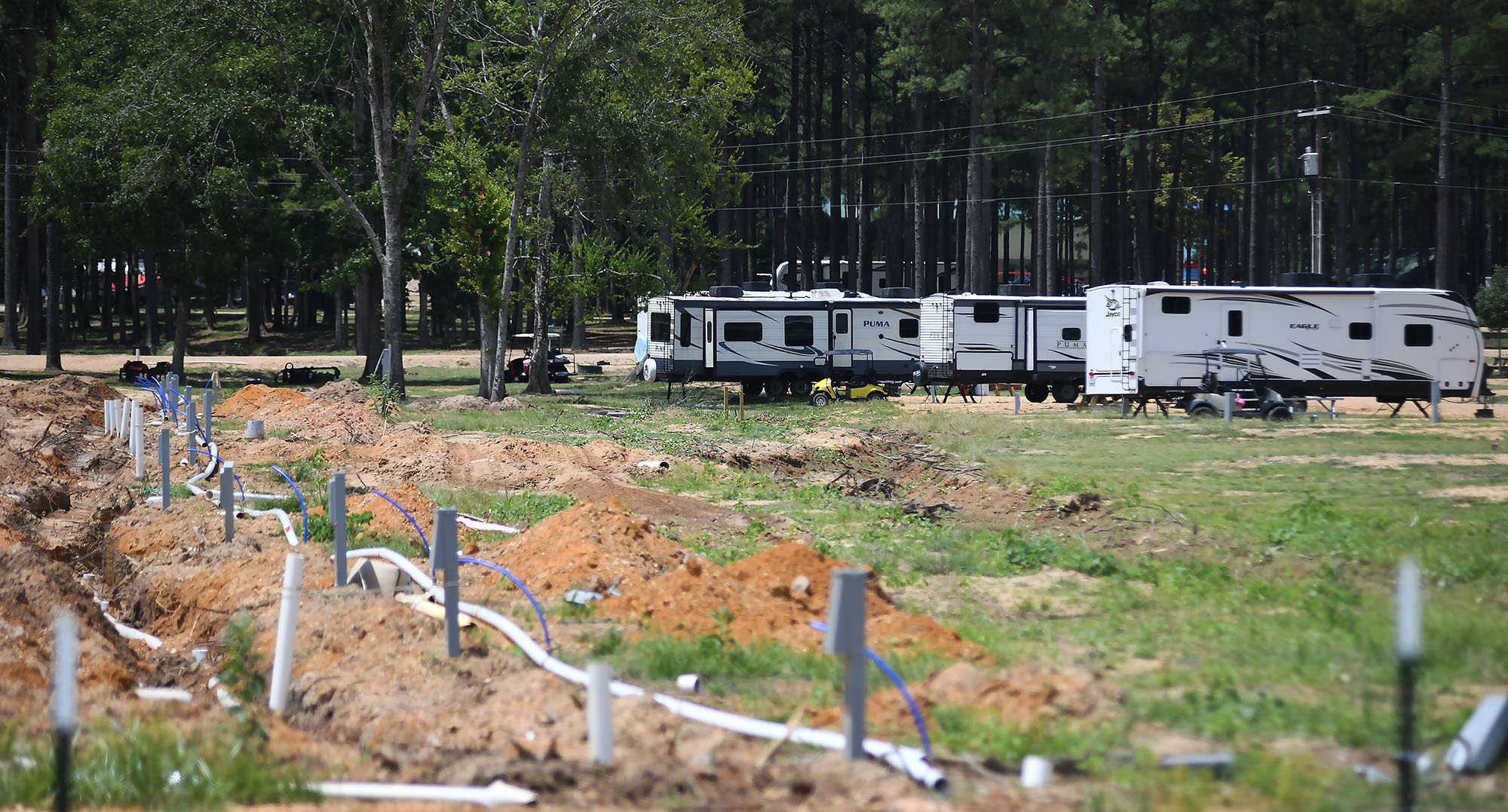

In Mississippi, frustration festered during wait for aid
The tornado that struck Anthony’s home in rural Tylertown on March 15 packed winds up to 140 mph. It was part of a powerful system that wrecked homes, businesses and lives across multiple states.
Mississippi’s governor requested a federal disaster declaration on April 1. Trump granted that request 50 days later, on May 21, while approving aid for both individuals and public entities.
On that same day, Trump also approved eight other major disaster declarations for storms, floods or fires in seven other states. In most cases, more than a month had passed since the request and about two months since the date of those disasters.
