Robert Kopack
Robert A. Kopack, University of South Carolina
If there is a leader in the aerospace industry, SpaceX is it. The company’s Crew Dragon and Cargo Dragon spacecrafts are the current go-to vehicles to deliver astronauts and supplies to the International Space Station.
NASA contracts awarded to SpaceX through 2030 alone are worth nearly US$5 billion and include research and development for the Artemis mission to return astronauts to the Moon.
Over the past decade, SpaceX has also emerged as a key vendor to the U.S. Department of Defense, seen most recently with a $733.5 million contract for projects such as launching defense satellite networks and contributing to other national security space objectives.
As a human geographer, I’m interested in how commercial space and defense companies affect the local communities where they conduct launches and tests.
For instance, I spent over two years in Kazakhstan researching the privatization of the Soviet space program and the beginning of a global commercial space industry.
Elon Musk and SpaceX’s influence
Politically, SpaceX is an enormous boon to the United States.
As a U.S.-based defense supplier and contractor, the company’s technology has helped to nearly end an almost two-decade dependency on the Russian Federation for access to the International Space Station. Its billionaire CEO, Elon Musk, has even expressed plans to colonize Mars.
Musk’s decision to spend $250 million helping Donald Trump win the 2024 presidential election is expected to lead to more support for SpaceX.
In the new administration, Musk is poised to lead a newly created advisory agency called the Department of Government Efficiency, which could lead to benefits for his business and widen his space ambitions.
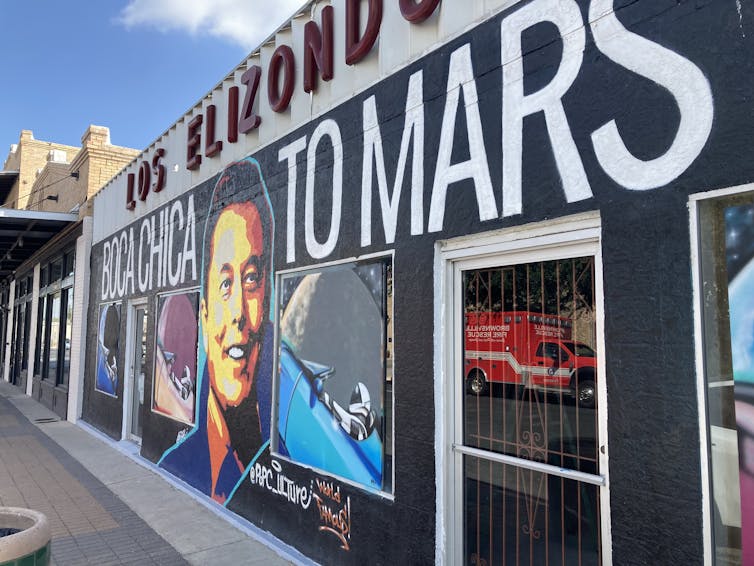
Boca Chica, Texas, is home to SpaceX’s flagship assembly and test installation, Starbase. Since 2021, I have been conducting research with environmental groups and multigenerational community members of Latino and Indigenous descent in south Texas who see space exploration as a landscape-altering industry that affects their well-being.
After watching Starbase’s development proceed since 2014, locals there told me that there is much unseen and unsaid about what happens on the ground while an aerospace giant shoots for the stars.
Breaking eggs to make an omelet
Starbase is an industrial installation built by SpaceX to fabricate and test a number of the company’s rocket types.
The area around it is a unique and delicate ecosystem that includes estuaries and coastal grasslands, mud flats and more, where falcons, hawks, ravens, gulls and songbirds live.
Since construction began, SpaceX engineers have had to drain water-logged soils, level them and pour concrete to support ground tracking stations, assembly buildings, engine test stands, a nearly 500-foot (152-meter) launch tower and onsite fuel mixing and storage.
In a lengthy response to local environmental groups’ claims of environmental abuses, the company maintains that it is dedicated to environmental stewardship.
But developing rockets is a dangerous and messy business. Sites chosen for this kind of work are often, though not always, remote and highly secured installations.
