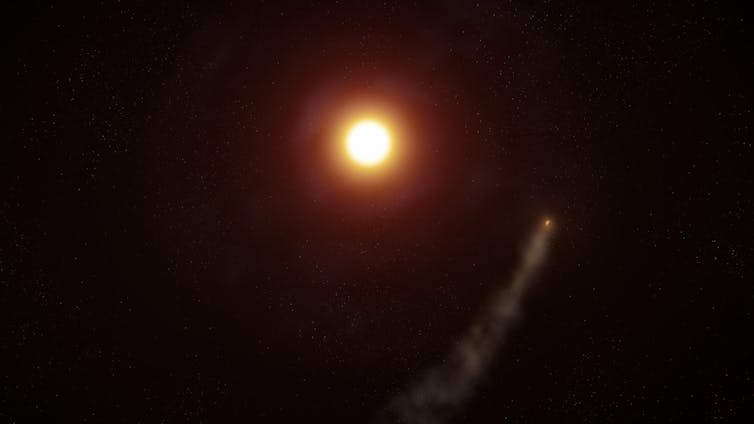
WASP-69b closely orbits its sun.
Dakotah Tyler, University of California, Los Angeles
Located 163 light-years from Earth, a Jupiter-sized exoplanet named WASP-69b offers astrophysicists a window into the dynamic processes that shape planets across the galaxy. The star it orbits is baking and stripping away the planet’s atmosphere, and that escaped atmosphere is being sculpted by the star into a vast, cometlike tail at least 350,000 miles long.
I’m an astrophysicist. My research team published a paper in the Astrophysical Journal describing how and why WASP-69b’s tail formed, and what its formation can illuminate about the other types of planets astronomers tend to detect outside of our solar system.
Artist’s interpretation of an aerial view of the exoplanet WASP-69b on its 3.8-day orbit around its host star. Its atmosphere is being stripped away and sculpted into a long cometlike tail that trails the planet.
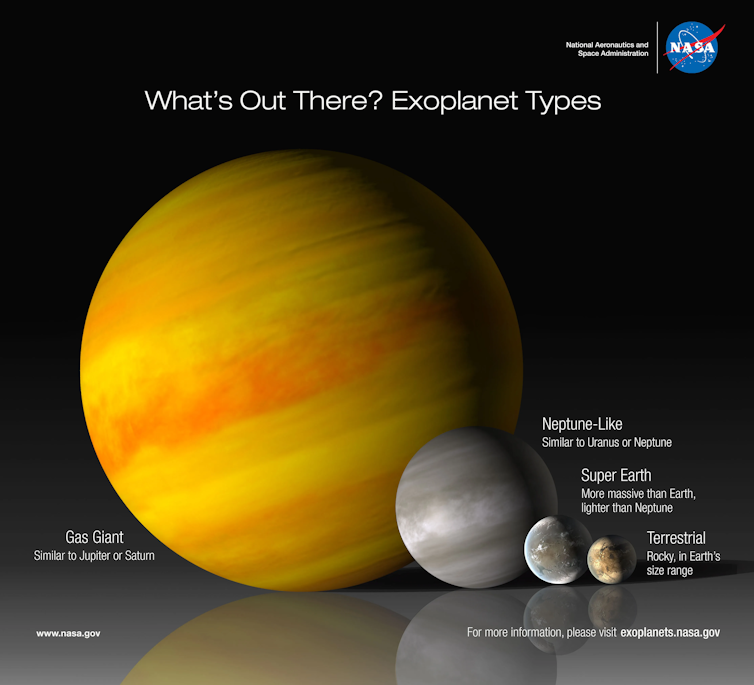
A universe filled with exoplanets
When you look up at the night sky, the stars you see are suns, with distant worlds, known as exoplanets, orbiting them. Over the past 30 years, astronomers have detected over 5,600 exoplanets in our Milky Way galaxy.
It isn’t easy to detect a planet light-years away. Planets pale in comparison, in both size and brightness, to the stars that they orbit. But despite these limitations, exoplanet researchers have uncovered an astonishing variety – everything from small rocky worlds barely larger than our own moon to gas giants so colossal that they’ve been dubbed “super-Jupiters.”
However, the most common exoplanets astronomers detect are larger than Earth, smaller than Neptune, and orbit their stars more closely than Mercury orbits our Sun.
These ultra-common planets tend to fall into one of two distinct groups: super-Earths and sub-Neptunes. Super-Earths have a radius that’s up to 50% larger than Earth’s radius, while sub-Neptunes typically have a radius that’s two to four times larger than Earth’s radius.