If a presidential declaration and federal money had come sooner, Anthony said he wouldn’t have needed to spend weeks sleeping in a truck before he could afford to rent the trailer where he is now living. His house was uninsured, Anthony said, and FEMA eventually gave him $30,000.
In nearby Jayess in Lawrence County, Dana Grimes had insurance but not enough to cover the full value of her damaged home. After the eventual federal declaration, Grimes said FEMA provided about $750 for emergency expenses, but she is now waiting for the agency to determine whether she can receive more.

“We couldn’t figure out why the president took so long to help people in this country,” Grimes said. “I just want to tie up strings and move on. But FEMA — I’m still fooling with FEMA.”
Jonathan Young said he gave up on applying for FEMA aid after the Tylertown tornado killed his 7-year-old son and destroyed their home. The process seemed too difficult, and federal officials wanted paperwork he didn’t have, Young said. He made ends meet by working for those cleaning up from the storm.
“It’s a therapy for me,” Young said, “to pick up the debris that took my son away from me.”
Historically, presidential disaster declarations containing individual assistance have been approved more quickly than those providing assistance only to public entities, according to the AP’s analysis. That remains the case under Trump, though declarations for both types are taking longer.
About half the major disaster declarations approved by Trump this year have included individual assistance.
Some people whose homes are damaged turn to shelters hosted by churches or local nonprofit organizations in the initial chaotic days after a disaster. Others stay with friends or family or go to a hotel, if they can afford it.
But some insist on staying in damaged homes, even if they are unsafe, said Chris Smith, who administered FEMA’s individual assistance division under three presidents from 2015-2022. If homes aren’t repaired properly, mold can grow, compounding the recovery challenges.
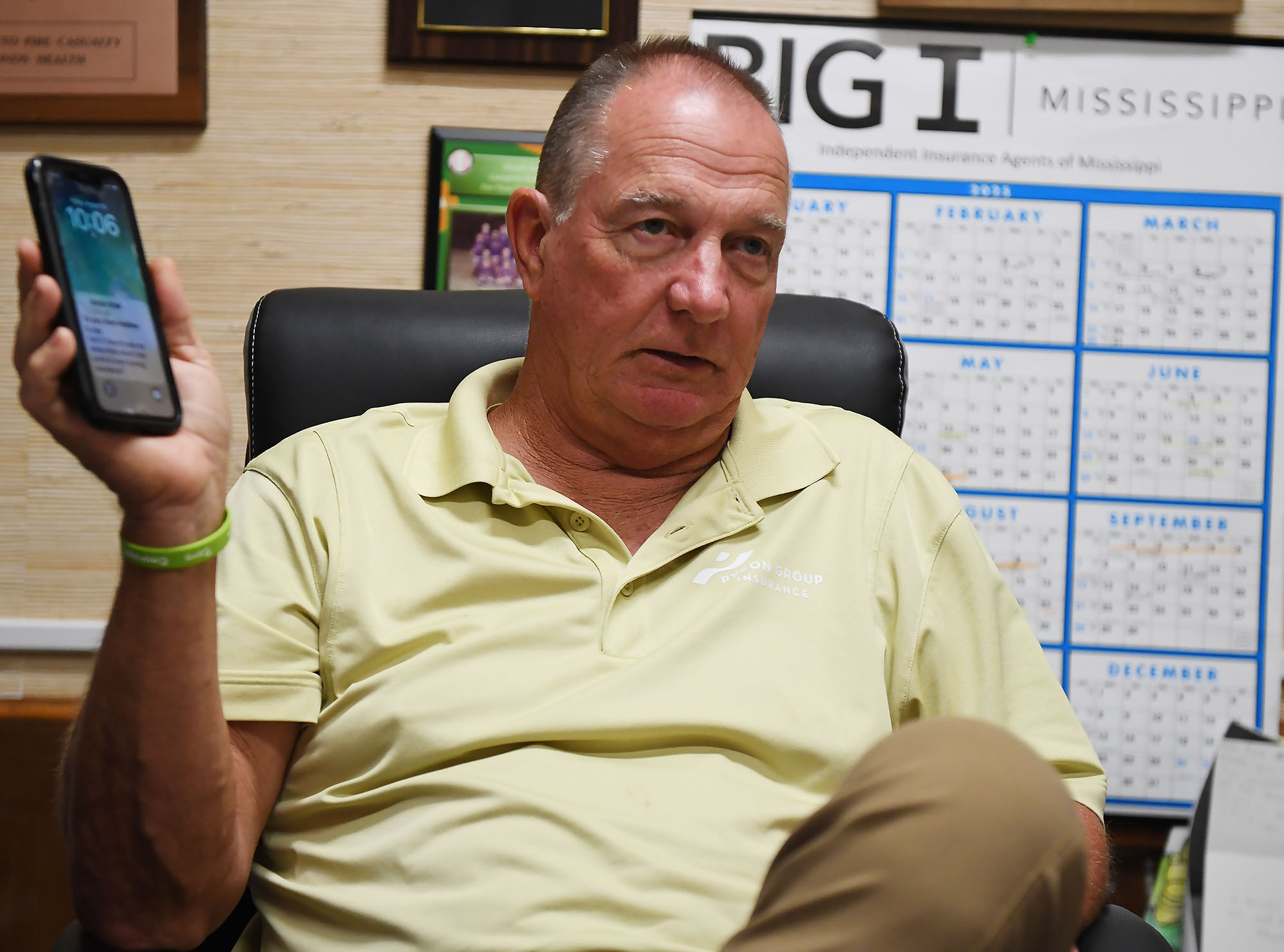

That’s why it’s critical for FEMA’s individual assistance to get approved quickly — ideally, within two weeks of a disaster, said Smith, who’s now a disaster consultant for governments and companies.