Fiery explosions on the ground or in the air aren’t unheard of over the past several years. Rocket tests in Scotland, China and Japan have all ended in accidents.
In April 2023, one of SpaceX’s prototype Starship rockets exploded over the Gulf of Mexico shortly after liftoff.
This is not the only time that a rocket has exploded at places where SpaceX operates.
SpaceX runs a compact though growing operation at Boca Chica that has transformed the area. The hamlet was previously known as Kopernik Shores, and SpaceX purchased nearly all of the approximately 35 ranch homes in the area. Some residents have reported pressure to sell their property for suboptimal prices following rumors that the county would use eminent domain to seize their residences.
I spoke to Rebekah Hinojosa, a local activist and member of the Carrizo-Comecrudo Tribe of Texas, while researching in the area. To many locals, including Hinojosa, it seems like Musk is so well connected that SpaceX is insulated from public criticism.
In a 2018 press conference, Musk said, “We’ve got a lot of land with no one around, and so if it blows up, it’s cool,” referring to a rocket he planned to test at Starbase.
Changes to the landscape
An installation the size of Starbase cannot avoid disturbing the wildlife in the four distinct state and federal wildlife protection areas that surround it.
If you walk through the protected areas you may see shrapnel, segments of rocket chassis and other random debris from any number of explosions – that is, if someone else hasn’t picked them up first.
In December 2022, I visited a luxury campground near Starbase. It displayed various fragments of rocket debris, which they called memorabilia to the new space age, throughout the site.
Within SpaceX, as well as NASA, the explosion of 2023 was celebrated as a crucial step in developing the Starship rocket. The event did produce valuable data on the rocket’s performance – it has done little to tarnish the company’s reputation.
There is tremendous support for SpaceX in Texas. The company has promised to drive high-tech industry jobs into a region ranked among the country’s poorest.
SpaceX has created about 2,100 jobs. However, reporting shows that local and state politicians have seen more personal gains in their real estate holdings and campaign budgets than the region’s economy has overall.

Robert Kopack
A laboratory near the community
At the end of the day, to develop a rocket, you need a place to test your design.
“Our local beach is the laboratory,” local activist Hinojosa told me.
Resident coalitions of Indigenous, Latino and Chicano people as well as conservation groups are suing the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department, the Federal Aviation Administration and others to combat SpaceX.
These groups argue that SpaceX misled state and federal regulators about Starbase’s operations. They claim SpaceX changed how frequently it planned to launch tests and built new facilities for several rocket types, which rendered the company’s original environmental impact statement for the area inaccurate.
Some key issues these groups are fighting against include a bid to expand Starbase into more protected areas. Another point of contention is the deluge system, which creates thousands of gallons of toxic wastewater to cool launch pads and rocket engines after testing.
While the EPA and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality have notified SpaceX about violations of the Clean Water Act, claimants in a recent lawsuit contend that these agencies have not held the company accountable for breaking the law. The company has denied any wrongdoing and refutes claims of environmental harms.
“As we have built up capacity to launch and developed new sites across the country, we have always been committed to public safety and mitigating impacts to the environment,” a SpaceX statement reads. “The list of measures we take just for operations in Texas is over two hundred items long, including constant monitoring and sampling of the short and long-term health of local flora and fauna. The narrative that we operate free of, or in defiance of, environmental regulation is demonstrably false.”
So, what does the future hold? Many people from conservation agencies, activist groups and Indigenous communities in Texas want the company out. Given the high public support for space exploration in the U.S. and the burgeoning friendship between Musk and Trump, a SpaceX evacuation from the area seems unlikely.
While it may take difficult negotiations that require concessions from each party, I hope that somewhere there is a middle ground on which space exploration and environmental protections can coexist.
This article was updated on Jan. 17, 2024 to reflect the amount of money Musk spent helping Trump win the 2024 election as $250 million and the correct speed of light.
Robert A. Kopack, Faculty Instructor of Human Geographies, University of South Carolina
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.