Sub-Neptunes, or Neptune-like planets, look at lot like a super-Earth, but with a thick atmosphere.
Between those two radius ranges, there’s a gap, known as the “Radius Gap,” in which researchers rarely find planets. And, Neptune-sized planets that complete orbits around their stars in less than four days are exceedingly rare. Researchers call that gap the “Hot Neptune Desert.”
Some underlying astrophysical processes must be preventing these planets from forming – or surviving.
Planet formation
As a star forms, a large disk of dust and gas forms around it. In that disk, planets can form. As young planets gain mass, they can accumulate significant gas atmospheres. But as the star matures, it starts to emit high amounts of energy in the form of ultraviolet and X-ray radiation. This stellar radiation can bake away the atmospheres that the planets have accumulated in a process called photoevaporation.
However, some planets resist this process. More massive planets have stronger gravity, which helps them hold onto their original atmospheres. Additionally, planets that are farther away from their star aren’t hit with as much radiation, so their atmospheres erode less.
So, maybe a significant portion of super-Earths are actually the rocky cores of planets that had their atmospheres completely stripped, while sub-Neptunes were massive enough to retain their puffy atmospheres.
As for the Hot Neptune Desert, most Neptune-sized planets simply are not massive enough to completely resist the stripping power of their star if it orbits too closely. In other words, a sub-Neptune orbiting its star in four days or fewer will quickly lose its entire atmosphere. When observed, the atmosphere has already been lost and what remains is a bare rocky core – a super-Earth.
To put this theory to the test, research teams like mine have been collecting observational evidence.
WASP-69b: A unique laboratory
Enter WASP-69b, a unique laboratory for studying photoevaporation. The name “WASP-69b” comes from the way it was discovered. It was the 69th star with a planet, b, found in the Wide Angle Search for Planets survey.
Despite being 10% larger than Jupiter in radius, WASP-69b is actually closer to the mass of much lighter Saturn – it’s not very dense, and it has only about 30% the mass of Jupiter. In fact, this planet has about the same density as a piece of cork.
This low density results from its ultra-close 3.8-day orbit around its star. Being so close, the planet receives an immense amount of energy, which causes it to heat up. As gas heats, it expands. Once the gas expands enough, it begins to escape the planet’s gravity for good.
When we observed this planet, my colleagues and I detected helium gas escaping WASP-69b rapidly – about 200,000 tons per second. This translates to the mass of the Earth lost every billion years.
Over the star’s lifetime, this planet will end up losing a total atmospheric mass equivalent of nearly 15 times the mass of Earth. This sounds like a lot, but WASP-69b is approximately 90 times Earth’s mass, so even at this extreme rate, it will only ever lose a small fraction of the total amount of gas from which it is comprised.
The cometlike tail of WASP-69b
Perhaps most striking is the discovery of WASP-69b’s extended helium tail, which my team detected trailing behind the planet for at least 350,000 miles (about 563,000 kilometers). Strong stellar winds, which are a constant flow of charged particles emitted from stars, sculpt tails like this. These particle winds ram into the escaping atmosphere and shape it into a cometlike tail behind the planet.
Our study is actually the first to suggest that WASP-69b’s tail was so extensive. Past observations of this system suggested the planet had only a modest tail or even no tail at all.
This difference likely comes down to two main factors. For one, each research group used different instruments to make their observations, which could result in varying detection levels. Or, there could be actual variability in the system.
A star like our Sun has a magnetic activity cycle, called the “solar cycle.” The Sun’s lasts for 11 years. During peak activity years, the Sun has more flares, sunspots and changes to the solar wind.
To complicate things even more, each cycle is unique – no two solar cycles are the same. Solar scientists are still trying to better understand and predict our Sun’s activity. Other stars have their own magnetic cycles, but scientists just don’t have enough data to understand them yet.
So the variability observed for WASP-69b may come from the fact that every time it gets observed, the host star is behaving differently. Astronomers will have to continue to observe this planet more in the future to get a better idea of exactly what’s going on.
Our direct look at WASP-69b’s mass loss tells exoplanet researchers like me more about how planetary evolution works. It gives us real-time evidence for atmospheric escape and supports the theory that hot Neptunes and Radius Gap planets are hard to find because they just aren’t massive enough to retain their atmospheres. And once they lose them, all that is left to observe is a rocky super-Earth core.
The WASP-69b study highlights the delicate balance between a planet’s composition and its stellar environment, shaping the diverse planetary landscape we observe today. As astronomers continue to probe these distant worlds, each discovery brings us closer to understanding the complex tapestry of our universe.
Dakotah Tyler, Ph.D. Candidate in Astrophysics, University of California, Los Angeles
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.