“You want to keep the people where they are living. You want to ensure those communities are going to continue to be viable and recover,” Smith said. “And the earlier that individual assistance can be delivered … the earlier recovery can start.”
In the periods waiting for declarations, the pressure falls on local officials and volunteers to care for victims and distribute supplies.
In Walthall County, where Tylertown is, insurance agent Les Lampton remembered watching the weather news as the first tornado missed his house by just an eighth of a mile. Lampton, who moonlights as a volunteer firefighter, navigated the collapsed trees in his yard and jumped into action. About 45 minutes later, the second tornado hit just a mile away.
“It was just chaos from there on out,” Lampton said.
Walthall County, with a population of about 14,000, hasn’t had a working tornado siren in about 30 years, Lampton said. He added there isn’t a public safe room in the area, although a lot of residents have ones in their home.
Rural areas with limited resources are hit hard by delays in receiving funds through FEMA’s public assistance program, which, unlike individual assistance, only reimburses local entities after their bills are paid. Long waits can stoke uncertainty and lead cost-conscious local officials to pause or scale-back their recovery efforts.
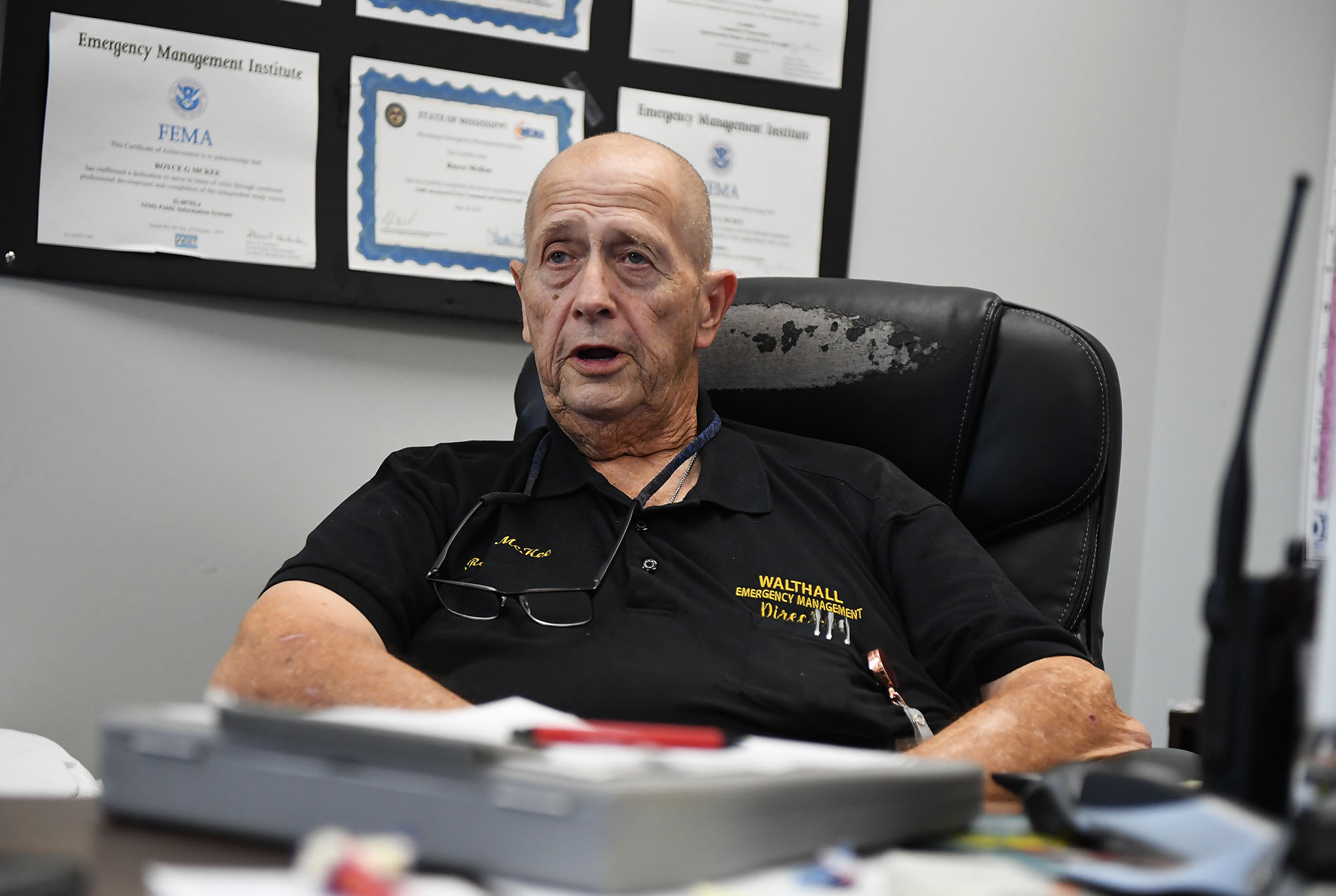

In Walthall County, officials initially spent about $700,000 cleaning up debris, then suspended the cleanup for more than a month because they couldn’t afford to spend more without assurance they would receive federal reimbursement, said county emergency manager Royce McKee. Meanwhile, rubble from splintered trees and shattered homes remained piled along the roadside, creating unsafe obstacles for motorists and habitat for snakes and rodents.
When it received the federal declaration, Walthall County took out a multimillion-dollar loan to pay contractors to resume the cleanup.
“We’re going to pay interest and pay that money back until FEMA pays us,” said Byran Martin, an elected county supervisor. “We’re hopeful that we’ll get some money by the first of the year, but people are telling us that it could be [longer].”
Lampton, who took after his father when he joined the volunteer firefighters 40 years ago, lauded the support of outside groups such as Cajun Navy, Eight Days of Hope, Samaritan’s Purse and others. That’s not to mention the neighbors who brought their own skid steers and power saws to help clear trees and other debris, he added.
“That’s the only thing that got us through this storm, neighbors helping neighbors,” Lampton said. “If we waited on the government, we were going to be in bad shape.”
Lieb reported from Jefferson City, Missouri, and Wildeman from Hartford, Connecticut.
Update 98/25: This story has been updated to include a White House statement released after publication.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Presidents are taking longer to declare major natural disasters. For some, the wait is agonizing appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Center-Left
This article presents a critical view of the Trump administration’s handling of disaster declarations, highlighting delays and their negative impacts on affected individuals and communities. It emphasizes concerns about government downsizing and reduced federal support, themes often associated with center-left perspectives that favor robust government intervention and social safety nets. However, it also includes statements from Trump administration officials defending their approach, providing some balance. Overall, the tone and framing lean slightly left of center without being overtly partisan.
Mississippi Today
Northeast Mississippi speaker and worm farmer played key role in Coast recovery after Hurricane Katrina
The 20th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina slamming the Mississippi Gulf Coast has come and gone, rightfully garnering considerable media attention.
But still undercovered in the 20th anniversary saga of the storm that made landfall on Aug. 29, 2005, and caused unprecedented destruction is the role that a worm farmer from northeast Mississippi played in helping to revitalize the Coast.
House Speaker Billy McCoy, who died in 2019, was a worm farmer from the Prentiss, not Alcorn County, side of Rienzi — about as far away from the Gulf Coast as one could be in Mississippi.
McCoy grew other crops, but a staple of his operations was worm farming.
Early after the storm, the House speaker made a point of touring the Coast and visiting as many of the House members who lived on the Coast as he could to check on them.
But it was his action in the forum he loved the most — the Mississippi House — that is credited with being key to the Coast’s recovery.
Gov. Haley Barbour had called a special session about a month after the storm to take up multiple issues related to Katrina and the Gulf Coast’s survival and revitalization. The issue that received the most attention was Barbour’s proposal to remove the requirement that the casinos on the Coast be floating in the Mississippi Sound.
Katrina wreaked havoc on the floating casinos, and many operators said they would not rebuild if their casinos had to be in the Gulf waters. That was a crucial issue since the casinos were a major economic engine on the Coast, employing an estimated 30,000 in direct and indirect jobs.
It is difficult to fathom now the controversy surrounding Barbour’s proposal to allow the casinos to locate on land next to the water. Mississippi’s casino industry that was birthed with the early 1990s legislation was still new and controversial.
Various religious groups and others had continued to fight and oppose the casino industry and had made opposition to the expansion of gambling a priority.
Opposition to casinos and expansion of casinos was believed to be especially strong in rural areas, like those found in McCoy’s beloved northeast Mississippi. It was many of those rural areas that were the homes to rural white Democrats — now all but extinct in the Legislature but at the time still a force in the House.
So, voting in favor of casino expansion had the potential of being costly for what was McCoy’s base of power: the rural white Democrats.
Couple that with the fact that the Democratic-controlled House had been at odds with the Republican Barbour on multiple issues ranging from education funding to health care since Barbour was inaugurated in January 2004.
Barbour set records for the number of special sessions called by the governor. Those special sessions often were called to try to force the Democratic-controlled House to pass legislation it killed during the regular session.
The September 2005 special session was Barbour’s fifth of the year. For context, current Gov. Tate Reeves has called four in his nearly six years as governor.
There was little reason to expect McCoy to do Barbour’s bidding and lead the effort in the Legislature to pass his most controversial proposal: expanding casino gambling.
But when Barbour ally Lt. Gov. Amy Tuck, who presided over the Senate, refused to take up the controversial bill, Barbour was forced to turn to McCoy.
The former governor wrote about the circumstances in an essay he penned on the 20th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina for Mississippi Today Ideas.
“The Senate leadership, all Republicans, did not want to go first in passing the onshore casino law,” Barbour wrote. “So, I had to ask Speaker McCoy to allow it to come to the House floor and pass. He realized he should put the Coast and the state’s interests first. He did so, and the bill passed 61-53, with McCoy voting no.
“I will always admire Speaker McCoy, often my nemesis, for his integrity in putting the state first.”
Incidentally, former Rep. Bill Miles of Fulton, also in northeast Mississippi, was tasked by McCoy with counting, not whipping votes, to see if there was enough support in the House to pass the proposal. Not soon before the key vote, Miles said years later, he went to McCoy and told him there were more than enough votes to pass the legislation so he was voting no and broached the idea of the speaker also voting no.
It is likely that McCoy would have voted for the bill if his vote was needed.
Despite his no vote, the Biloxi Sun Herald newspaper ran a large photo of McCoy and hailed the Rienzi worm farmer as a hero for the Mississippi Gulf Coast.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Northeast Mississippi speaker and worm farmer played key role in Coast recovery after Hurricane Katrina appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Centrist
The article presents a factual and balanced account of the political dynamics surrounding Hurricane Katrina recovery efforts in Mississippi, focusing on bipartisan cooperation between Democratic and Republican leaders. It highlights the complexities of legislative decisions without overtly favoring one party or ideology, reflecting a neutral and informative tone typical of centrist reporting.
-
Our Mississippi Home6 days ago
Screech Owls – Small but Cute
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
NW Arkansas Championship expected to bring money to Rogers
-
News from the South - Tennessee News Feed7 days ago
What to know about Trump’s National Guard deployment to Memphis
-
Local News6 days ago
New findings by NASA Mars rover provide strongest hints yet of potential signs of ancient life
-
The Center Square5 days ago
What are data centers and why do they matter? | National
-
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed7 days ago
Is nail gel actually harmful? It's complicated
-
Our Mississippi Home5 days ago
Rolling Through History: The Comfort and Culture of Dumplings
-
Local News5 days ago
Steven Spielberg celebrates ‘awesome’ 50th anniversary ‘Jaws’ exhibition at Academy Museum